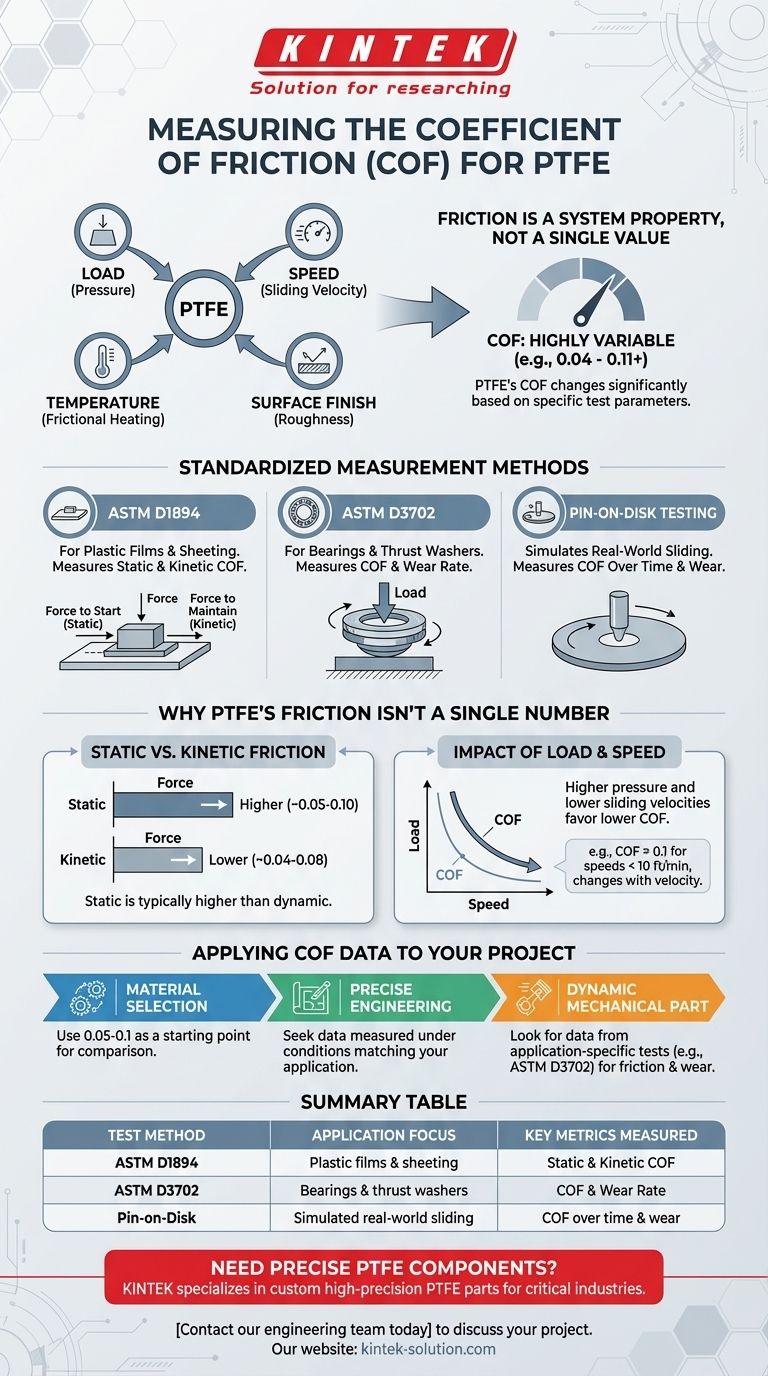
To measure the coefficient of friction (COF) for PTFE, engineers rely on standardized laboratory procedures that simulate specific conditions. The most common standard is ASTM D1894, which determines both static (the force to start movement) and kinetic (the force to maintain movement) friction. However, the resulting value is not a single constant; it is highly dependent on the precise test parameters.
The core challenge isn't finding a single COF value for PTFE, but understanding that friction is a system property. The measured coefficient of friction changes significantly with factors like load, speed, and temperature, making the specific test method and its conditions paramount.
