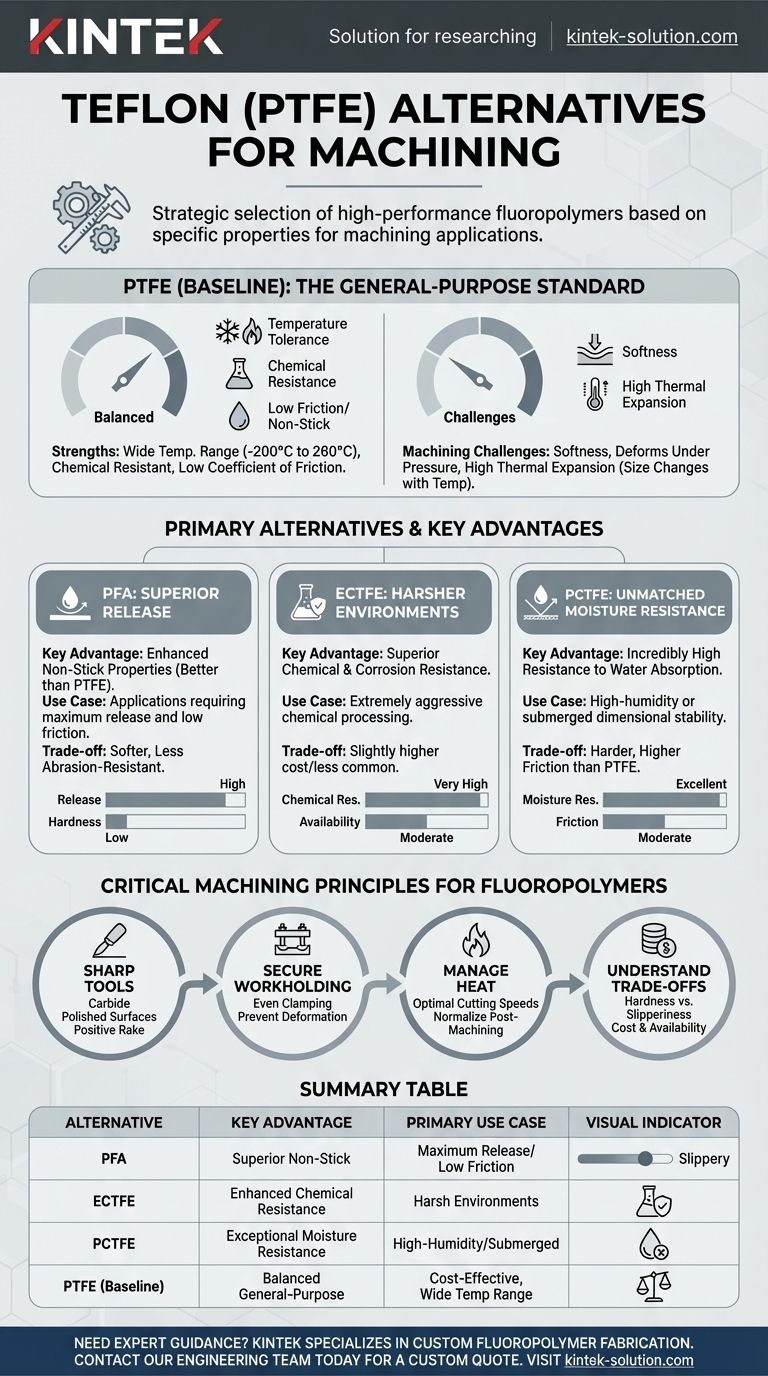
For machining applications, the primary alternatives to Teflon (PTFE) are other high-performance fluoropolymers such as PFA, ECTFE, and PCTFE. The ideal choice is not a simple replacement but a strategic selection based on which specific property—such as chemical resistance, water absorption, or non-stick performance—is most critical for your application.
While Teflon (PTFE) sets the standard for general-purpose use, its inherent softness and high thermal expansion create distinct machining challenges. Its alternatives are not universally "better," but rather specialized materials that enhance a specific property at the cost of another.

A Baseline: Understanding Teflon (PTFE)
To choose the right alternative, we must first benchmark against the material you are looking to replace. Teflon (PTFE) is valued for its unique combination of properties.
Core Strengths
PTFE offers an excellent balance of benefits, including a very wide temperature tolerance (from -200°C to 260°C), near-universal chemical resistance, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. It is also a superior electrical insulator and is famously non-stick.
