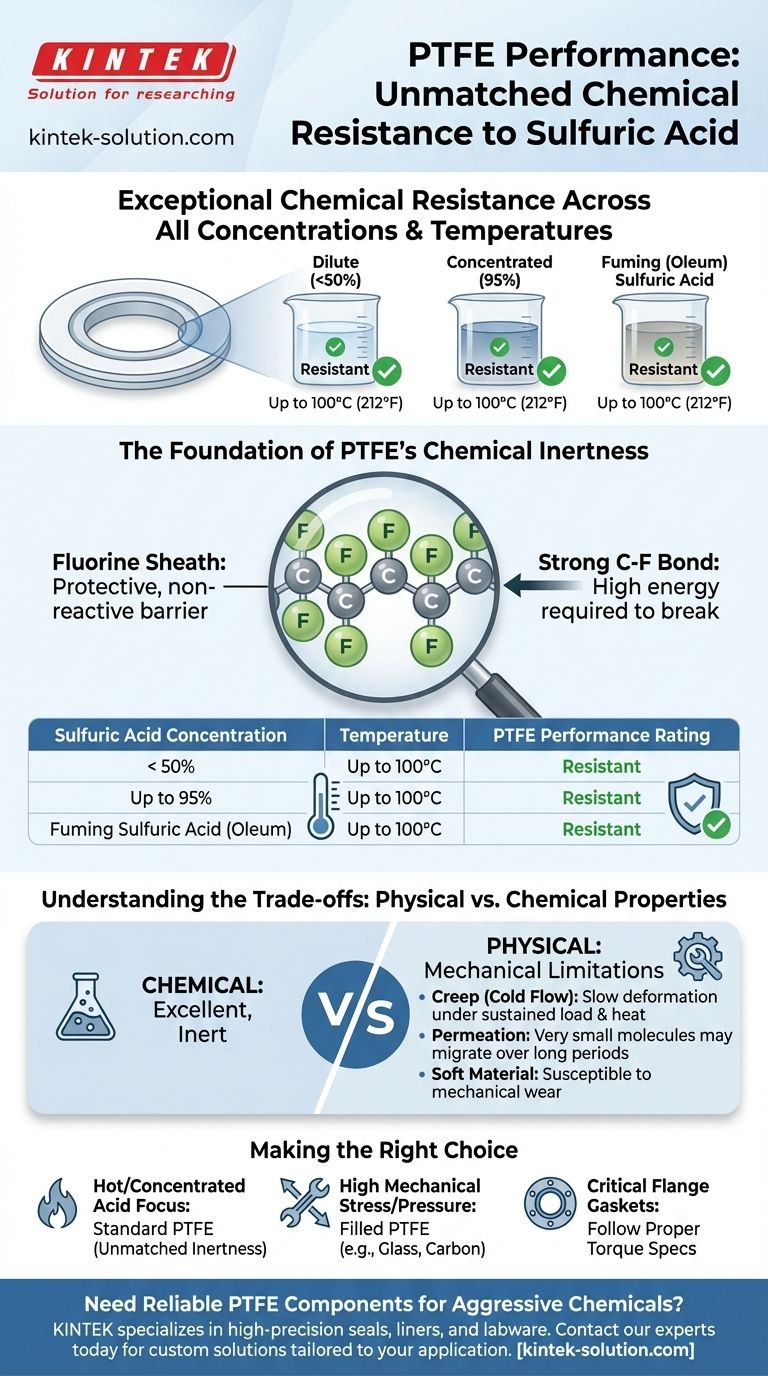
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits exceptional chemical resistance to sulfuric acid across all concentrations and a wide range of temperatures. The provided data confirms that PTFE is rated as "Resistant" to sulfuric acid at concentrations below 50%, up to 95%, and even to fuming sulfuric acid at temperatures as high as 100°C (212°F).
The exceptional stability of PTFE's carbon-fluorine bonds makes it virtually inert to sulfuric acid, regardless of concentration or temperature. This inherent chemical resilience is not a surface treatment but a fundamental property of the material, ensuring reliable performance in demanding chemical applications.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Inertness
To understand why PTFE performs so well, we must look at its molecular structure. Its resistance is not an additive or a coating; it is an intrinsic property of the material itself.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms, with each carbon atom bonded to two fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
This incredible bond strength means that a tremendous amount of energy is required to break it. Aggressive chemicals like sulfuric acid simply do not have enough reactive energy to sever these bonds under normal service conditions.
A Protective Fluorine Sheath
The fluorine atoms are larger than the carbon atoms they are attached to. They effectively form a tight, dense, and non-reactive "sheath" around the vulnerable carbon backbone.
This helical sheath acts as a physical barrier at the molecular level, preventing oxidizing agents like concentrated sulfuric acid from even reaching the carbon chain to initiate a chemical attack.
Performance Across the Spectrum of Sulfuric Acid
The data clearly shows that changes in sulfuric acid concentration have virtually no impact on PTFE's integrity within the specified temperature range.
Dilute and Moderate Concentrations (<95%)
In applications involving dilute or moderately concentrated sulfuric acid, PTFE is completely unaffected. It will not swell, soften, or degrade, even with prolonged exposure at temperatures up to 100°C (212°F).
Concentrated and Fuming Sulfuric Acid
This is where PTFE truly distinguishes itself from lesser polymers. Even when exposed to 95% concentrated sulfuric acid or highly aggressive fuming sulfuric acid (oleum), PTFE remains stable and reliable.
Its inert nature means it is a standard material of choice for gaskets, seals, linings, and tubing in systems handling the most potent forms of this acid.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its chemical resistance is nearly absolute in this context, it is critical to consider PTFE's physical properties. Material failure in a PTFE component is far more likely to be mechanical than chemical.
Chemical vs. Physical Properties
An engineer's primary concern with PTFE is not chemical degradation but its physical limitations. It is a relatively soft material compared to metals or even other high-performance polymers.
Susceptibility to Creep (Cold Flow)
Under sustained mechanical load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE is subject to creep, also known as cold flow. This means the material can slowly deform over time.
For components like gaskets or valve seats, this deformation can lead to a loss of sealing pressure and eventual leakage. This is a critical design consideration in high-pressure systems.
Permeation
While PTFE is an excellent barrier, it is not completely impermeable. Over long periods, very small molecules can sometimes migrate slowly through the polymer matrix.
In standard industrial applications, this is rarely a concern. However, in ultra-high purity systems or sensitive laboratory environments, permeation rates may need to be evaluated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be based on both the chemical environment and the mechanical demands of the application.
- If your primary focus is containing hot or highly concentrated sulfuric acid: PTFE is an industry-standard choice due to its unmatched and reliable chemical inertness.
- If your application involves high mechanical stress or pressure: Consider using a filled grade of PTFE (e.g., glass-, carbon-, or bronze-filled) to significantly improve its resistance to creep and wear.
- If you are designing a flange gasket for critical service: Ensure you are following proper torque specifications, as over-tightening can accelerate cold flow and lead to premature failure.
Ultimately, PTFE's fundamental chemical stability provides a high degree of confidence when specifying materials for sulfuric acid service.
Summary Table:
| Sulfuric Acid Concentration | Temperature | PTFE Performance Rating |
|---|---|---|
| < 50% | Up to 100°C | Resistant |
| Up to 95% | Up to 100°C | Resistant |
| Fuming Sulfuric Acid (Oleum) | Up to 100°C | Resistant |
Need reliable PTFE components for handling aggressive chemicals like sulfuric acid?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get components that deliver unmatched chemical resistance and long-term performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements and receive a custom solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance



















