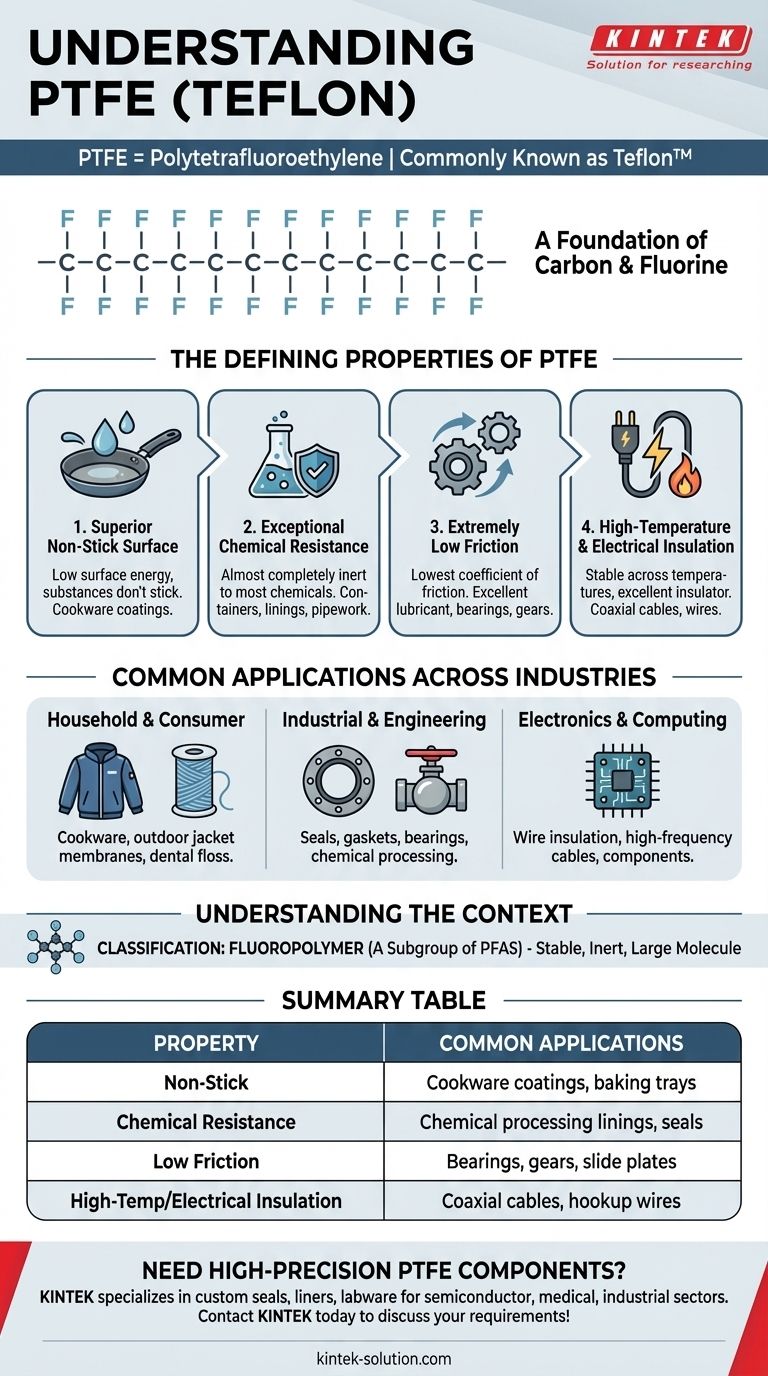
In professional and consumer contexts, PTFE is most commonly known by the registered trademark name Teflon. The acronym PTFE stands for Polytetrafluoroethylene, a versatile and high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer composed of carbon and fluorine atoms.
While many associate the name "Teflon" with non-stick cookware, this is just one application. The true significance of PTFE lies in its unique chemical structure, which gives it a combination of properties—chemical inertness, low friction, and heat resistance—making it a critical material across dozens of industries.

What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)?
A Foundation of Carbon and Fluorine
PTFE is a high-molecular-weight polymer, meaning it consists of very long, repeating chains of molecules. Its structure is composed exclusively of a carbon backbone completely surrounded by fluorine atoms.