Key Machining Challenges
The primary challenge in machining PTFE is its softness and lack of rigidity. This can lead to part deformation under clamping pressure, tool chatter, and difficulty holding tight tolerances. Furthermore, its high coefficient of thermal expansion means the part can change size significantly with even minor temperature fluctuations during machining.
Exploring the Primary Alternatives
Each alternative offers a targeted improvement over a specific PTFE characteristic, making them suitable for specialized applications.
PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy): For Superior Release
PFA’s main advantage is having even better non-stick properties than PTFE.
However, this comes at a cost. PFA is generally softer and less abrasion-resistant than PTFE, making it a poor choice for components that will experience mechanical wear.
ECTFE (Ethylene Chlorotrifluoroethylene): For Harsher Environments
ECTFE provides slightly superior chemical and corrosion resistance when compared to PTFE.
This makes it an excellent candidate for components used in extremely aggressive chemical processing environments where even PTFE might be compromised over time.
PCTFE (Polychlorotrifluoroethylene): For Unmatched Moisture Resistance
PCTFE is distinguished by its incredibly high resistance to water absorption. It has one of the lowest moisture vapor transmission rates of any plastic.
This property makes it ideal for applications requiring exceptional dimensional stability in high-humidity or submerged conditions, where PTFE might swell slightly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting one of these materials requires a clear understanding of the engineering compromises you are making. No single fluoropolymer is perfect for every job.
The Hardness vs. Slipperiness Spectrum
There is often an inverse relationship between a material's non-stick quality and its mechanical strength. PFA is the most "slippery" but also the softest. PCTFE is much harder and more rigid but has a higher coefficient of friction than PTFE.
Thermal Expansion is a Shared Challenge
All of these fluoropolymers have a high coefficient of thermal expansion. While some are better than others, this is a fundamental characteristic you must account for when machining any of them. Precision work requires careful heat management and, often, a post-machining normalization or stress-relief process.
Always Factor in Cost and Availability
Specialty polymers like PFA, ECTFE, and PCTFE are typically more expensive and less readily available than standard PTFE. This practical constraint should always be part of your material selection process.
Principles for Machining Any Fluoropolymer
Regardless of which material you choose, the following machining principles are critical for success due to their shared softness and thermal sensitivity.
Tool Selection is Non-Negotiable
Use extremely sharp tools, preferably made from carbide with polished surfaces to reduce friction and material buildup. Tools with positive rake angles help produce a cleaner shearing action rather than pushing the material.
Secure Workholding is Paramount
Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped to prevent vibration, which is a primary cause of a poor surface finish. Use fixtures that distribute clamping force evenly to avoid deforming or marring the soft material.
Manage Heat and Cutting Speed
Use appropriate cutting speeds to minimize heat generation. Excessive heat will cause the material to expand during the cut, leading to inaccurate final dimensions once the part cools.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the single most important performance requirement of the finished part.
- If your primary focus is maximum release/non-stick properties: PFA is your best choice, but be prepared for its lower abrasion resistance.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical or corrosion resistance: ECTFE offers a slight but meaningful upgrade over standard PTFE for the harshest environments.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability in wet or humid conditions: PCTFE's near-zero water absorption makes it the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is a balanced, general-purpose component: Standard Teflon (PTFE) remains an excellent and cost-effective baseline.
By matching the material's peak strength to your application's greatest demand, you can ensure a successful outcome for your project.
Summary Table:
| Alternative | Key Advantage | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| PFA | Superior non-stick/release properties | Applications requiring maximum release, low friction |
| ECTFE | Enhanced chemical/corrosion resistance | Harsh chemical processing environments |
| PCTFE | Exceptional moisture resistance & dimensional stability | High-humidity or submerged applications |
| PTFE (Baseline) | Balanced general-purpose performance | Cost-effective components with wide temperature range |
Struggling to choose the right fluoropolymer for your precision component? KINTEK specializes in custom fabrication of PTFE, PFA, ECTFE, and PCTFE components for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Our expertise in precision machining ensures your parts meet exact specifications—from prototypes to high-volume production. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project requirements and receive a custom quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Evaporating Dishes for Diverse Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key chemical properties of PTFE balls? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability
- How do the chemical properties of PTFE balls influence their performance? Unmatched Durability in Harsh Environments
- What are the advantages of PTFE balls over metals or alloys? Superior Chemical & Friction Resistance
- What temperature range can Teflon (PTFE) balls withstand? -200°C to +260°C Performance Guide
- What are the overall advantages of using PTFE balls in fluid management systems? Enhance Reliability & Efficiency



