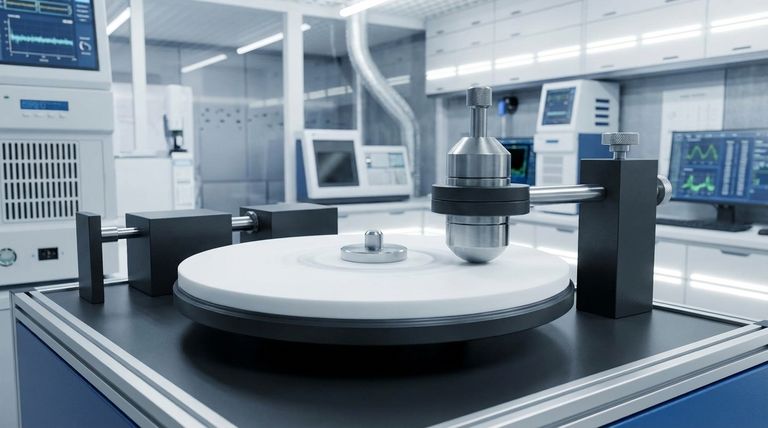

Standardized Measurement Methods
To obtain reliable and repeatable data, specific testing protocols are used to quantify the frictional properties of PTFE under controlled conditions.
ASTM D1894: The Baseline Standard
This is the most common test for plastic films and sheeting. It involves pulling a weighted sled coated with the test material across a flat surface, also coated with the material.
The force required to initiate movement gives the static coefficient of friction. The average force required to maintain movement at a constant speed provides the kinetic coefficient of friction.
ASTM D3702: For Mechanical Components
This method is designed to test materials for applications like thrust washers or bearings. It involves rotating a test specimen against a stationary one under a specific load.
This test is crucial for engineering applications because it measures both the coefficient of friction and the wear rate under conditions that more closely resemble a dynamic mechanical assembly.
Pin-on-Disk Testing
This is another common technique used to simulate real-world sliding conditions. A "pin" or ball of a specific material is moved in a circular path against a flat disk of PTFE.
This method allows engineers to study the effects of continuous sliding and wear over time, providing valuable data for components that experience prolonged dynamic friction.
Why PTFE's Friction Isn't a Single Number
You will see many different COF values cited for PTFE, ranging from 0.04 to 0.11 or higher. This is not an error; it reflects the material's response to different physical conditions.
Static vs. Kinetic Friction
PTFE, like most materials, has a different static and kinetic COF. The static value (~0.05 to 0.10) is typically higher than the dynamic or kinetic value (~0.04 to 0.08).
The Impact of Load and Speed
The coefficient of friction in PTFE is highly dependent on system variables. Generally, higher pressure and lower sliding velocities favor a lower coefficient of friction.
For example, a COF of 0.1 is often cited for speeds less than 10 ft/min, but this value can change as velocity increases.
The Role of Temperature and Surface Finish
Frictional heating can alter the properties of the material at the contact surface, which in turn affects the COF.
Furthermore, the roughness of the mating surface plays a critical role. A smoother surface will generally result in a different friction measurement than a rougher one. This is why standardized tests are essential for comparison.
Applying COF Data to Your Project
The most common pitfall is taking a single published COF value and applying it to a design without considering the context. Data from a standardized test is a baseline, not a guarantee of real-world performance.
The conditions in your application—including load, speed, temperature, and mating surfaces—will determine the actual effective friction. Because PTFE's COF is so low, even small variations in these factors can be significant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
-
If your primary focus is general material selection: Use the commonly cited range of 0.05 - 0.1 as a valid starting point to compare PTFE against other materials.
-
If your primary focus is precise engineering design: You must seek COF data measured under conditions that closely match your application's specific load, speed, and temperature.
-
If your primary focus is a dynamic mechanical part: Look for data from application-specific tests like ASTM D3702, which provides insight into both friction and wear resistance.
Ultimately, understanding the conditions behind the measurement is more important than the number itself.
Summary Table:
| Test Method | Application Focus | Key Metrics Measured |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM D1894 | Plastic films & sheeting | Static & Kinetic COF |
| ASTM D3702 | Bearings & thrust washers | COF & Wear Rate |
| Pin-on-Disk | Simulated real-world sliding | COF over time & wear |
Need PTFE components with precisely characterized frictional properties?
For engineers in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, accurate friction data is critical for performance and reliability. KINTEK specializes in the custom fabrication of high-precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware.
We understand that your application's specific conditions (load, speed, temperature) define the required material performance. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your PTFE parts meet exact specifications.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project requirements and leverage our precision manufacturing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments



















