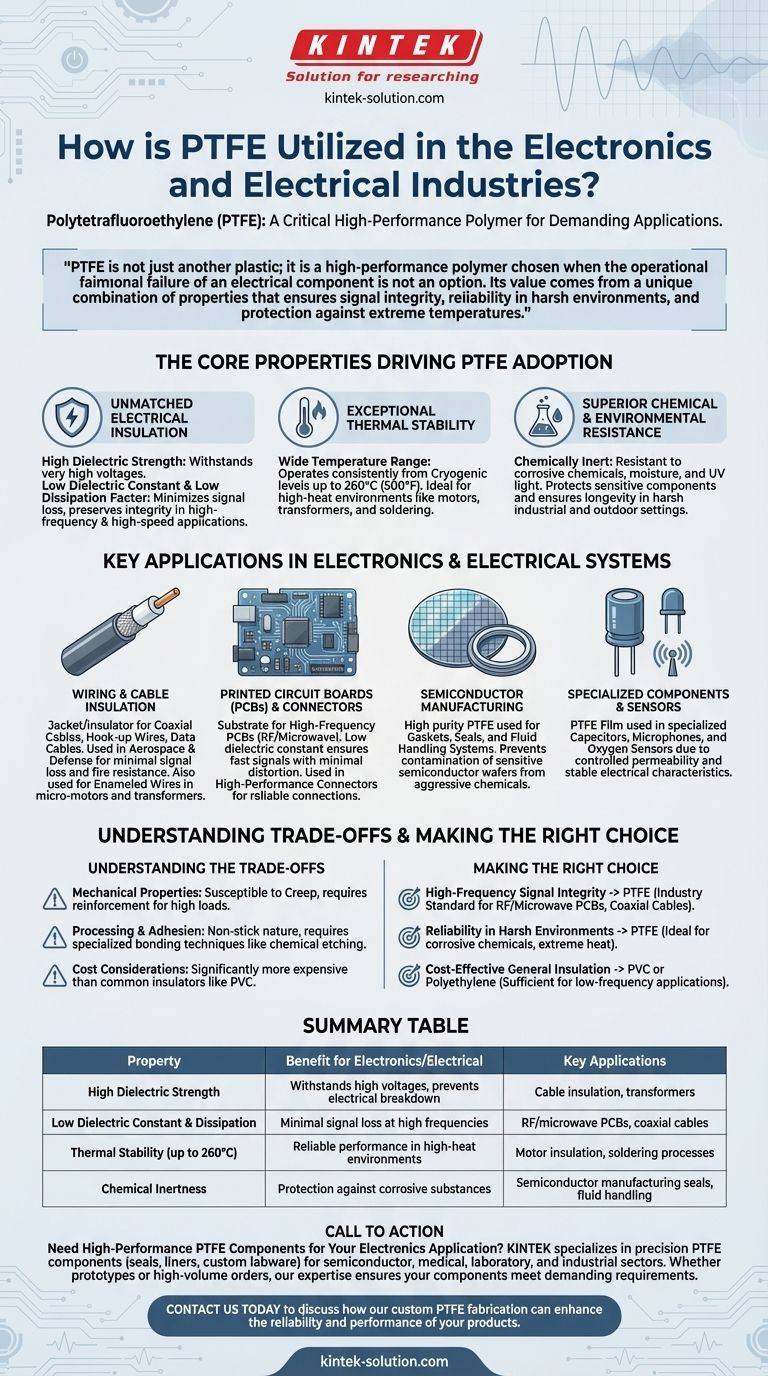
In the electronics and electrical industries, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is primarily utilized for its exceptional electrical insulation, high-temperature stability, and chemical inertness. It serves as a critical material for insulating high-frequency wires and cables, manufacturing flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs), and protecting sensitive semiconductor components from heat and corrosion.
PTFE is not just another plastic; it is a high-performance polymer chosen when the operational failure of an electrical component is not an option. Its value comes from a unique combination of properties that ensures signal integrity, reliability in harsh environments, and protection against extreme temperatures.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE Adoption
The widespread use of PTFE in demanding electrical applications is not accidental. It stems from a specific set of intrinsic material properties that other polymers cannot easily match.
