In short, a filled PTFE bush is a high-performance bearing made from Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) that has been blended with specific additives, or "fillers." These fillers are not impurities; they are intentionally added to overcome the inherent weaknesses of pure PTFE, such as its softness and tendency to deform under pressure, transforming it into a robust material suited for demanding industrial applications.
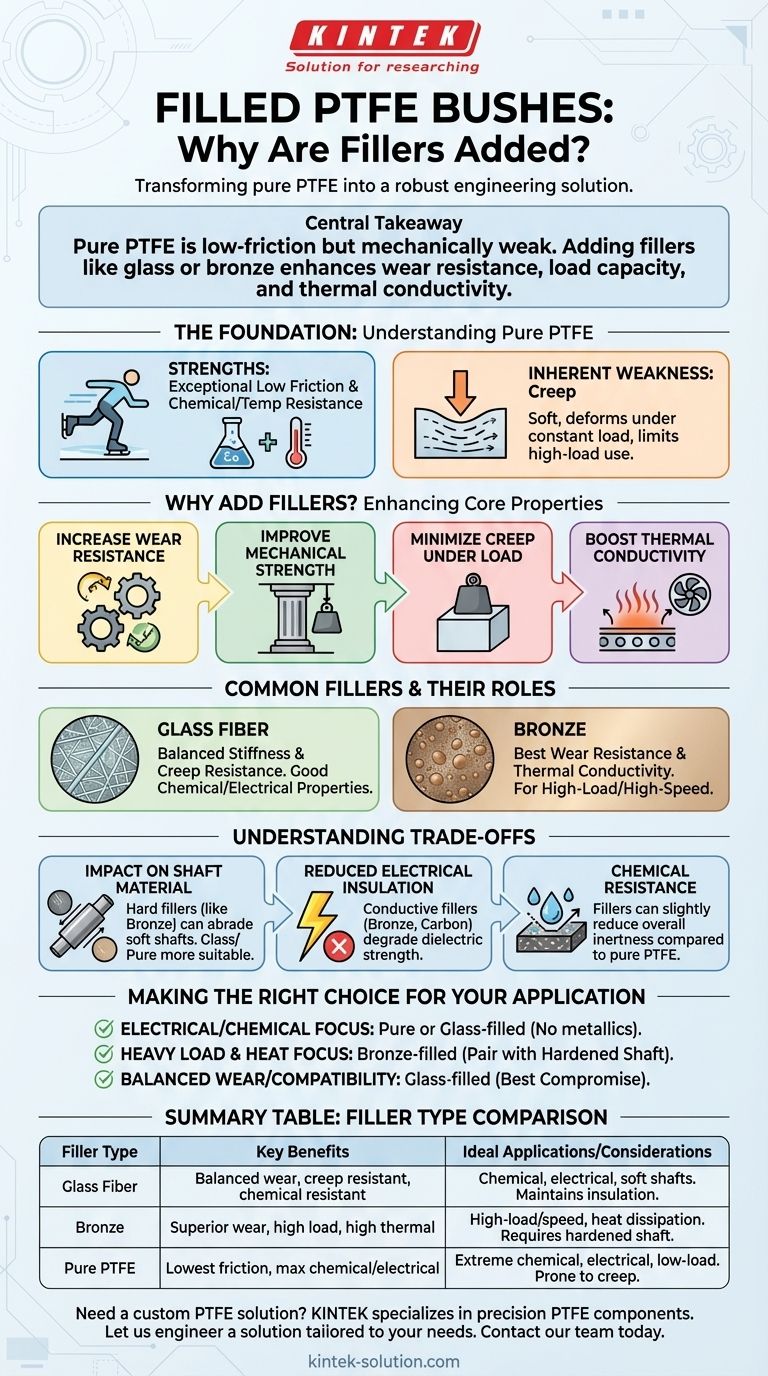
The central takeaway is this: while pure PTFE offers exceptional low friction and chemical resistance, it is mechanically weak. Adding fillers like glass or bronze is a strategic engineering choice to enhance specific properties like wear resistance, load capacity, and thermal conductivity, tailoring the material for its intended job.

The Foundation: Understanding Pure PTFE
To appreciate the role of fillers, we must first understand the baseline characteristics of pure, or "virgin," PTFE. It is a remarkable material on its own, but with distinct limitations for mechanical use.
