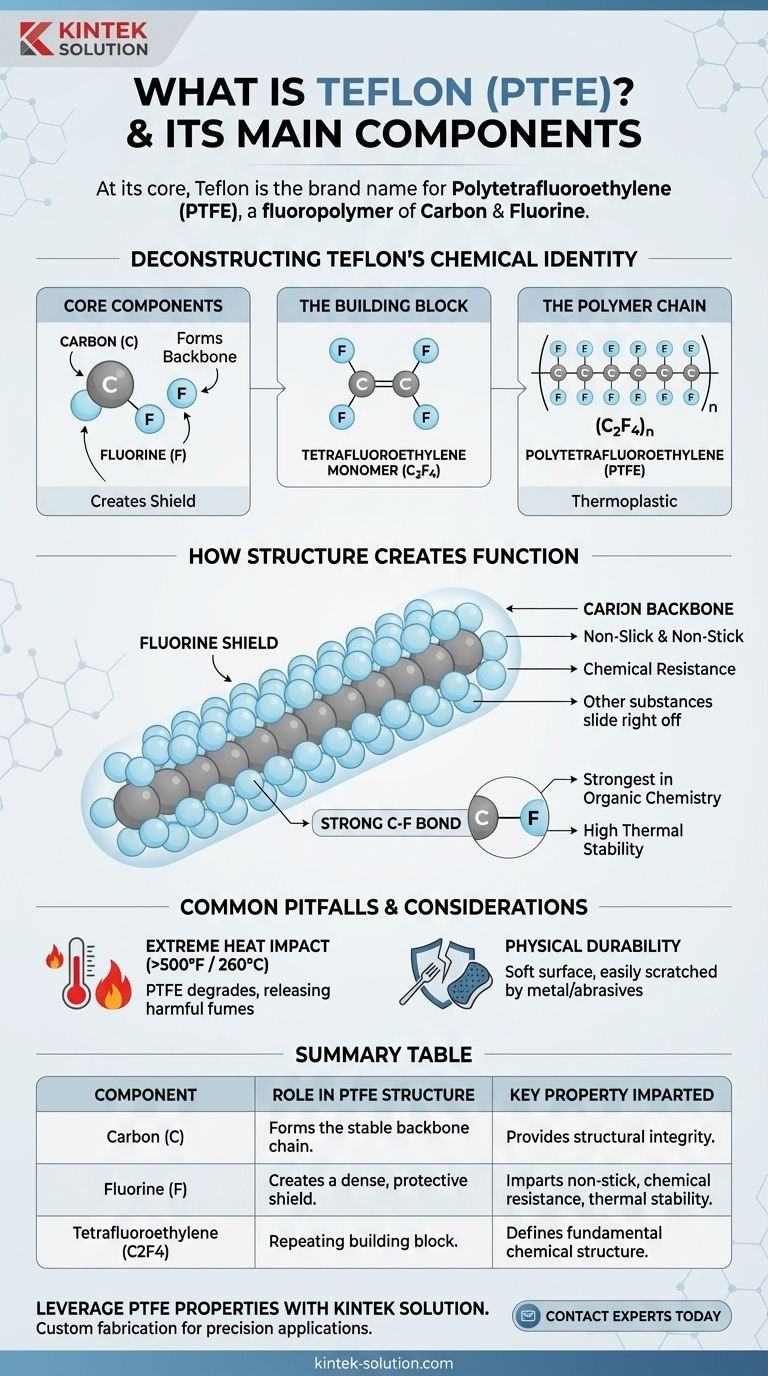
At its core, Teflon is the brand name for a synthetic material called Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This high-molecular-weight compound is a fluoropolymer, meaning its chemical structure consists exclusively of two core components: carbon and fluorine atoms linked together in long, repeating chains.
The essential thing to understand is that Teflon's famous non-stick and highly resistant properties are a direct result of its simple but powerful chemical structure: a stable carbon backbone completely shielded by a non-reactive layer of fluorine atoms.
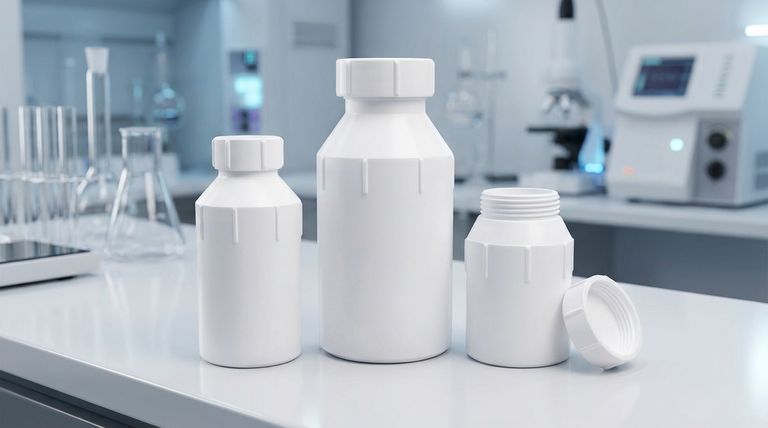

Deconstructing Teflon's Chemical Identity
To truly understand Teflon, we must look at how its basic components assemble into a unique and robust material. It is a polymer, which means it is a large molecule made of many smaller, repeating units bonded together.
