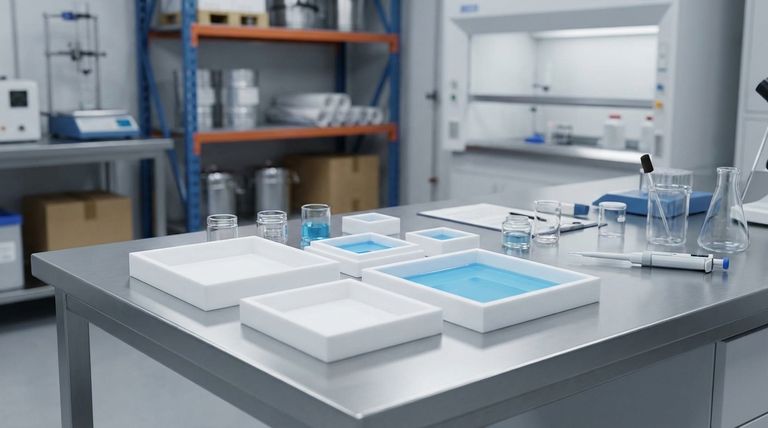
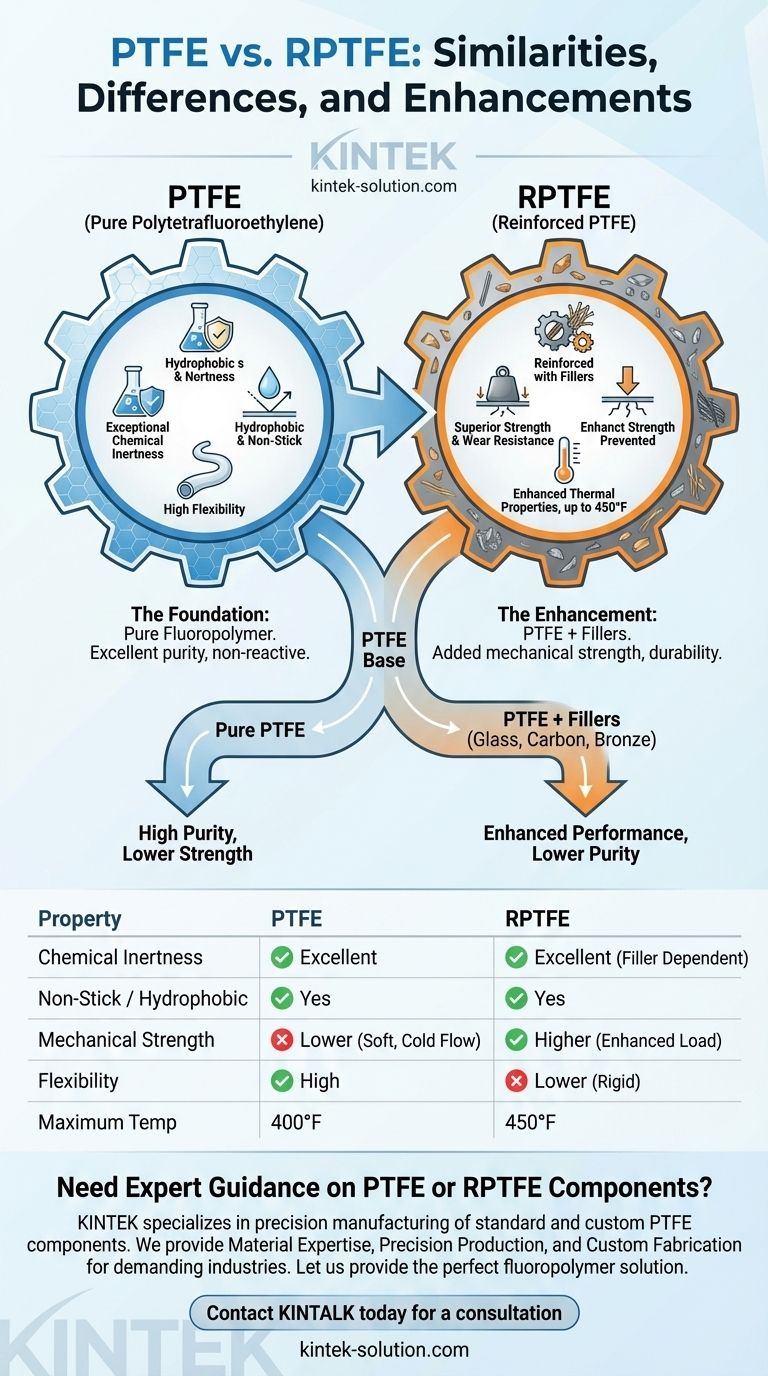
At their core, RPTFE and PTFE are fundamentally the same material. RPTFE, or Reinforced Polytetrafluoroethylene, is simply a variant of PTFE that has been mixed with strengthening agents. Therefore, RPTFE inherits all of PTFE’s foundational properties, including exceptional chemical resistance, a non-stick surface, and hydrophobic (water-repelling) characteristics.