Exceptional Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This gives it a natural, self-lubricating quality, making it ideal for applications where external lubricants are undesirable or impractical.
Broad Chemical and Temperature Resistance
PTFE is almost entirely chemically inert and can withstand a very wide range of temperatures. This makes it a default choice in corrosive environments or applications with extreme temperature swings.
The Inherent Weakness: Creep
The primary drawback of pure PTFE in mechanical systems is creep. It is a relatively soft material that will slowly deform or "flow" over time when subjected to a constant load, even at room temperature. This deformation limits its use in high-load bearing applications.
Why Add Fillers? Enhancing Core Properties
Adding fillers directly addresses the mechanical shortcomings of pure PTFE, turning a good material into a great one for specific engineering challenges.
To Increase Wear Resistance
Fillers add a reinforcing matrix within the PTFE, making the composite material significantly harder and more resistant to abrasion and wear, which dramatically extends the service life of the bushing.
To Improve Mechanical Strength
Fillers like glass and bronze substantially increase the compressive strength and load-bearing capacity of the material. This allows the bushing to handle much higher pressures without being crushed or deformed.
To Minimize Creep Under Load
This is the most critical enhancement. The rigid particles of the filler material provide a structural backbone, drastically reducing the tendency of the PTFE to creep under a sustained load and ensuring dimensional stability.
To Boost Thermal Conductivity
Pure PTFE is a thermal insulator, which can be a problem in high-speed applications where friction generates heat. Fillers like bronze are thermally conductive, allowing them to draw heat away from the bearing surface and prevent overheating.
Common Fillers and Their Specific Roles
The choice of filler is not arbitrary; it is selected to achieve a specific performance outcome.
Glass Fiber
Glass-filled PTFE offers a balanced set of properties. It provides a significant increase in stiffness and creep resistance while maintaining excellent chemical resistance and good electrical insulation.
Bronze
Bronze-filled PTFE provides the best wear resistance and thermal conductivity. This makes it the ideal choice for high-load, high-speed applications or situations requiring rapid heat dissipation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Enhancing one property with a filler often means compromising another. Being aware of these trade-offs is critical for proper material selection.
Impact on Shaft Material
The hardness that makes fillers effective can also damage the mating surface. Bronze, being abrasive, requires the use of a hardened steel shaft to avoid excessive wear. Pure or glass-filled PTFE is much more suitable for use with softer shafts, such as stainless steel or aluminum.
Reduced Electrical Insulation
While pure PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator, adding conductive fillers like bronze or carbon will degrade this property. For applications requiring high dielectric strength, pure or glass-filled PTFE is the necessary choice.
Chemical Resistance
Although still highly resistant, certain fillers can slightly reduce the overall chemical inertness of the composite compared to pure PTFE. In the most aggressive chemical environments, this minor difference can be a deciding factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE formulation depends entirely on the demands of your specific system.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation or chemical purity: Pure or glass-filled PTFE is the correct choice, as metallic fillers will compromise these properties.
- If your primary focus is handling heavy loads and dissipating heat: Bronze-filled PTFE offers superior mechanical strength and thermal conductivity, but be sure to pair it with a hardened shaft.
- If your primary focus is a balance of wear resistance and compatibility with softer shafts: Glass-filled PTFE often provides the best compromise between performance and system compatibility.
By understanding the role of fillers, you can specify a PTFE bushing that moves beyond a simple plastic part to become a precisely engineered solution for your mechanical system.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Benefits | Ideal Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glass Fiber | Balanced wear resistance, good creep resistance, excellent chemical resistance | Chemical processing, electrical insulation, applications with softer shafts | Maintains good electrical insulation |
| Bronze | Superior wear resistance, high load capacity, excellent thermal conductivity | High-load, high-speed applications, situations requiring heat dissipation | Requires hardened steel shaft to prevent wear |
| Pure PTFE | Lowest friction, maximum chemical resistance, excellent electrical insulation | Extreme chemical environments, electrical applications, low-load scenarios | Prone to creep under sustained load |
Need a custom PTFE solution for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including custom-filled bushes, seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise in material science ensures you get the optimal balance of wear resistance, load capacity, and chemical compatibility for your system.
Let us engineer a solution tailored to your needs: Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