The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong. This powerful chemical bond is the source of PTFE's most valuable and unique characteristics.
A Note on Naming
While PTFE is the precise chemical name, it is almost universally recognized by the brand name Teflon.
It's important to note that the Teflon™ brand is also applied to other, similar fluoropolymers like PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) and FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene), so context is key in highly technical specifications.
The Defining Properties of PTFE
The unique molecular structure of PTFE gives it a powerful combination of commercially valuable properties.
Superior Non-Stick Surface
PTFE's most famous characteristic is its low surface energy, which means other substances do not readily stick to it. This is why it is the go-to material for non-stick coatings on cookware like pans and baking trays.
Exceptional Chemical Resistance
The strong carbon-fluorine bonds make PTFE almost completely inert. It does not react with the vast majority of corrosive chemicals, making it indispensable for containers, linings, and pipework in the chemical processing and oil & gas industries.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This property makes it an excellent lubricant, often used in machinery components like gears, bearings, and slide plates to reduce friction and wear.
High-Temperature and Electrical Insulation
The material maintains its properties across a wide range of temperatures and is an excellent electrical insulator. This makes it ideal for use in computer applications, including hookup wires and the insulating layers in coaxial cables.
Common Applications Across Industries
PTFE's versatility means it is found in a surprisingly wide range of products, from everyday items to highly specialized industrial components.
Household and Consumer Goods
Beyond cookware, PTFE is used for its water-repellent properties in membranes for outdoor jackets, as well as in products like dental floss and ski wax.
Industrial and Engineering
In demanding industrial environments, PTFE is fabricated into seals, gaskets, ball valves, and bearings. Its durability and chemical resistance make it a cost-effective solution for harsh conditions.
Electronics and Computing
Due to its excellent dielectric properties, PTFE is a critical insulator for wiring and cables, particularly in high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Understanding the Context
To fully understand PTFE, it's helpful to know where it fits within the broader landscape of chemical compounds.
Classification as a Fluoropolymer
PTFE belongs to a very large group of man-made chemicals known as PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances). Specifically, it is classified within a subgroup called fluorinated polymers.
Polymers like PTFE are noted for being stable, inert, and too large to be bioavailable, giving them a different profile from other, more controversial PFAS compounds.
Key Takeaways for Practical Understanding
Your reason for investigating PTFE will determine which of its properties is most important to you.
- If your primary focus is consumer products: You will most often encounter PTFE as the non-stick coating on your cookware, valued for its ease of use and cleaning.
- If your primary focus is industrial engineering: You will value PTFE for its extreme chemical inertness, low friction, and temperature stability in demanding applications like seals, bearings, and linings.
- If your primary focus is electronics: You will specify PTFE for its outstanding electrical insulation properties, which are critical for performance in high-frequency cables and components.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE is about recognizing how its simple but powerful chemical structure creates one of the most versatile problem-solving materials in modern science.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Stick | Extremely low surface energy | Cookware coatings, baking trays |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to most corrosive substances | Chemical processing linings, seals |
| Low Friction | One of the lowest coefficients of friction | Bearings, gears, slide plates |
| High-Temp/Electrical Insulation | Stable across wide temperature range, excellent dielectric | Coaxial cables, hookup wires, high-frequency components |
Need high-precision PTFE components for your industry?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing custom PTFE seals, liners, labware, and more for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get components that leverage PTFE's full potential for chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the electrical insulation capability of PTFE? Unmatched Reliability for Demanding Applications
- What defines a technical plastic? An engineered polymer for demanding applications.
- Why is PTFE/Teflon used in non-stick cookware? Unlock the Science of Frictionless Cooking
- What is PTFE and what makes it versatile? The Ultimate High-Performance Polymer
- What is PTFE commonly known as and when was it developed? The 'Plastics King' for Extreme Performance
- What is PTFE and how was it first manufactured? The Accidental Discovery of Teflon
- What are the benefits of using Teflon in fiberglass? Achieve Unmatched Durability and Chemical Resistance
- What is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and what are its main types? Unlock High-Performance Solutions



















