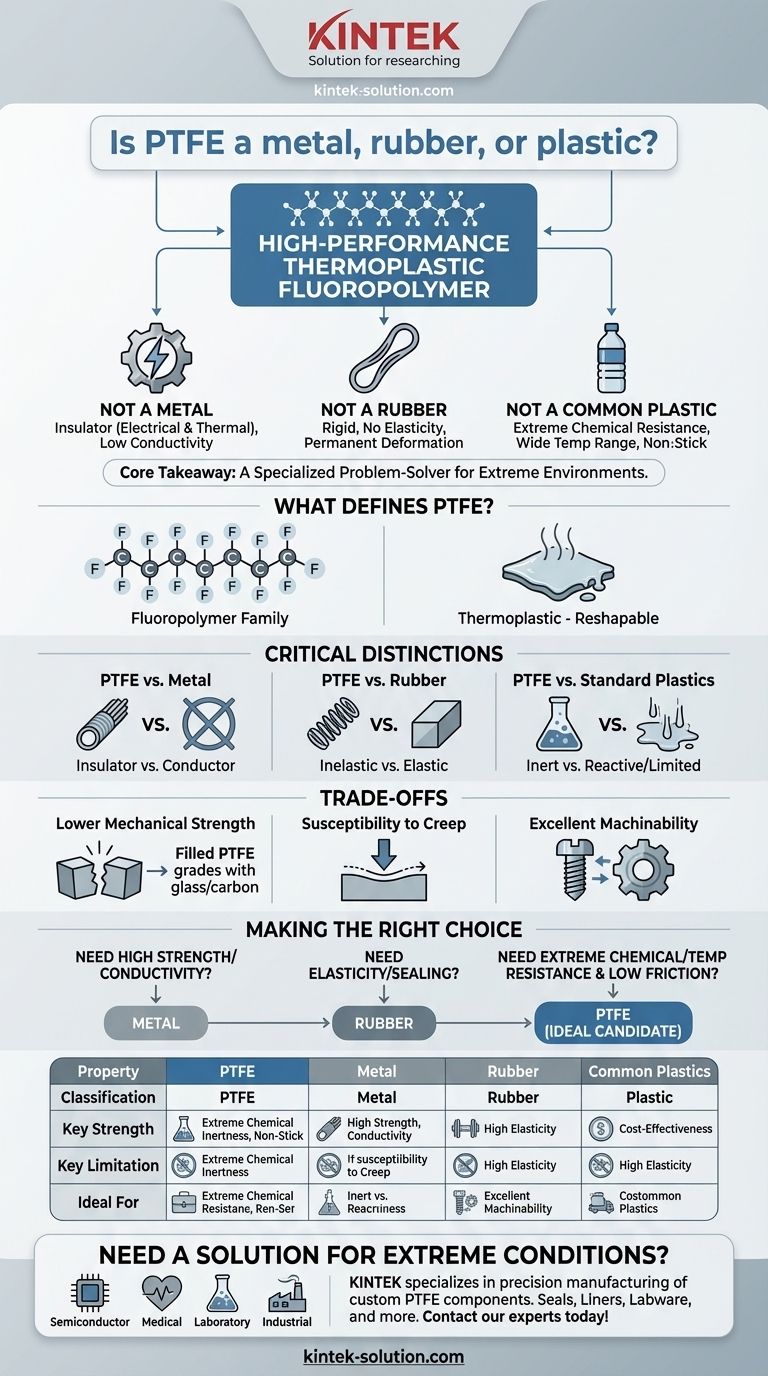
While often categorized simply as a plastic, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is more accurately defined as a high-performance thermoplastic polymer. It is definitively not a metal or a rubber. Its unique molecular structure gives it a combination of properties—such as extreme chemical resistance and a non-stick surface—that distinguish it even from most common plastics.
The core takeaway is that PTFE is a specialized fluoropolymer, a class of plastic prized for capabilities that metals and rubbers cannot provide. Thinking of it as a "problem-solver" material for extreme environments is more useful than trying to fit it into a conventional category.