The critical insight is that RPTFE is not a different material, but an enhanced version of PTFE. The similarities are the baseline fluoropolymer properties, while the differences are targeted improvements in mechanical strength and wear resistance.

The Shared Foundation: Understanding the PTFE Core
Both materials originate from the same fluorocarbon base, which is why they share an identical set of core chemical and surface properties. This shared identity is why both are often sold under the common brand name Teflon.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
Both PTFE and RPTFE are highly resistant to corrosion and chemical attack. This is because the underlying molecular structure consists of strong carbon-fluorine bonds, which are extremely stable and non-reactive. This makes them ideal for use in harsh chemical environments.
Hydrophobic and Non-Stick Surface
The fluoropolymer base gives both materials a very low coefficient of friction. This results in the well-known non-stick, or dry-lubricity, characteristic. It also makes the surface hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and does not absorb moisture.
A Common Fluoropolymer Identity
RPTFE is a composite material made from a PTFE base. It always starts as PTFE before fillers are added. Think of it like reinforced concrete—it's still fundamentally concrete, but with steel rebar added to improve its tensile strength.
Where RPTFE Diverges: The Role of Reinforcement
The "R" in RPTFE stands for "Reinforced," and this is the sole point of divergence. Fillers are added to the PTFE base to overcome its inherent mechanical weaknesses.
The Concept of "Fillers"
RPTFE contains additives that pure PTFE lacks. These fillers can include materials like glass fibers, carbon, graphite, or bronze. Each filler is chosen to enhance specific properties of the base PTFE.
Overcoming PTFE's Weaknesses
Standard PTFE is a relatively soft material. While flexible, it is susceptible to deformation and "cold flow" when placed under sustained pressure or load. RPTFE was developed specifically to solve this problem by adding rigidity and stability.
Enhanced Mechanical and Thermal Properties
The addition of fillers gives RPTFE superior strength, durability, and resistance to wear. It also slightly increases its maximum service temperature, with some RPTFE variants rated to 450°F compared to standard PTFE's 400°F.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing RPTFE for its strength introduces compromises that are important to recognize. The enhancements are not free; they come at the cost of some of PTFE's other valued properties.
Sacrificing Purity for Performance
The most significant trade-off is chemical purity. While pure PTFE is one of the most inert substances available, the fillers in RPTFE can potentially react with certain chemicals. For applications requiring absolute non-reactivity, such as in the medical or semiconductor industries, pure PTFE is often the only option.
The Impact on Flexibility
The reinforcement that gives RPTFE its strength also makes it more rigid. In applications that require the high flexibility of a standard PTFE seal or gasket, the stiffness of RPTFE may be a disadvantage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision depends entirely on the mechanical demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and flexibility: Standard PTFE is the superior choice due to its pure, inert composition.
- If your primary focus is strength and wear resistance under load: RPTFE is specifically engineered to provide the necessary mechanical stability that PTFE lacks.
- If your primary focus is a non-stick, corrosion-resistant surface for general use: Begin with standard PTFE, as its benefits are substantial and it is often the more cost-effective solution.
Understanding that RPTFE builds upon PTFE's strengths allows you to select the precise material for your engineering needs.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE | RPTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Excellent | Excellent (with potential filler limitations) |
| Non-Stick / Hydrophobic | Yes | Yes |
| Base Material | Pure PTFE | PTFE with fillers (e.g., glass, carbon) |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower (soft, prone to cold flow) | Higher (enhanced wear & load resistance) |
| Flexibility | High | Lower (more rigid) |
Need Expert Guidance on PTFE or RPTFE Components?
Choosing between PTFE and its reinforced variant (RPTFE) is critical for the performance of your seals, liners, or labware. The right material ensures optimal chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and longevity for your application.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of both standard and custom PTFE components. We serve demanding industries like semiconductor, medical, and laboratory, where material purity and performance are non-negotiable.
We help you navigate the choice by:
- Providing Material Expertise: Our team will analyze your specific requirements for chemical exposure, pressure, temperature, and flexibility to recommend the ideal material—pure PTFE for maximum inertness or RPTFE for superior strength.
- Delivering Precision Production: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we manufacture components that meet exact specifications, ensuring reliability in your most critical processes.
- Offering Custom Fabrication: Need a unique solution? We tailor PTFE and RPTFE parts to fit your unique design and performance needs.
Let us provide the perfect fluoropolymer solution for your project. Contact KINTALK today for a consultation and quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE ideal for high-purity applications? Ensuring Absolute Chemical and Biological Inertness
- How does PTFE perform when exposed to different types of water? Unmatched Chemical Resistance in Any Aqueous Environment
- How do Teflon and UHMW compare in terms of applications and characteristics? Choose the Right High-Performance Polymer
- What are the key physical and chemical properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- How are PTFE coatings applied? A Guide to Spray, Electrostatic, and Dip-Spin Methods
- What should users consider when using the chemical compatibility chart for PTFE? Ensure Material Safety and Reliability
- What are the characteristics of PFA material? A Guide to Its High-Performance Balance
- How can the right PTFE filler be selected for an application? Match Your Needs to the Perfect Filler



















