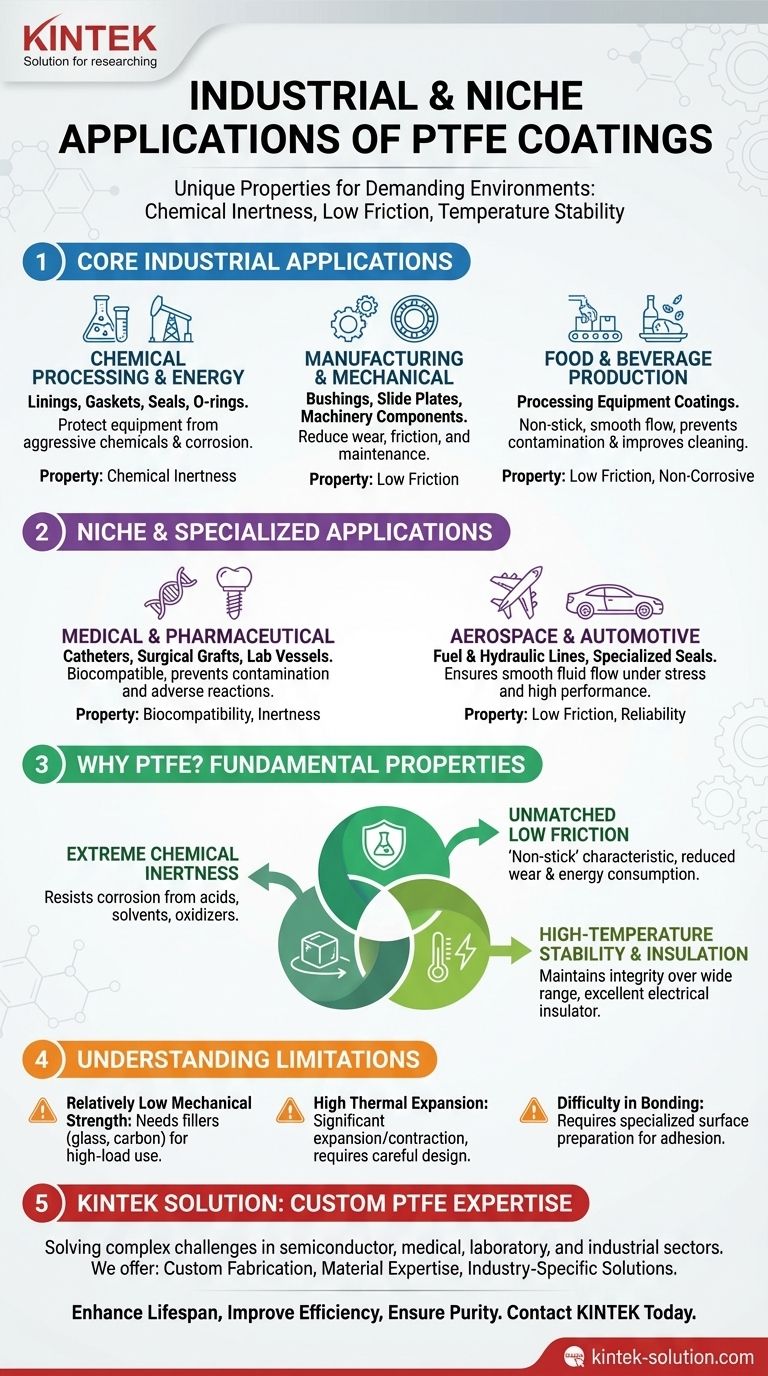
In industrial settings, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) coatings are most recognized for their use in chemical processing equipment, machinery components, and food production due to their extreme chemical inertness and low friction. Niche applications leverage these same properties for highly specialized uses, such as in medical implants, aerospace fuel lines, and advanced electrical insulation.
PTFE is rarely chosen for a single characteristic. Its value lies in the unique combination of properties—chemical inertness, low friction, and temperature stability—making it a critical problem-solver in environments where other materials would quickly fail.

Why PTFE is a Go-To Industrial Material
The widespread adoption of PTFE is not accidental. It is a direct result of three fundamental properties that make it uniquely suited for demanding operational conditions. Understanding these is key to identifying its ideal applications.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive substances known. It resists corrosion and degradation from a vast range of aggressive chemicals, including strong acids, solvents, and oxidizing agents.
