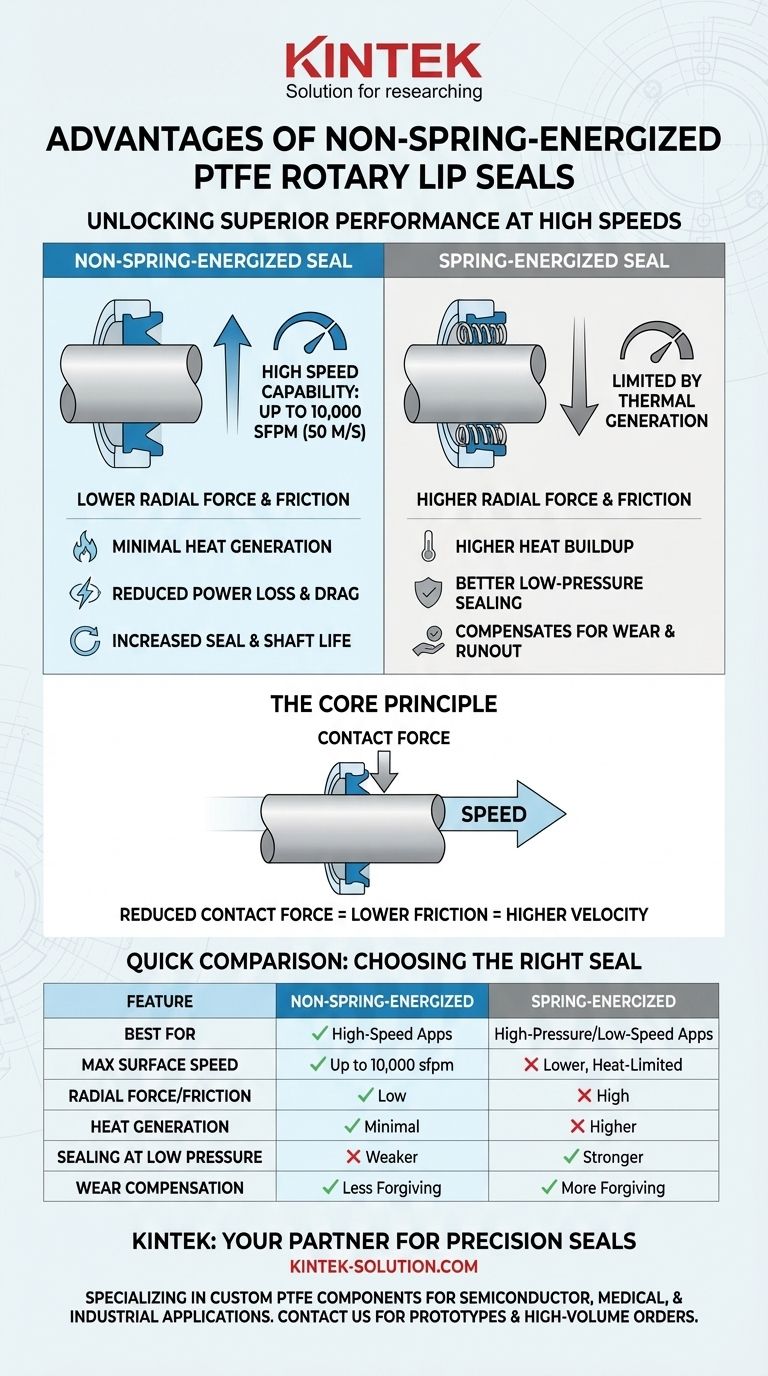
The primary advantage of a non-spring-energized PTFE rotary lip seal is its ability to operate at significantly higher rotational speeds. The absence of a spring results in lower radial contact forces against the shaft, which reduces friction and heat generation, making these seals ideal for high-velocity applications.
The core principle is simple: removing the spring lowers the contact force. This reduction in friction is the key that unlocks superior performance at high surface speeds, a domain where spring-energized seals would generate excessive heat and fail prematurely.