What Truly Defines PTFE?
To understand where PTFE fits, we must look at its fundamental nature. Its classification comes from its molecular makeup and its response to heat.
A High-Performance Fluoropolymer
PTFE belongs to a family of materials called fluoropolymers. Its structure consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely surrounded by fluorine atoms.
This carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong and stable, which is the source of PTFE's most valuable traits: its resistance to heat, chemicals, and its famous low-friction, non-stick surface.
A Thermoplastic, Not a Thermoset
PTFE is a thermoplastic. This means it can be softened by heating and reshaped, which is the primary reason it falls under the broad umbrella of "plastics."
This is different from thermoset plastics, which undergo an irreversible chemical change when heated and cannot be remelted.
The Critical Distinctions: PTFE vs. Other Materials
Understanding what PTFE is becomes clearer when you understand what it is not. Its value comes from solving problems where metals, rubbers, and standard plastics are unsuitable.
Why It's Not a Metal
The defining difference is conductivity. Metals are excellent conductors of electricity and heat.
PTFE is the opposite. It is an outstanding electrical and thermal insulator, which is why it's used in high-performance wiring and electronics.
Why It's Not a Rubber
The key distinction here is elasticity. Rubbers and elastomers are defined by their ability to stretch significantly and return to their original shape.
PTFE is a relatively rigid material. It has no meaningful elastic properties and will deform permanently under sufficient stress.
Why It Stands Apart from Standard Plastics
While technically a plastic, comparing PTFE to common plastics like polyethylene or PVC is misleading. PTFE offers a superior performance profile.
It maintains its properties over an extremely wide temperature range and is almost completely chemically inert, meaning it won't react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. While PTFE has remarkable strengths, its weaknesses are just as important to understand for any technical application.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals, PTFE has significantly lower tensile strength and rigidity. It is not suitable for high-load structural applications on its own.
To counteract this, "filled PTFE" grades are produced, which incorporate additives like glass, carbon, or bronze to enhance mechanical properties.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can slowly deform over time. This phenomenon, known as creep, must be accounted for in the design of seals, gaskets, and bearings.
Excellent Machinability
A significant advantage is that PTFE is an inexpensive and highly machinable material. It can be easily milled, turned, and shaped into complex components like screws, washers, and bolts for specialized applications where its inert properties are critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires aligning its core properties with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high strength and conductivity: A metal is the only appropriate choice, as PTFE is a soft insulator.
- If your primary focus is elasticity and flexible sealing: A rubber or elastomer is superior, as PTFE is rigid and lacks memory.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance, high-temperature stability, or low friction: PTFE is the ideal candidate, outperforming nearly all other plastics in these specific domains.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE as a specialized polymer allows you to leverage its distinct advantages precisely where other materials fall short.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE | Metal | Rubber | Common Plastics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Classification | High-Performance Thermoplastic Polymer | Element/Alloy | Elastomer | Thermoplastic/Thermoset |
| Key Strength | Extreme Chemical Inertness, Non-Stick | High Strength, Conductivity | High Elasticity, Flexibility | Cost-Effectiveness, Versatility |
| Key Limitation | Lower Mechanical Strength, Creep | Corrosion, Weight | Limited Temp/Chemical Resistance | Limited Temp/Chemical Resistance |
| Ideal For | Seals, Liners, Insulators in Harsh Environments | Structural Components, Wiring | Flexible Seals, Gaskets | General-Purpose Parts, Packaging |
Need a Material Solution for Extreme Conditions?
PTFE's unique properties make it the ideal choice for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Its extreme chemical resistance, non-stick nature, and thermal stability solve problems where metals, rubbers, and standard plastics fail.
KINTEK specializes in precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components. We deliver high-quality seals, liners, labware, and more—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Let us help you engineer the perfect solution. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions



