This property makes it indispensable for lining vessels, pipes, and reactors in the chemical processing and pharmaceutical industries, preventing equipment failure and product contamination.
Unmatched Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, a quality often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This "non-stick" characteristic is its most famous attribute.
In industrial machinery, this translates to reduced wear on gears, bearings, and slide plates. This not only extends component life but also significantly cuts down on energy consumption.
High-Temperature Stability and Insulation
PTFE maintains its integrity over a wide temperature range and is an excellent electrical insulator.
This combination makes it a primary material for high-performance cable and wire insulation, especially in applications where both heat resistance and signal integrity are critical.
Key Industrial Applications Explained
The core properties of PTFE directly translate into its most common and critical industrial uses across multiple sectors.
Chemical Processing and Energy Sectors
In hostile environments like chemical plants or offshore oil and gas operations, equipment protection is paramount.
PTFE is used for gaskets, seals, and O-rings to create reliable, chemically-resistant seals. It is also used to line reactors, columns, and pipes to protect the structural metal from corrosive contents.
Manufacturing and Mechanical Systems
Efficiency and longevity are the primary goals in mechanical design.
Coatings are applied to machinery components to reduce the energy needed to overcome friction. Using PTFE on parts like bushings and slide plates minimizes maintenance and replacement costs by drastically reducing wear.
Food and Beverage Industry
Beyond simple non-stick cookware, PTFE plays a crucial role in commercial food production.
Its non-corrosive and non-stick nature is ideal for coating processing equipment, ensuring that materials flow smoothly without sticking or becoming contaminated. This improves efficiency and simplifies cleaning.
Specialized and Niche Applications
PTFE's unique profile allows it to solve highly specific challenges in advanced industries where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
Medical and Pharmaceutical
Biocompatibility and purity are essential in medical applications.
PTFE's inertness makes it suitable for coating catheters, surgical grafts, and other implantable devices, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions. In laboratories, PTFE vessels and tubes prevent chemical corrosion and microbial contamination.
Automotive and Aerospace
Fluid dynamics and component reliability are critical in these high-performance sectors.
PTFE coatings are used to line fuel and hydraulic lines, ensuring smooth, unimpeded fluid flow. Its low-friction properties are also leveraged in specialized seals and components where performance under stress is required.
Understanding PTFE's Limitations
While incredibly versatile, PTFE is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its trade-offs is crucial for proper application.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. In high-load or abrasive environments, an unmodified PTFE coating can wear away quickly. Fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze are often added to enhance its wear resistance and mechanical strength.
High Thermal Expansion
Compared to metals, PTFE expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes. This must be accounted for in engineering designs, especially when it is used as a seal or gasket in applications with wide thermal cycling.
Difficulty in Bonding
Due to its non-stick nature, bonding PTFE to other surfaces can be challenging. It typically requires specialized surface preparation techniques, such as chemical etching, to create a strong and durable adhesive bond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a PTFE coating depends entirely on the primary problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is equipment lifespan in corrosive environments: Leverage PTFE's chemical inertness for linings, gaskets, and seals to protect your assets.
- If your primary focus is reducing energy consumption and mechanical wear: Apply PTFE to gears, bearings, and sliding parts to dramatically lower friction and maintenance needs.
- If your primary focus is purity in medical or food-grade applications: Use PTFE for its non-reactive and non-stick surfaces to prevent contamination and ensure process integrity.
Ultimately, PTFE is the material of choice when you need reliable performance under conditions that would compromise lesser materials.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Industrial Application | Niche/Specialized Use |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Chemical processing linings, gaskets | Medical implants, pharmaceutical vessels |
| Low Friction | Machinery components (gears, bearings) | Aerospace fuel lines, automotive seals |
| Temperature Stability | High-performance wire insulation | Components for high-heat environments |
Need a Custom PTFE Solution for Your Application?
PTFE's unique properties make it ideal for solving complex challenges in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need corrosion-resistant seals, low-friction liners, or custom labware, KINTEK can help.
We specialize in precision manufacturing of PTFE components, offering:
- Custom Fabrication: From initial prototypes to high-volume production runs.
- Material Expertise: Ensuring the right PTFE formulation for your specific environment.
- Industry-Specific Solutions: Components designed for the demanding needs of your sector.
Let us help you enhance equipment lifespan, improve efficiency, and ensure product purity.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















