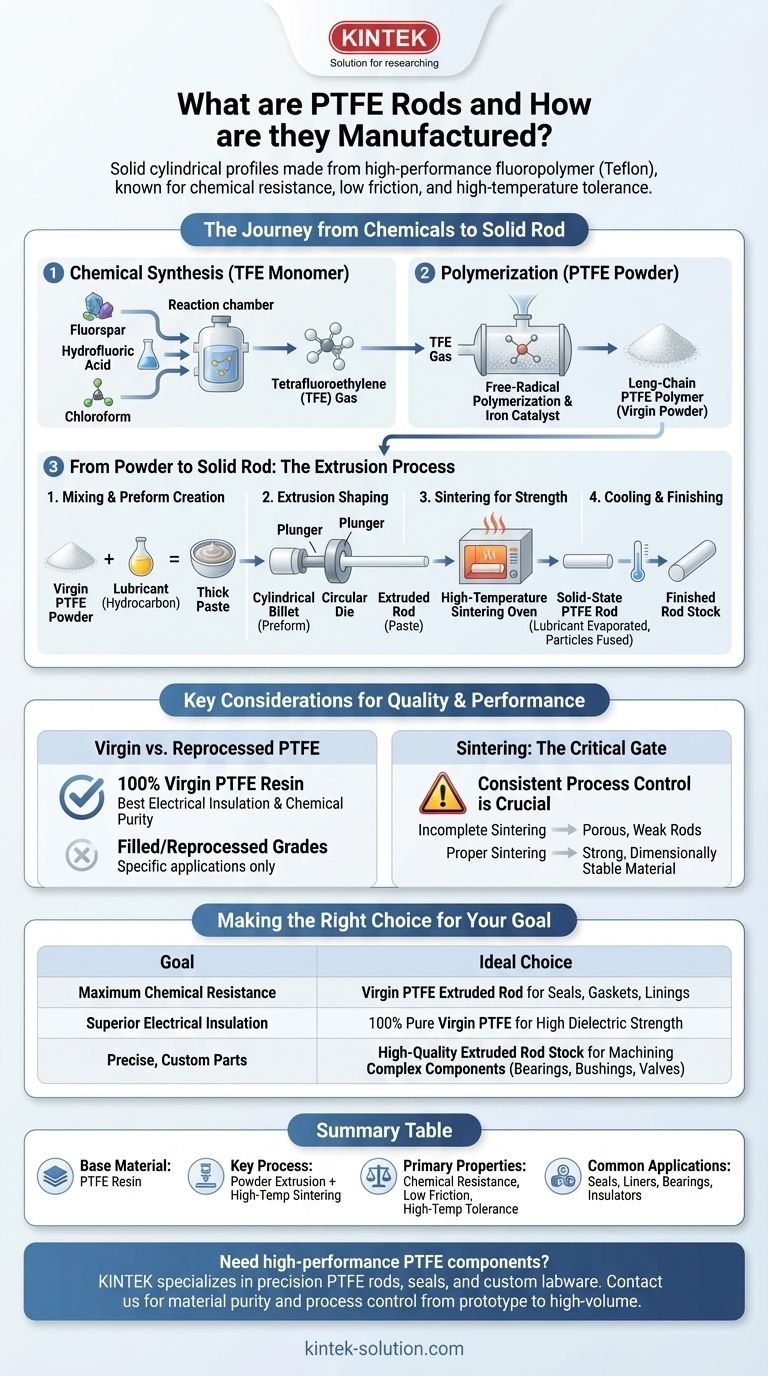
At its core, a PTFE rod is a solid, cylindrical profile made from polytetrafluoroethylene resin, a high-performance fluoropolymer commonly known by the trade name Teflon. These rods are valued for their exceptional chemical resistance, extremely low coefficient of friction, and high-temperature tolerance. They are manufactured through a multi-stage process where raw PTFE powder is mixed with a lubricant, extruded into the rod shape, and then sintered at high temperatures to create a solid, stable final product.
The key takeaway is that the manufacturing process is not simply melting and molding. It is a precise journey of chemical synthesis, powder extrusion, and high-temperature sintering that directly creates the legendary low-friction and chemically inert properties for which PTFE is known.

