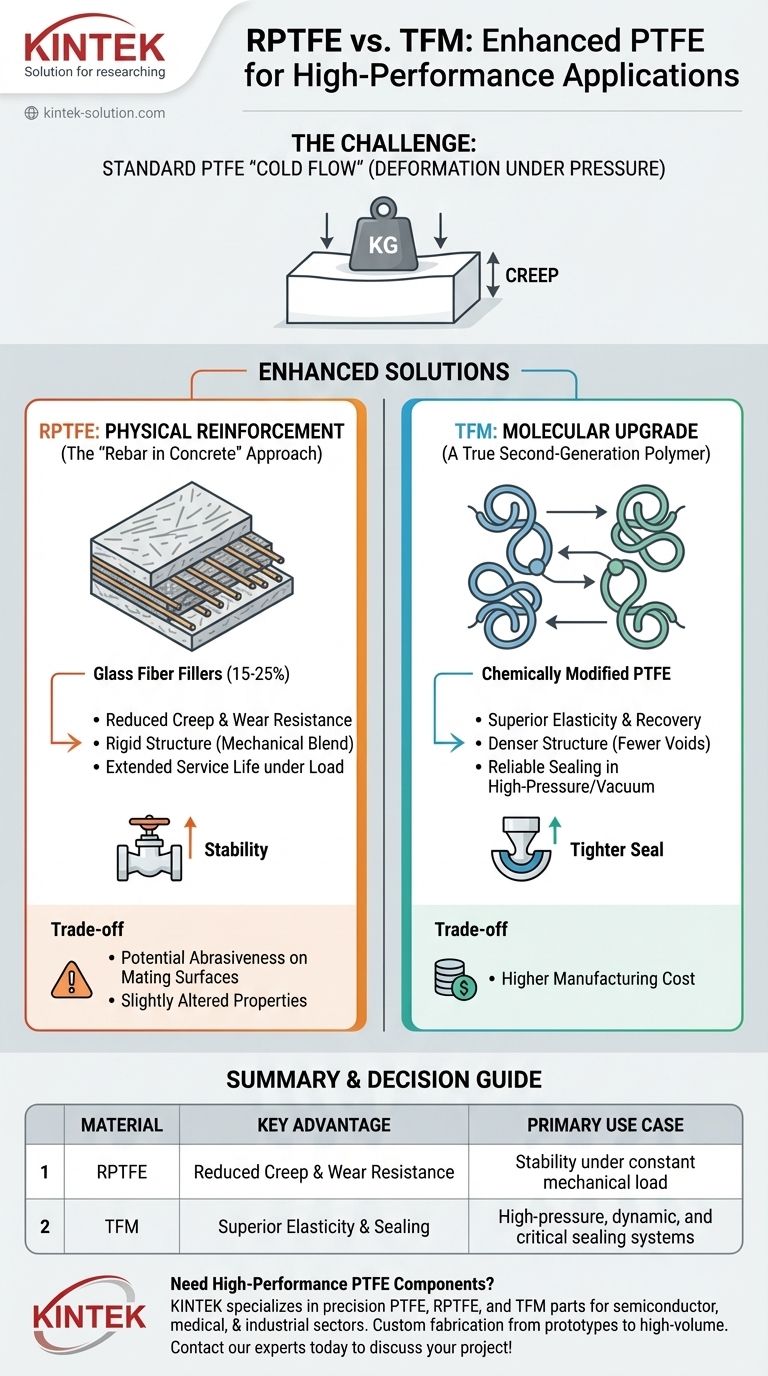
In short, RPTFE and TFM are enhanced versions of standard PTFE designed to overcome its primary mechanical weakness. Reinforced PTFE (RPTFE) gains physical strength and wear resistance by adding fillers like glass fiber, significantly improving its service life under mechanical stress. TFM, a second-generation PTFE, is a chemically modified polymer that offers superior elasticity, resilience, and sealing performance under high pressure.