The Physics of High-Speed Sealing
To understand the advantage, we must first look at the forces at play. A rotary seal's effectiveness depends on the precise amount of force its lip exerts on the rotating shaft.
The Role of Radial Force
Every seal lip must press against the shaft with a certain amount of force, known as radial force, to prevent leakage. In a spring-energized seal, a metal spring provides a constant, high radial force to ensure a tight seal across a wide range of conditions.
Friction as the Limiting Factor
This radial force creates friction. As rotational speed increases, this friction generates a proportional amount of heat. Too much heat can damage the seal, the lubricant, and the shaft itself, creating a hard limit on performance.
How Non-Energized Seals Overcome the Limit
A non-spring-energized PTFE seal generates much lower radial force, relying on the inherent properties of the PTFE material and system pressure to create a seal. This fundamental difference drastically reduces friction and heat buildup.
This lower friction is what allows the seal to function effectively at surface speeds up to 10,000 sfpm (approximately 50 m/s), far exceeding the thermal limits of many spring-energized designs.
Key Performance Benefits Explained
The lower radial force of a non-energized seal translates directly into tangible engineering advantages for specific applications.
Superior High-Speed Capability
This is the most significant benefit. Applications like high-speed spindles, motors, and gearboxes require seals that can withstand extreme velocities without overheating. The non-spring-energized design is purpose-built for this environment.
Reduced Frictional Drag and Power Loss
Because there is less friction to overcome, the system wastes less energy. This results in improved mechanical efficiency and can be a critical factor in power-sensitive or battery-operated equipment.
Lower Heat Generation and Increased Life
Less friction means less destructive heat. This not only extends the operational life of the seal itself but also preserves the integrity of the shaft surface and the system's lubricant, leading to greater overall reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a non-spring-energized seal is an engineering decision with clear trade-offs. Its strengths in high-speed applications are balanced by limitations in other areas.
Sealing Force at Low Pressure
The primary drawback is a weaker sealing capability in low-pressure or static conditions. Without a spring to provide constant positive engagement, the seal may not be as effective at preventing leaks when the shaft is stationary or rotating slowly.
Compensation for Wear and Imperfections
A spring helps a seal maintain contact with the shaft as the PTFE lip gradually wears down over time. It can also better accommodate minor shaft imperfections or runout. A non-energized seal is less forgiving in these scenarios.
Application Specificity is Crucial
Neither design is universally "better." A spring-energized seal excels where a robust, constant sealing force is required, especially in high-pressure or low-speed applications. A non-spring-energized seal excels where high rotational speed is the single most critical performance demand.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the primary operational demand of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is maximum rotational speed and efficiency: A non-spring-energized PTFE seal is the definitive choice due to its low friction and minimal heat generation.
- If your primary focus is robust sealing at high pressures or low speeds: A spring-energized seal provides the constant, positive force required for reliable performance in these conditions.
- If you need to accommodate significant shaft runout or plan for long-term wear: The spring in an energized seal offers a clear advantage in maintaining consistent lip contact over the seal's lifetime.
By understanding the direct relationship between radial force, friction, and speed, you can confidently select the sealing technology that aligns perfectly with your engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Non-Spring-Energized PTFE Seal | Spring-Energized PTFE Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | High-speed applications | High-pressure / low-speed applications |
| Max Surface Speed | Up to 10,000 sfpm (50 m/s) | Lower, limited by heat |
| Radial Force / Friction | Low | High |
| Heat Generation | Minimal | Higher |
| Sealing at Low Pressure | Weaker | Stronger |
| Wear Compensation | Less forgiving | More forgiving |
Need a high-performance seal for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision-manufactured PTFE components, including custom rotary lip seals. Whether your priority is extreme speed, efficiency, or pressure resistance, our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get the perfect seal for your needs in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your equipment's reliability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications



















