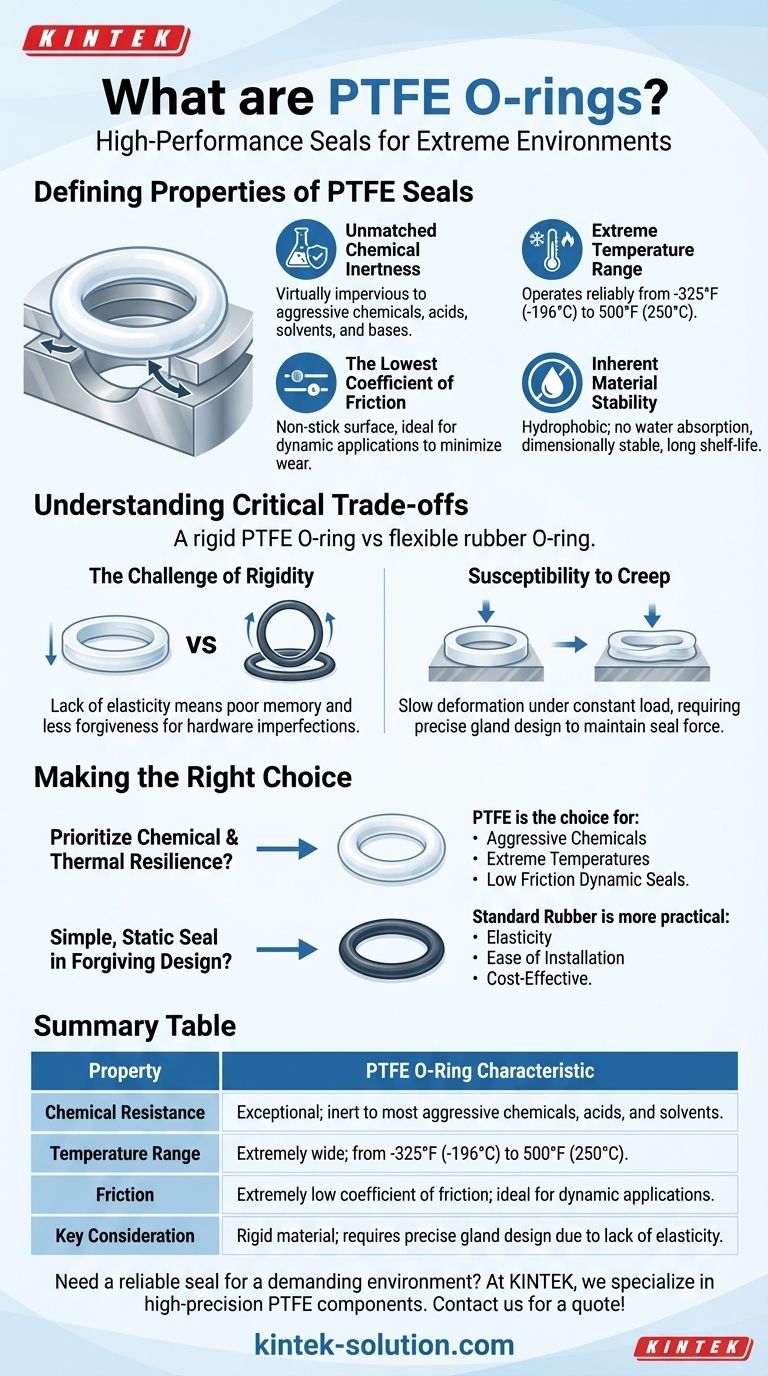
In short, a PTFE O-ring is a high-performance mechanical seal made from the synthetic polymer Polytetrafluoroethylene. Unlike common rubber O-rings, they are prized for their near-universal chemical resistance, ability to withstand extreme temperatures, and exceptionally low-friction surface. They function by creating a barrier in a groove between two mating parts, preventing the leakage of fluids or gases.
The core reason to select a PTFE O-ring is for its extreme resilience in environments where traditional elastomeric (rubber) seals would quickly degrade or fail. However, this performance comes with a critical trade-off: PTFE is a rigid plastic, not a flexible rubber, which fundamentally changes its sealing behavior and installation requirements.

The Defining Properties of PTFE Seals
To understand why PTFE is chosen for demanding applications, we must examine its unique material characteristics. These properties are what set it apart from virtually all other sealing materials.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually impervious to chemical attack. It offers exceptional resistance to the most aggressive chemicals, acids, solvents, and bases, making it indispensable in chemical processing and laboratory equipment.
Extreme Temperature Range
These seals operate reliably across a vast temperature spectrum. They maintain their integrity in cryogenic conditions as low as -325°F (-196°C) and can withstand continuous service at temperatures up to 500°F (250°C).
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any solid material. This creates a non-stick, slippery surface that is ideal for dynamic applications where parts move against each other, as it minimizes wear and drag.
Inherent Material Stability
Because PTFE is hydrophobic, it does not absorb water or swell when exposed to moisture. This ensures dimensional stability and consistent sealing performance. It is also resistant to UV radiation and has a very long shelf-life without degradation.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not a universal solution. Its primary distinction from rubber—its rigidity—is also its main limitation. Understanding this is key to using it successfully.
The Challenge of Rigidity
Unlike an elastomer, a PTFE O-ring is not elastic. It has a poor "compression set," meaning it does not readily spring back to its original shape after being compressed. This lack of memory means it is less forgiving of imperfections in hardware surfaces.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under constant compressive load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can slowly deform over time. This phenomenon, known as "creep" or "cold flow," can lead to a gradual loss of sealing force if not accounted for in the design of the gland (the groove holding the O-ring).
Installation Demands Precision
Because PTFE O-rings do not stretch, they cannot be installed in the same way as rubber O-rings. They often require split designs or carefully designed hardware that allows the ring to be seated without being damaged. The gland must be manufactured to very precise dimensions to ensure a proper initial seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sealing material requires matching its properties to the demands of the application. PTFE is a specialist material for problems that standard seals cannot solve.
- If your primary focus is resisting aggressive chemicals: PTFE is almost always the correct choice due to its near-universal inertness.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability: PTFE's performance in both cryogenic and high-heat environments makes it a superior option where elastomers would fail.
- If your primary focus is low friction for a dynamic seal: PTFE's slippery surface provides unparalleled performance, reducing wear and operational force.
- If your primary focus is a simple, static seal in a forgiving design: A standard rubber O-ring is often a more practical and cost-effective solution due to its elasticity and ease of installation.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE O-ring is a decision to prioritize chemical and thermal resilience above all else.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE O-Ring Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional; inert to most aggressive chemicals, acids, and solvents. |
| Temperature Range | Extremely wide; from -325°F (-196°C) to 500°F (250°C). |
| Friction | Extremely low coefficient of friction; ideal for dynamic applications. |
| Key Consideration | Rigid material; requires precise gland design due to lack of elasticity. |
Need a reliable seal for a demanding environment?
PTFE O-rings are the solution for applications where chemical resistance, extreme temperatures, or low friction are critical. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom O-rings, seals, liners, and labware.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, providing custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Our expertise ensures you get a seal that performs reliably under pressure.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific sealing challenge and get a quote for a precision-engineered solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















