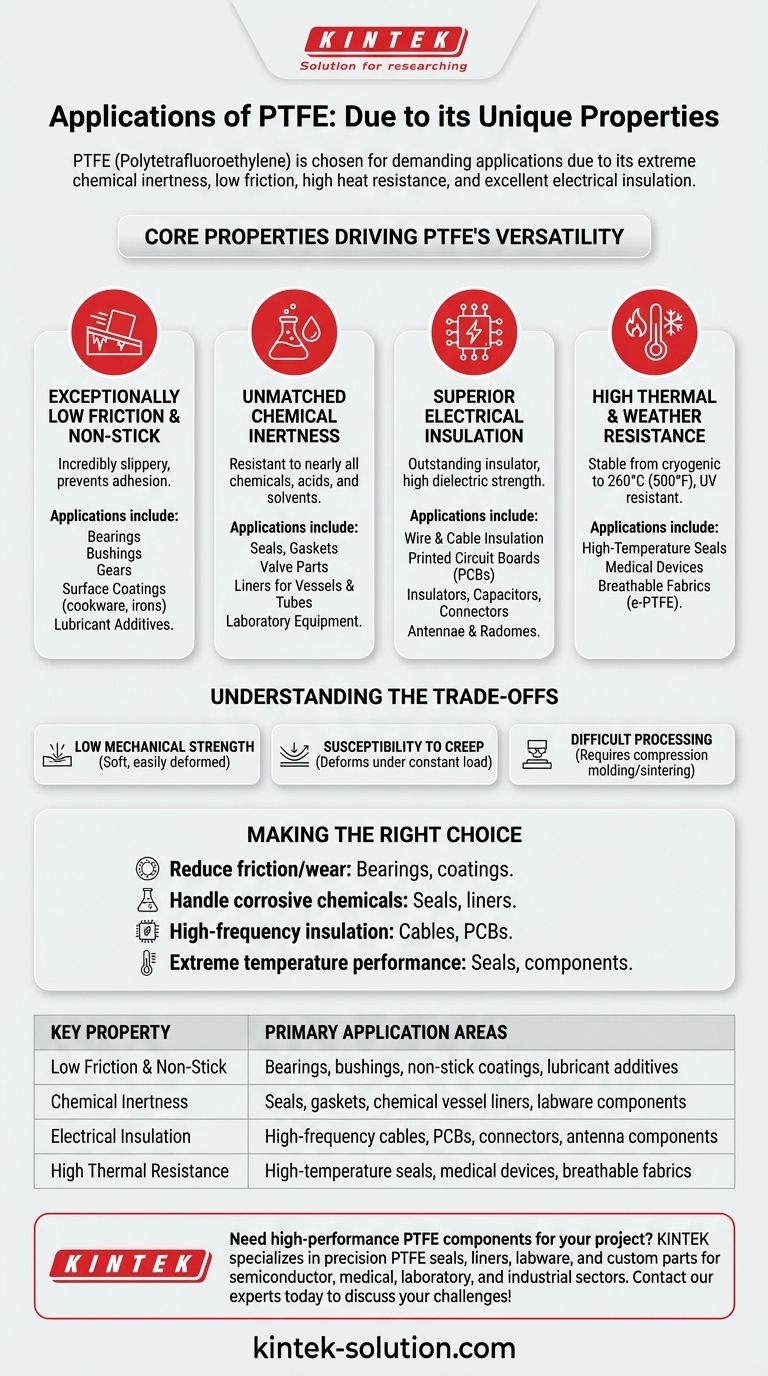
Due to its unique combination of properties, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is used in a vast range of demanding applications. Its value stems from its extreme chemical inertness, exceptionally low coefficient of friction, high heat resistance, and excellent electrical insulation, making it a critical material for everything from industrial seals and gaskets to high-frequency circuit boards and non-stick coatings.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread adoption is that no other single polymer combines its near-universal chemical resistance, elite non-stick characteristics, and high-performance electrical and thermal stability. It is the material of choice where other plastics would fail.
