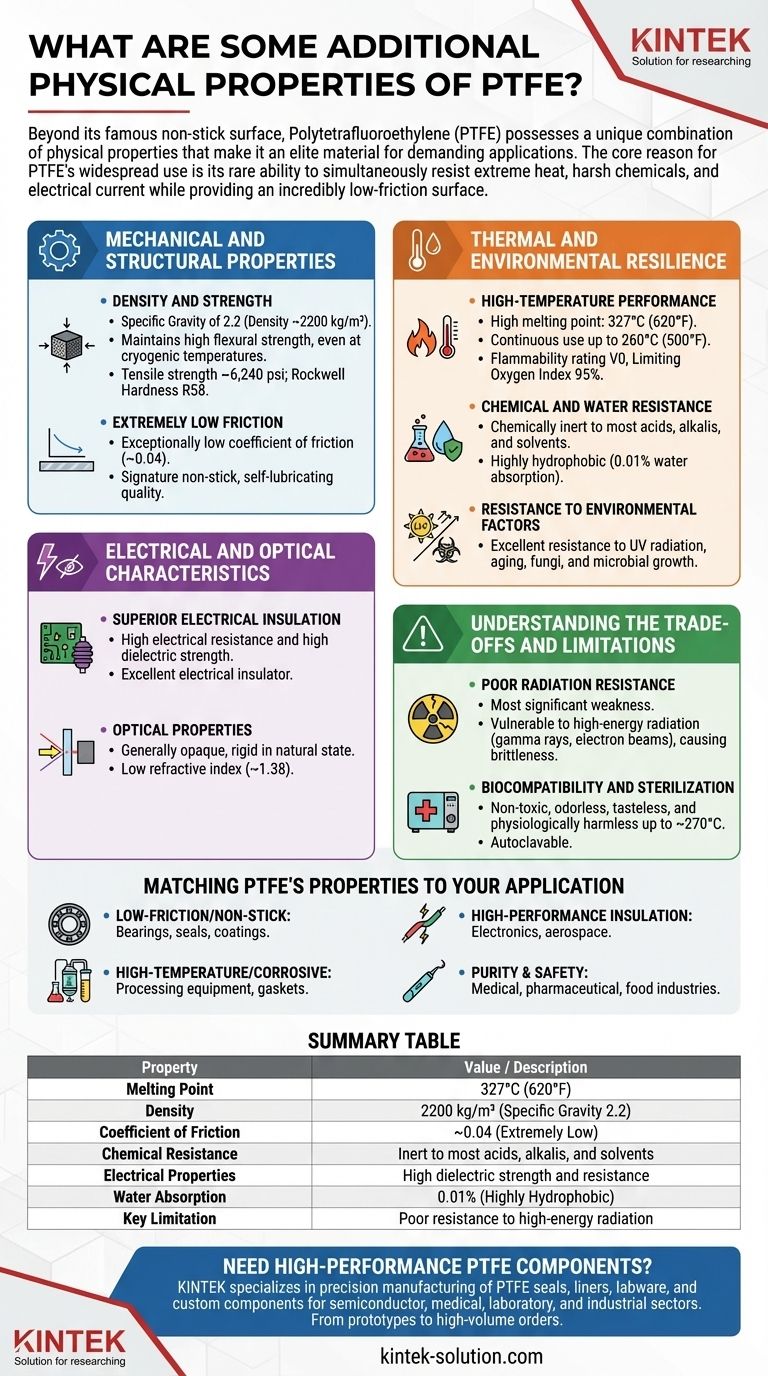
Beyond its famous non-stick surface, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) possesses a unique combination of physical properties that make it an elite material for demanding applications. These include exceptional thermal stability with a melting point of 327°C, a high density of 2200 kg/m³, excellent electrical resistance, and high flexural strength that persists even at very low temperatures. Its chemical inertness is matched by its resistance to UV radiation, water, and biological growth.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread use is not a single property, but its rare ability to simultaneously resist extreme heat, harsh chemicals, and electrical current while providing an incredibly low-friction surface.

