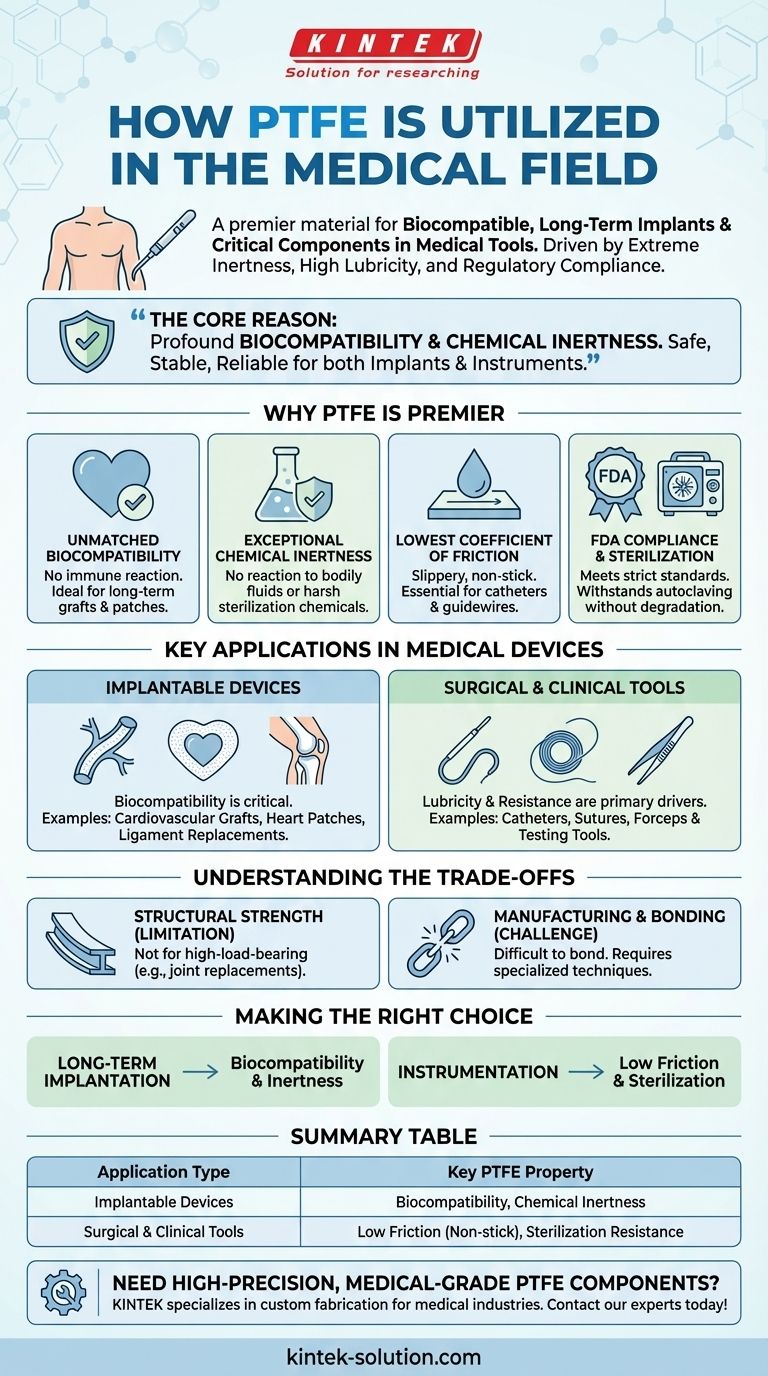
In the medical field, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is utilized in two primary ways: for biocompatible, long-term implants inside the human body and for critical components in medical tools and equipment. Its selection is driven by a unique combination of properties, including extreme chemical inertness, high lubricity, and compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
The core reason PTFE is invaluable in medicine is its profound biocompatibility and chemical inertness. The human body does not reject it, and it remains stable when exposed to aggressive bodily fluids or harsh sterilization processes, making it a uniquely safe and reliable material for both implants and instruments.

Why PTFE is a Premier Material for Medical Applications
The suitability of PTFE for sensitive medical applications is not based on a single characteristic, but on the powerful synergy of several key properties. These features ensure patient safety, device reliability, and procedural effectiveness.
Unmatched Biocompatibility
PTFE is highly biocompatible, meaning the human body's immune system generally does not react to its presence. This allows it to be used for implants like grafts and patches that remain in the body for extended periods without causing inflammation or rejection.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
The material is almost completely inert, meaning it does not react with chemicals. This is critical for medical use, as it ensures the material will not degrade when exposed to bodily fluids or the aggressive chemicals used in sterilization.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it a uniquely slippery, non-stick surface. This property is essential for devices like catheters, which must be inserted and guided through blood vessels with minimal tissue damage.
FDA Compliance and Sterilization
Medical-grade PTFE meets the strict requirements set by regulatory bodies like the FDA. Furthermore, its high-temperature resistance and chemical stability mean it can be reliably sterilized using methods like autoclaving without compromising its structural integrity.
Key Applications in Medical Devices
PTFE's properties make it a versatile solution for a wide range of medical components, from permanent implants to disposable tools.
Implantable Devices
For devices that are placed inside the body, biocompatibility is the most critical factor.
- Cardiovascular Grafts: PTFE is formed into tubes used to bypass or replace diseased blood vessels, as its smooth inner surface helps prevent blood clotting.
- Heart Patches: Sheets of PTFE are used to repair defects within the heart, providing a strong, non-reactive patch that tissue can grow over.
- Ligament Replacements: The material's strength and flexibility make it a candidate for repairing and replacing damaged ligaments.
Surgical and Clinical Tools
For instruments and equipment, lubricity and chemical resistance are often the primary drivers for using PTFE.
- Catheters: The outer surface of catheters is often coated with PTFE to allow for smooth, low-friction insertion into the body.
- Sutures: PTFE is used as a monofilament suture material, prized for its smooth passage through tissue and minimal inflammatory response.
- Forceps and Testing Tools: The non-stick surface prevents tissues and other materials from adhering to surgical instruments, making procedures cleaner and more efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is an exceptional material, it is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper application design.
Structural Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft polymer. It is not suitable for high-load-bearing applications like joint replacements, which require the compressive strength of materials like titanium or specialized ceramics.
Manufacturing and Bonding
The same non-stick properties that make PTFE so valuable also make it notoriously difficult to bond to other materials. Manufacturing complex parts often requires specialized etching or fabrication techniques to achieve adhesion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE depends entirely on the specific demands of the medical application.
- If your primary focus is long-term implantation: PTFE's industry-defining biocompatibility and chemical inertness are its most critical features.
- If your primary focus is instrumentation or temporary devices: PTFE's exceptionally low friction and resilience to sterilization are the key advantages.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique profile has made it an indispensable material that enhances patient safety and enables innovation across the medical industry.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Key PTFE Property | Examples of Use |
|---|---|---|
| Implantable Devices | Biocompatibility, Chemical Inertness | Cardiovascular grafts, heart patches, ligament replacements |
| Surgical & Clinical Tools | Low Friction (Non-stick), Sterilization Resistance | Catheters, sutures, forceps, and testing equipment |
Need high-precision, medical-grade PTFE components for your next project?
KINTEK specializes in the custom fabrication of PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the medical, semiconductor, and laboratory industries. We ensure every component meets the stringent requirements for biocompatibility and performance, from initial prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our precision PTFE solutions can enhance the safety and reliability of your medical devices.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