The Core Components: Carbon and Fluorine
The entire structure of Teflon is built from just two elements. A long chain of carbon atoms forms the central backbone of the molecule.
Attached to this carbon backbone are fluorine atoms. These atoms are what give Teflon its defining characteristics.
The Building Block: The Tetrafluoroethylene Monomer
The small, repeating unit that forms Teflon is a molecule called tetrafluoroethylene. Its chemical formula is C2F4.
This monomer consists of two carbon atoms bonded together, with four fluorine atoms attached to them.
The Polymer Chain: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Teflon is created through a process called polymerization, where countless tetrafluoroethylene monomers link up end-to-end.
This forms the final material: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). The "(C2F4)n" in its chemical formula signifies this long, repeating chain structure. It is also classified as a thermoplastic, meaning it can be softened with heat and reformed.
How Structure Creates Function
The arrangement of these atoms is not accidental; it is precisely what gives Teflon its well-known properties. The a a a material's behavior is a direct consequence of its molecular architecture.
The Fluorine Shield
Imagine the long carbon chain as a spine. The fluorine atoms are larger and pack tightly around this spine, creating a protective, non-reactive "shield."
This fluorine shield is what makes the surface so slick and non-stick. Other substances have nothing to chemically "grab onto," causing them to slide right off. It also makes Teflon highly resistant to corrosion from most chemicals.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between a carbon atom and a fluorine atom is one of the strongest single bonds known in organic chemistry.
This incredible bond strength contributes to Teflon's high thermal stability, allowing it to withstand extreme temperatures without easily breaking down.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While incredibly useful, it's important to understand the material's limitations. Its properties are not infinite, and misuse can negate its benefits.
The Impact of Extreme Heat
The primary consideration for PTFE is its behavior at very high temperatures.
When heated above approximately 500°F (260°C), PTFE can begin to degrade. This decomposition can release polymer fumes that may be harmful if inhaled.
Physical Durability
While chemically robust, the non-stick surface of Teflon is physically soft.
Using metal utensils or abrasive scouring pads can easily scratch and damage the PTFE coating, compromising its non-stick performance and causing it to flake off.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your reason for understanding Teflon's composition determines which details matter most.
- If your primary focus is simple identification: Know that Teflon is the brand name for PTFE, a type of plastic made from carbon and fluorine that is famous for being non-stick.
- If your primary focus is the chemistry: Focus on how tetrafluoroethylene monomers (C2F4) polymerize to create a long chain with a fluorine sheath, and that the strong carbon-fluorine bond is key to its stability.
- If your primary focus is practical safety: Recognize that its main benefit is chemical and thermal resistance, but you must avoid overheating it (above 500°F / 260°C) to prevent degradation.
Understanding the link between a material's simple chemical makeup and its powerful properties allows you to use it more effectively and safely.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in PTFE Structure | Key Property Imparted |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | Forms the stable backbone chain of the polymer. | Provides structural integrity. |
| Fluorine (F) | Creates a dense, protective shield around the carbon backbone. | Imparts non-stick, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. |
| Tetrafluoroethylene (C2F4) Monomer | The repeating building block that polymerizes into PTFE. | Defines the fundamental chemical structure. |
Leverage the superior properties of PTFE (Teflon) in your precision applications.
At KINTEK, we specialize in the custom fabrication of high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and specialized industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures precision production from prototypes to high-volume orders, delivering the chemical resistance and reliability your projects demand.
Ready to enhance your equipment with durable PTFE solutions? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How was PTFE discovered and developed? From Lab Accident to Essential High-Performance Polymer
- What are the similarities between PTFE and RPTFE? Unlocking the Core Fluoropolymer Identity
- What are the additional properties of PTFE? Beyond Non-Stick: Extreme Chemical, Thermal & Electrical Performance
- How does PTFE react to common solvents? Discover Its Near-Total Chemical Immunity
- What is PTFE and what class of plastics does it belong to? A Guide to High-Performance Fluoropolymers



