The Foundation: Creating the PTFE Polymer
Before a rod can be formed, the base PTFE material must be synthesized. This is a two-stage chemical process that builds the unique molecular structure of the polymer.
From Raw Chemicals to a Monomer
The process begins with common industrial ingredients: fluorspar, hydrofluoric acid, and chloroform. These are heated within a chemical reaction chamber to synthesize tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), a colorless, odorless gas. TFE is the fundamental molecular building block, or monomer, of PTFE.
The Polymerization Process
The TFE gas is then subjected to free-radical polymerization. This process, often conducted in an aqueous medium with an iron catalyst, links the individual TFE molecules together into extremely long, stable chains. The result is a linear polymer structure that forms solid grains or a fine powder of pure PTFE resin.
From Powder to Solid Rod: The Extrusion Process
The raw PTFE powder cannot be melted and processed like a typical thermoplastic. Instead, a specialized extrusion method is required to consolidate the powder into a dense, solid rod.
Step 1: Mixing and Preform Creation
The process starts with pure, virgin PTFE powder. This powder is mixed with a liquid lubricant, often a hydrocarbon, to form a thick paste. This paste is then compacted into a cylindrical billet known as a "preform."
Step 2: Extrusion Shaping
The preform is placed into an extruder. A plunger then forces this lubricated paste through a circular die at high pressure. This action shapes the material into a continuous, uniform cylindrical rod.
Step 3: Sintering for Strength
The extruded rod, still containing the lubricant, is then moved into a specialized oven for sintering. It is baked at a precise high temperature (below its melting point). This critical step accomplishes two goals: it evaporates the lubricant and fuses the individual PTFE particles together, creating a strong, solid-state material.
Step 4: Cooling and Finishing
Finally, the sintered rods are carefully cooled to ensure dimensional stability and prevent stress fractures. Once cooled, they are cut to standard or custom lengths, ready for use or further machining.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
The manufacturing method directly impacts the quality and performance of the final product. Understanding these nuances is critical for any technical application.
The Importance of Virgin PTFE
The highest quality PTFE rods are made from 100% virgin PTFE resin. While filled or reprocessed grades exist for specific applications, virgin PTFE provides the best electrical insulation properties and the highest degree of chemical purity.
Sintering is the Critical Quality Gate
The sintering phase is arguably the most important step. Incomplete or improper sintering can result in a porous, mechanically weak rod with compromised chemical resistance. Consistent process control here is the hallmark of a quality manufacturer.
Extrusion vs. Other Fabrication
It's important to distinguish between manufacturing the rod and fabricating a part from the rod. Extrusion creates the raw material stock. Processes like die-cutting, stamping, and CNC machining are secondary operations used to create finished parts like gaskets, seals, and insulators from that rod stock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct material specification is crucial for project success. Your decision should be guided by the primary demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical resistance: A standard, extruded rod made from virgin PTFE is the ideal choice for seals, gaskets, and linings in corrosive environments.
- If your primary focus is superior electrical insulation: Specify rods made from 100% pure, unfilled virgin PTFE to leverage its exceptional dielectric strength.
- If your primary focus is creating precise, custom parts: High-quality extruded rod stock provides a stable and consistent material base for machining complex components like bearings, bushings, and valves.
By understanding how PTFE is synthesized and formed, you can better specify and utilize this remarkable material to solve your most demanding engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Base Material | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) resin |
| Key Process | Powder extrusion followed by high-temperature sintering |
| Primary Properties | Excellent chemical resistance, low friction, high-temperature tolerance |
| Common Applications | Seals, liners, bearings, insulators in semiconductor, medical, and lab industries |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your project? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE rods, seals, liners, and custom labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure material purity and process control from prototype to high-volume production. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and leverage our expertise in custom PTFE fabrication!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How are PTFE extruded rods applied in the food processing industry? Enhancing Hygiene and Efficiency
- How are PTFE rods used in the chemical industry? Ensure Safety and Reliability in Corrosive Environments
- How does PTFE rod perform in chemically harsh environments? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications
- What industrial applications utilize extruded PTFE rods? Key Uses in Chemical, Aerospace & More
- What are the machining advantages of PTFE rod? Achieve Cost-Effective, Complex Parts



















