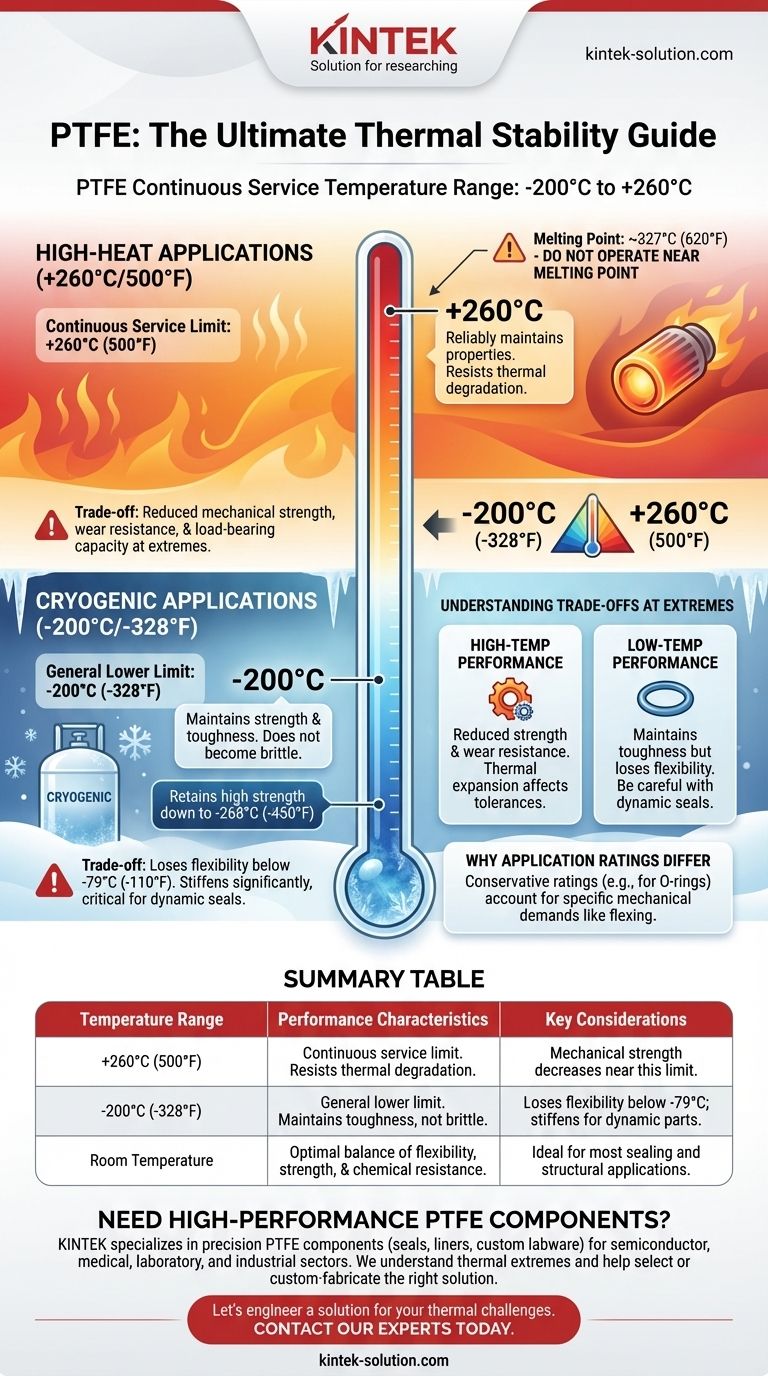
In short, the accepted continuous service temperature range for PTFE is from -200°C (-328°F) up to +260°C (500°F). This exceptionally wide range makes Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) one of the most thermally stable plastics available, suitable for both cryogenic and high-heat applications where other materials would fail.
While PTFE has a very wide and well-defined temperature range, its mechanical properties change at the extremes. Understanding this behavior, particularly its loss of flexibility at very low temperatures and reduced strength at very high temperatures, is the key to using it successfully.

The Exceptional Thermal Stability of PTFE
The remarkable performance of PTFE stems from its molecular structure. The strong, stable bonds between carbon and fluorine atoms create a material that is highly resistant to thermal degradation.
The High-Temperature Limit
The upper service limit for continuous use is consistently cited as +260°C (500°F). This is the temperature at which it reliably maintains its critical properties.
It's important to distinguish this service temperature from its melting point, which is significantly higher at approximately 327°C (620°F). Operating near this point is not recommended as the material's structural integrity will be compromised long before it fully melts.
The Low-Temperature Limit
The general lower service limit for PTFE is -200°C (-328°F). It performs exceptionally well in cryogenic conditions.
Unlike many polymers that become brittle and fracture at low temperatures, PTFE maintains its strength and toughness. It has been shown to retain high strength down to -268°C (-450°F).
Understanding the Trade-offs at Temperature Extremes
The usable temperature range is not just about survival; it's about performance. The properties of PTFE are not constant across this entire spectrum.
Performance Near the Upper Limit
As PTFE approaches its +260°C limit, its mechanical strength, wear resistance, and load-bearing capacity begin to decrease. Thermal expansion also becomes a more significant factor in applications with tight tolerances.
Performance Near the Lower Limit
While PTFE remains tough at cryogenic temperatures, it does lose flexibility. One reference notes good flexibility is maintained down to -79°C (-110°F), but below this, it becomes progressively stiffer.
This is a critical consideration for dynamic applications like seals or O-rings, which need to remain pliable to function correctly. For a static component, this stiffness is rarely an issue.
Why Application-Specific Ratings Differ
You may see slightly different temperature ranges quoted for specific PTFE products, such as O-rings. These ratings, which can be more conservative (e.g., -65ºF to 500ºF), often account for the specific mechanical demands of the application.
A dynamic seal that needs to flex will have a more restricted low-temperature rating than a static gasket made from the exact same raw material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if PTFE is right for your project, consider the specific performance you need at your target temperature.
- If your primary focus is high-heat continuous service: Rely on the +260°C (500°F) limit, but design for slightly reduced mechanical strength compared to room temperature.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic stability: PTFE is an excellent choice for static components down to -200°C, as it will not become brittle.
- If your primary focus is dynamic sealing: Be mindful that flexibility decreases significantly at very low temperatures, and you should consult the specific data sheet for the component in question.
Ultimately, PTFE's vast operating range makes it a uniquely versatile material for the most demanding thermal environments.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Performance Characteristics | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| +260°C (500°F) | Continuous service limit. Resists thermal degradation. | Mechanical strength decreases near this limit. |
| -200°C (-328°F) | General lower limit. Maintains toughness, does not become brittle. | Loses flexibility below -79°C; stiffens for dynamic parts. |
| Room Temperature | Optimal balance of flexibility, strength, and chemical resistance. | Ideal for most sealing and structural applications. |
Need high-performance PTFE components that can handle your extreme temperature requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand how thermal extremes affect material performance and can help you select or custom-fabricate the right solution, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let's engineer a solution for your specific thermal challenges. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE



