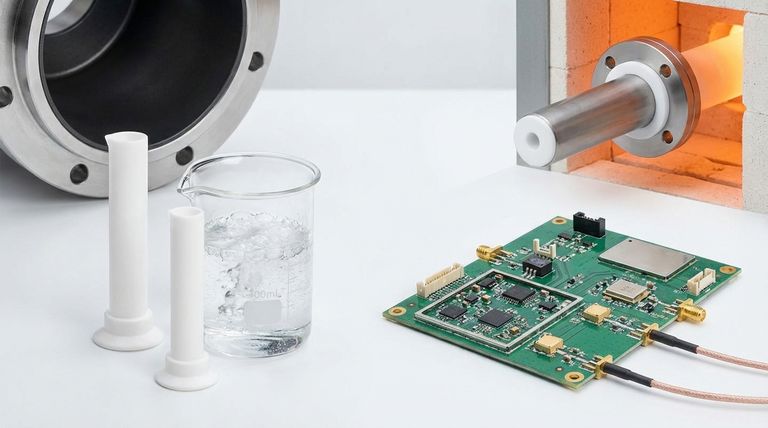

The Core Properties Driving PTFE's Versatility
To understand PTFE's applications, you must first understand the fundamental characteristics that make it so effective. Each primary use case is a direct result of one or more of its key properties.
Exceptionally Low Friction & Non-Stick Nature
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This property, often compared to wet ice on wet ice, means it is incredibly slippery and that other materials do not readily adhere to it.
This leads to applications in mechanical systems and coatings, including:
- Bearings, Bushings, and Gears: Where parts must slide against each other with minimal energy loss and wear.
- Surface Coatings: The famous non-stick layer on cookware, baking sheets, clothing irons, and hair styling tools.
- Lubricant Additives: Finely powdered PTFE is added to greases and oils to significantly reduce friction in machinery and bike chains.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
The powerful carbon-fluorine bonds in PTFE's structure make it resistant to nearly all chemicals, including aggressive acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. It is essentially inert and insoluble.
This makes it indispensable for chemical processing and containment:
- Seals, Gaskets, and Valve Parts: Creating durable seals in pipes and reactors that handle corrosive fluids.
- Liners for Vessels and Tubes: Protecting pipes and tanks in chemical plants from their reactive contents.
- Laboratory Equipment: Used for plugs and components in lab glassware where contamination is unacceptable.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator. It has a high dielectric strength, a very low dielectric constant, and a low dissipation factor, meaning it resists the flow of electricity and performs exceptionally well in high-frequency applications.
This property is critical for the electronics and communications industries:
- Wire and Cable Insulation: Especially for high-frequency coaxial cables used in telecommunications and data transfer.
- Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): Used as the substrate material for circuits operating at microwave frequencies.
- Insulators, Capacitors, and Connectors: Providing stable insulation in high-performance electronic components.
- Antennae and Radomes: Used for protective coverings that must be transparent to radio waves.
High Thermal & Weather Resistance
PTFE is stable across an exceptionally wide range of temperatures, from cryogenic levels up to approximately 260°C (500°F). It is also highly resistant to UV radiation and weathering, meaning it does not degrade with outdoor exposure.
This resilience leads to applications in extreme environments:
- High-Temperature Seals: Maintaining integrity in automotive and aerospace applications where heat is a major factor.
- Medical Devices: Its inertness and lubricity make it suitable for items like catheters, where it can help prevent bacterial adhesion.
- Breathable Fabrics: Expanded PTFE (e-PTFE) creates a microporous membrane used in waterproof yet breathable outerwear and rainwear.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not the perfect material for every situation. Acknowledging its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE is relatively soft. It has low tensile strength and can be easily scratched or deformed. For structural parts, it is often reinforced with fillers like glass fiber or carbon to improve its strength and wear resistance.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a constant load, PTFE has a tendency to "creep," or slowly and permanently deform over time. While this can be beneficial for gaskets that need to conform to a surface, it makes pure PTFE unsuitable for precision components that must hold tight tolerances under pressure.
Difficult Processing
PTFE has a very high melting point and melt viscosity, which means it cannot be processed using conventional techniques like injection molding or extrusion. Instead, it typically requires more complex and costly methods like compression molding and sintering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice to use PTFE should be driven by the most critical demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: Use PTFE for bearings, slide plates, non-stick coatings, and as a lubricant additive.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive chemicals: Choose PTFE for seals, gaskets, pump components, and vessel linings.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: PTFE is the ideal material for high-performance cables, PCBs, and connectors.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: Select PTFE for seals and components that must operate in either very hot or very cold environments.
By matching PTFE's distinct advantages to your specific challenge, you can leverage it as a powerful problem-solving material in engineering and design.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Application Areas |
|---|---|
| Low Friction & Non-Stick | Bearings, bushings, non-stick coatings, lubricant additives |
| Chemical Inertness | Seals, gaskets, chemical vessel liners, labware components |
| Electrical Insulation | High-frequency cables, PCBs, connectors, antenna components |
| High Thermal Resistance | High-temperature seals, medical devices, breathable fabrics |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your project? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom parts for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet the exact demands of your application. Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can solve your unique challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of Teflon? Leverage Its Unique Properties for Your Industry
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments



















