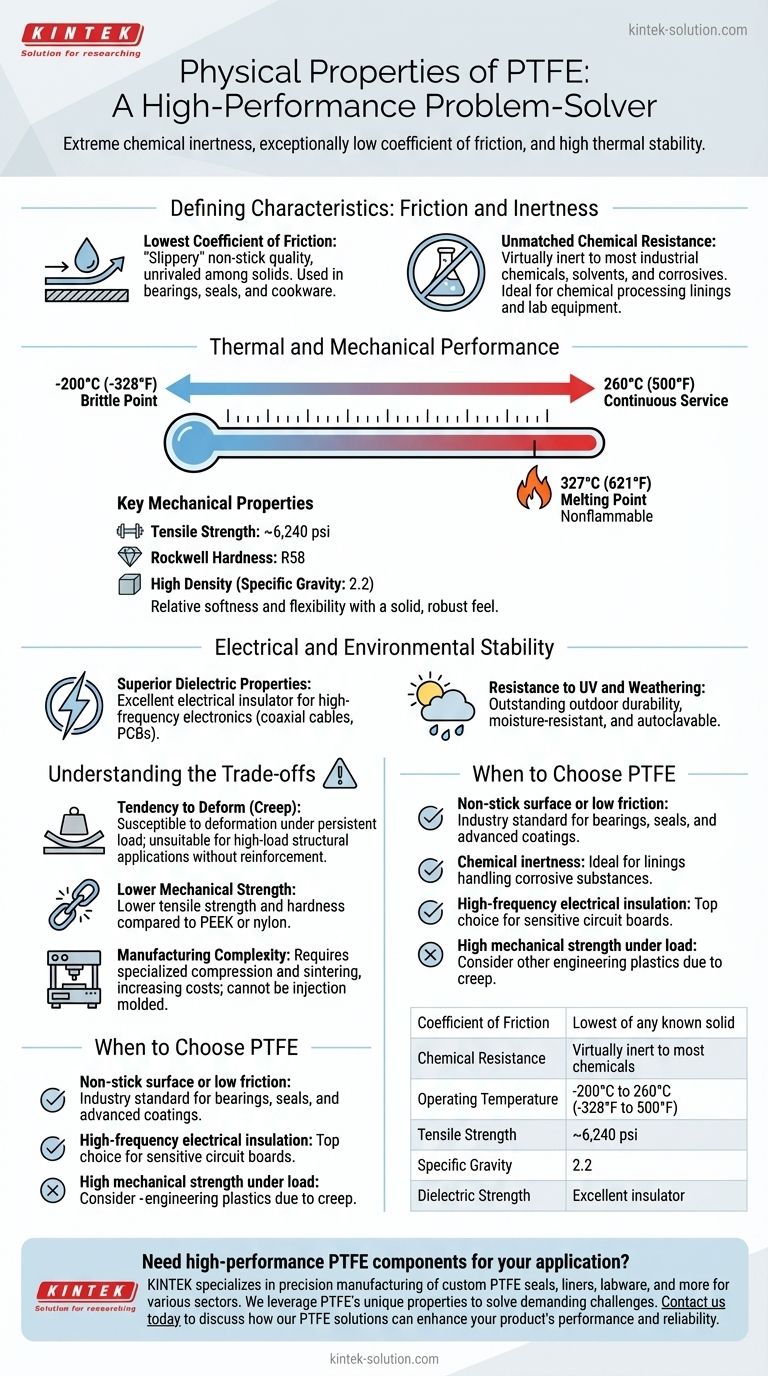
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer defined by three extraordinary properties: its extreme chemical inertness, its exceptionally low coefficient of friction, and its high thermal stability. These characteristics, along with its excellent dielectric strength, make it one of the most versatile and specialized materials for demanding engineering applications where conventional plastics would fail.
PTFE is not a general-purpose material; it is a problem-solver for extreme environments. Its unique combination of properties makes it the default choice for applications requiring resistance to corrosive chemicals, high temperatures, or the need for an ultra-low friction, non-stick surface.

The Defining Characteristics: Friction and Inertness
The molecular structure of PTFE, specifically its strong carbon-fluorine bonds, is the source of its most famous attributes.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE possesses the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid material. This gives it a "slippery" or non-stick quality that is nearly unmatched.
This property is the reason it is used for everything from non-stick cookware to low-friction bearings and seals that operate without lubrication.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert and does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals, solvents, or corrosive agents.
This makes it an ideal material for lining pipes, tanks, and vessels in chemical processing plants, as well as for laboratory equipment that must remain uncontaminated.
Thermal and Mechanical Performance
While not known for its raw strength, PTFE performs reliably across an impressive spectrum of temperatures and conditions.
A Wide Operating Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its properties across an exceptionally broad temperature range, from a brittle point of -200°C (-328°F) up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F).
Its melting point is approximately 327°C (621°F), and it is nonflammable, adding to its thermal stability.
Key Mechanical Properties
PTFE is a relatively soft, flexible polymer. It has a tensile strength of around 6,240 psi and a Rockwell hardness of R58.
While flexible even at low temperatures, it is also valued for its high strength-to-weight ratio and wear resistance in appropriate applications.
High Density
With a specific gravity of 2.2, PTFE is one of the denser engineering plastics. This contributes to its solid, high-quality feel and robust nature.
Electrical and Environmental Stability
PTFE's inertness extends beyond chemical reactions to include resistance to environmental factors and electrical currents.
Superior Dielectric Properties
PTFE has excellent dielectric strength, meaning it is a highly effective electrical insulator.
This property makes it indispensable in high-frequency electronics, such as for insulating coaxial cables and manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Resistance to UV and Weathering
PTFE exhibits outstanding resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and general weathering. This allows it to be used in outdoor applications for long periods without significant degradation. It is also moisture-resistant and autoclavable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. To use PTFE effectively, it is critical to understand its limitations.
Tendency to Deform (Creep)
PTFE's primary mechanical weakness is its susceptibility to "creep," or deformation over time when subjected to a persistent load. This makes it unsuitable for high-load structural applications without reinforcement.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics like PEEK or nylon, PTFE has lower tensile strength and hardness. It is not a material chosen for its rigidity or structural integrity alone.
Manufacturing Complexity
PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques like injection molding. It must be machined from stock shapes or formed using specialized compression and sintering methods, which can increase manufacturing costs.
When to Choose PTFE
Your application's specific requirements will determine if PTFE is the correct material.
- If your primary focus is a non-stick surface or low friction: PTFE is the industry standard for applications like bearings, seals, and advanced coatings.
- If your primary focus is chemical inertness: It is the ideal choice for lining pipes, vessels, and lab equipment handling corrosive substances.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Its excellent dielectric properties make it a top choice for coaxial cables and sensitive circuit boards.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical strength under load: You should consider other engineering plastics, as PTFE is prone to creep and deformation.
Ultimately, PTFE is the definitive material choice when performance in extreme chemical, thermal, or low-friction environments is the most critical factor.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Coefficient of Friction | Lowest of any known solid |
| Chemical Resistance | Virtually inert to most chemicals |
| Operating Temperature | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Tensile Strength | ~6,240 psi |
| Specific Gravity | 2.2 |
| Dielectric Strength | Excellent insulator |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE seals, liners, labware, and more for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We leverage PTFE's unique properties to solve your most demanding challenges, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F



