Unmatched Electrical Insulation
PTFE is one of the best-known electrical insulators. It possesses a high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand very high voltages before breaking down.
Its low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor are critical for high-frequency applications. This means it stores very little electrical energy and allows electromagnetic signals to pass through with minimal loss, preserving signal integrity in high-speed data cables and radio-frequency circuits.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Electronic components, from microprocessors to transformers, generate significant heat. PTFE can operate consistently across a very wide temperature range, from cryogenic levels up to 260°C (500°F).
This thermal resistance makes it ideal for insulating wires in motors and transformers and for use in soldering and heat-sealing processes where other materials would melt or degrade.
Superior Chemical and Environmental Resistance
PTFE is almost completely inert, meaning it does not react with corrosive chemicals, moisture, or UV light.
This property protects sensitive electronic components from environmental damage, ensuring the longevity and reliability of devices used in industrial, aerospace, or outdoor settings.
Key Applications in Electronics and Electrical Systems
These core properties translate into several critical applications where performance and reliability are paramount.
Wiring and Cable Insulation
This is PTFE's most common application in the field. It is used as a jacket or insulator for coaxial cables, hook-up wires, and data cables, especially in aerospace and defense where signal loss must be minimized and fire resistance is critical.
It is also used for the enameled wires found inside micro-motors and transformers, providing stable insulation in a high-heat, high-voltage environment.
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and Connectors
For high-frequency electronics, such as those used in radio and microwave communications, PTFE is the substrate material of choice for printed circuit boards. Its low dielectric constant ensures that signals travel quickly and with minimal distortion.
It is also used to insulate high-performance connectors, maintaining a reliable electrical connection without signal interference.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
In the semiconductor industry, PTFE is used for various parts due to its high purity and resistance to aggressive chemicals used in the manufacturing process.
It ensures that components like gaskets, seals, and fluid handling systems do not contaminate the highly sensitive semiconductor wafers.
Specialized Components and Sensors
PTFE's unique properties extend to niche applications. PTFE film, for example, is used in specialized capacitors, microphones, and even oxygen sensors due to its controlled permeability and stable electrical characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is a superior material in many respects, it is essential to understand its limitations to make an informed engineering decision.
Mechanical Properties
PTFE is a relatively soft material and can be susceptible to creep, which is deformation over time under a constant load. This makes it unsuitable for high-load structural applications without reinforcement.
Processing and Adhesion
PTFE is famously non-stick, which makes it very difficult to bond to other materials using conventional adhesives. Processing it often requires specialized techniques like chemical etching to prepare the surface for bonding.
Cost Considerations
As a high-performance polymer, PTFE is significantly more expensive than common insulators like PVC or polyethylene. Its use is typically justified only when the performance requirements of the application demand it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency signal integrity: PTFE is the industry standard for RF/microwave PCBs and coaxial cables due to its low dielectric constant and minimal signal loss.
- If your primary focus is reliability in harsh environments: PTFE's chemical inertness and wide operating temperature range make it the ideal choice for insulating components exposed to corrosive chemicals or extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective general insulation: For standard, low-frequency applications without extreme environmental demands, more common polymers like polyethylene or PVC are often sufficient and more economical.
Ultimately, PTFE is the material of choice when you need to guarantee electrical performance and long-term reliability under challenging conditions.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Electronics/Electrical | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High Dielectric Strength | Withstands high voltages, prevents electrical breakdown | Cable insulation, transformers |
| Low Dielectric Constant & Dissipation | Minimal signal loss at high frequencies | RF/microwave PCBs, coaxial cables |
| Thermal Stability (up to 260°C) | Reliable performance in high-heat environments | Motor insulation, soldering processes |
| Chemical Inertness | Protection against corrosive substances | Semiconductor manufacturing seals, fluid handling |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Electronics Application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your components meet the demanding electrical, thermal, and chemical requirements of your industry.
Contact us today to discuss how our custom PTFE fabrication can enhance the reliability and performance of your products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