Mechanical and Structural Properties
PTFE's physical makeup gives it a distinct profile combining density with slickness and resilience.
Density and Strength
PTFE is a dense polymer, with a specific gravity of 2.2 (a density of approximately 2200 kg/m³). This density contributes to its robust, high-quality feel.
It maintains high flexural strength, meaning it can resist bending forces without breaking, a property it notably retains even at cryogenic temperatures. It also has a tensile strength of around 6,240 psi and a Rockwell hardness of R58.
Extremely Low Friction
One of PTFE's most defining characteristics is its exceptionally low coefficient of friction, which is approximately 0.04.
This value is one of the lowest of any known solid material, giving it the signature "non-stick" or self-lubricating quality prized in applications from cookware to industrial bearings.
Thermal and Environmental Resilience
PTFE is engineered to withstand extreme conditions, from high temperatures to corrosive chemical and environmental exposure.
High-Temperature Performance
PTFE has a very high melting point of 327°C (620°F) and can be used continuously at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
This thermal stability is complemented by its inherent flame resistance. It has a flammability rating of V0 and a limiting oxygen index of 95%, meaning it will not burn in most atmospheric conditions.
Chemical and Water Resistance
Due to the strong carbon-fluorine bonds in its structure, PTFE is chemically inert to nearly all acids, alkalis, and solvents.
Furthermore, it is highly hydrophobic (water-repellent). Its water absorption is extremely low, measured at just 0.01% over a 24-hour period.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
PTFE demonstrates excellent resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, making it suitable for outdoor applications without degrading. It is also highly resistant to aging, fungi, and microbial growth.
Electrical and Optical Characteristics
PTFE's molecular structure makes it a premier material for electrical applications where insulation is critical.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE exhibits high electrical resistance and high dielectric strength. This means it is an excellent electrical insulator, capable of withstanding high voltages without conducting electricity.
This property makes it indispensable for high-frequency applications, such as in coaxial cables and printed circuit boards.
Optical Properties
PTFE is generally an opaque, rigid material in its natural state. It has a low refractive index of approximately 1.38.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PTFE is not the ideal choice for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Poor Radiation Resistance
The most significant weakness of PTFE is its poor resistance to high-energy radiation, such as gamma rays or electron beams. This type of radiation can break down the polymer's molecular structure, causing it to become brittle and lose its mechanical properties.
Biocompatibility and Sterilization
PTFE is considered non-toxic, odorless, tasteless, and physiologically harmless up to approximately 270°C.
This inertness, combined with its ability to be sterilized in an autoclave, makes it a suitable material for specific medical and food-processing applications.
Matching PTFE's Properties to Your Application
Choosing a material requires aligning its strengths with your primary goal. PTFE's unique profile makes it a clear choice for specific challenges.
- If your primary focus is low-friction or non-stick surfaces: PTFE's ultra-low coefficient of friction is its most valuable asset for bearings, seals, and coatings.
- If your primary focus is performance in high-temperature or corrosive environments: Its high melting point and near-total chemical inertness make it ideal for chemical processing equipment and gaskets.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electrical insulation: Its exceptional dielectric strength is critical for wiring, connectors, and components in the electronics and aerospace industries.
- If your primary focus is purity and safety: Its non-toxic and autoclavable nature makes it a reliable choice for select applications in the medical, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
Ultimately, PTFE should be chosen when you need a material that refuses to react—whether to heat, chemicals, electricity, or surface contact.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 327°C (620°F) |
| Density | 2200 kg/m³ (Specific Gravity 2.2) |
| Coefficient of Friction | ~0.04 (Extremely Low) |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to most acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Electrical Properties | High dielectric strength and resistance |
| Water Absorption | 0.01% (Highly Hydrophobic) |
| Key Limitation | Poor resistance to high-energy radiation |
Need high-performance PTFE components that leverage these elite properties?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise ensures your parts meet the highest standards for thermal stability, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let's discuss your application requirements – contact our team today for a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments



