The core decision between these materials hinges on how you need to solve the problem of "cold flow"—the tendency of standard PTFE to deform under pressure. RPTFE adds physical reinforcement to resist deformation, while TFM improves the polymer's inherent ability to spring back into shape.

The Foundation: Why Modify Standard PTFE?
The Unmatched Baseline of PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), often known by the brand name Teflon, is a remarkable material. Its performance is defined by an exceptional combination of properties.
It offers nearly universal chemical resistance, a very high working temperature (up to 260°C / 500°F), and an extremely low coefficient of friction, making it incredibly non-stick.
PTFE's Primary Limitation: Cold Flow
Despite its strengths, standard PTFE has a significant mechanical drawback: creep, also known as cold flow.
Under sustained pressure or load, especially at elevated temperatures, standard PTFE will slowly and permanently deform. This can be a critical failure point for components like seals, gaskets, and valve seats.
RPTFE: Reinforcing for Strength and Longevity
The "Rebar in Concrete" Approach
RPTFE is a composite material, not a different polymer. It is standard PTFE that has been mechanically blended with a filler material.
The most common variant uses 15%-25% glass fiber. Think of these fibers as microscopic rebar that provides a rigid structure within the softer PTFE matrix, physically holding it in place.
Key Advantage: Reduced Creep and Wear
The primary benefit of this glass reinforcement is a dramatic improvement in resistance to creep and cold flow.
This makes RPTFE far more durable in applications involving mechanical load or friction. The result is a significantly extended service life for parts like valve seats and bearings.
TFM: A Molecular Upgrade for Resilience
A True Second-Generation Polymer
Unlike RPTFE, TFM is not just PTFE with fillers. It is a chemically modified version of the PTFE polymer itself (a perfluoropropylvinylether-modified polytetrafluoroethylene, or PFA/PTFE copolymer).
This molecular-level change alters the material's physical properties while retaining the exceptional chemical and thermal resistance of standard PTFE.
Key Advantage: Superior Elasticity and Recovery
The main advantage of TFM is its enhanced elasticity and resilience. It has a denser polymer structure with fewer voids.
When compressed, TFM has a much better ability to "spring back" to its original shape. This leads to better stress recovery and a more reliable, tighter seal over many pressure cycles.
Higher Pressure and Sealing Performance
Because it recovers its shape so effectively, TFM provides a superior seal in high-pressure and vacuum applications. This reduces the risk of leaks and improves the overall performance and reliability of components like ball valve seats.
Understanding the Trade-offs
RPTFE: The Impact of Fillers
Adding glass fibers is not without consequence. While RPTFE is stronger, the glass filler can make the material more abrasive, potentially causing wear on softer mating surfaces like stainless steel balls in valves over time.
Furthermore, fillers can slightly alter electrical properties and, in extremely aggressive chemical services, can be less resistant than the pure PTFE matrix surrounding them.
TFM: Performance vs. Cost
As a chemically modified, premium material, the primary trade-off for TFM is cost. Its manufacturing process is more complex than simply blending fillers into standard PTFE.
The performance benefits—particularly in critical sealing applications—must justify the higher price point compared to both standard PTFE and RPTFE.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct material requires identifying the specific mechanical challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and stability under constant mechanical load: RPTFE is an excellent and cost-effective choice for improving durability.
- If your primary focus is achieving the best possible seal in a high-pressure or dynamic system: TFM's superior recovery and resilience make it the ideal material for critical sealing applications.
- If your primary focus is chemical compatibility with low mechanical stress: Standard, unfilled PTFE often provides the best price-to-performance ratio.
Ultimately, selecting the right enhanced PTFE is about matching the material's specific advantages to the demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Advantage | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| RPTFE | Reduced Creep & Wear Resistance | Stability under constant mechanical load |
| TFM | Superior Elasticity & Sealing | High-pressure, dynamic, and critical sealing systems |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Choosing the right material is critical for the reliability and longevity of your components. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE, RPTFE, and TFM components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your parts are engineered to meet the exact demands of your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Cleaning Rack
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Adjustable Height Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















