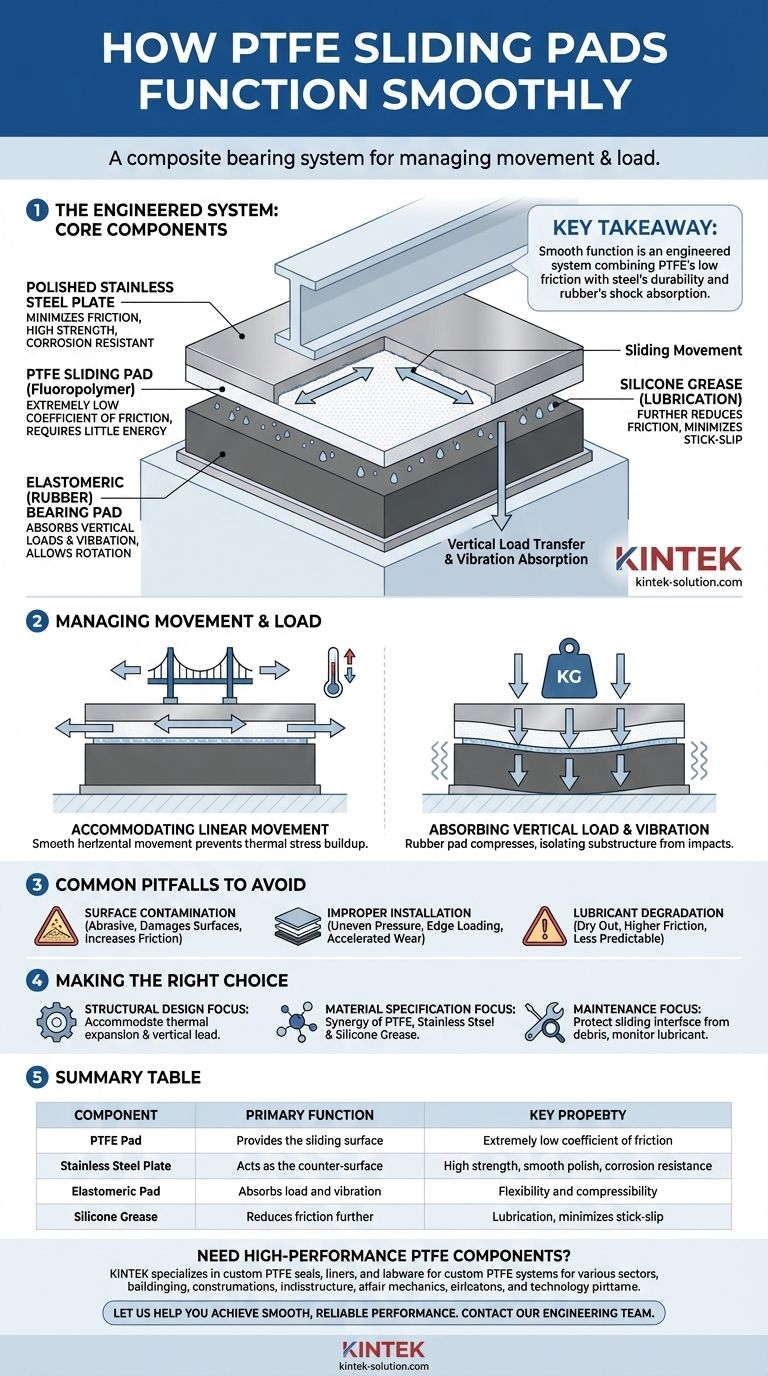
At its core, a PTFE sliding pad functions smoothly due to the inherently low coefficient of friction of its Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) surface. This effect is significantly enhanced when the PTFE plate is paired with a polished stainless steel plate and lubricated with silicone grease, creating a near-frictionless interface that allows massive structural components to move with minimal resistance.
The key takeaway is that smooth function is not the result of a single material, but of an engineered system. It combines the low-friction properties of PTFE with the durability of steel and the shock absorption of rubber to safely manage structural loads and movements.
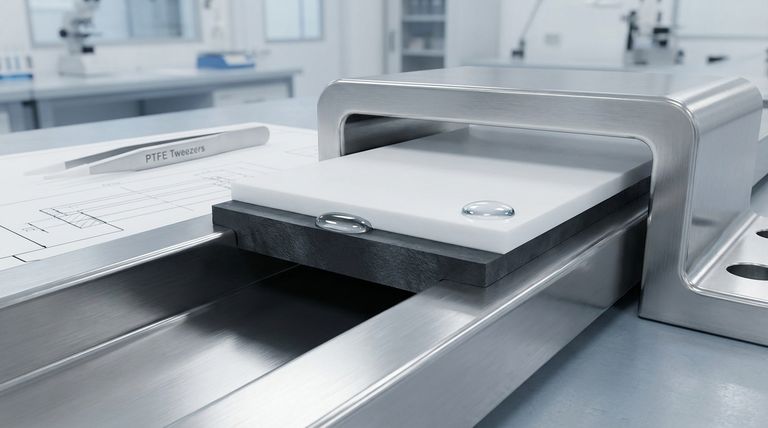

Understanding the Core Components
A PTFE sliding pad is a composite bearing, where each part serves a distinct and critical purpose. Understanding how these components interact is essential to grasping its function.
The PTFE Sliding Surface
The primary active component is the PTFE pad itself. This material, a fluoropolymer, possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid.
This property means it requires very little energy to initiate or sustain movement against another surface, forming the basis of the pad's smooth operation.
The Stainless Steel Plate
The PTFE pad slides against a highly polished stainless steel plate. This material is chosen for three key reasons.
First, its smoothness provides an ideal counter-surface for the PTFE, minimizing friction. Second, its high tensile strength can withstand immense pressures. Third, its corrosion resistance ensures the sliding surface remains pristine and functional over decades of exposure to the elements.
The Elastomeric (Rubber) Pad
Typically, the PTFE pad is bonded to a much thicker elastomeric, or rubber, bearing pad.
This rubber layer does not contribute to the sliding action. Instead, it absorbs vertical loads, dampens vibrations from traffic or seismic events, and allows for small rotational movements of the structure it supports.
The Role of Lubrication
Silicone grease is often applied in small dimples across the PTFE surface.
While PTFE has low friction on its own, this lubricant reduces it even further. It is especially important for minimizing the "stick-slip" phenomenon, ensuring movement starts and stops smoothly without jarring the structure.
How the System Manages Movement and Load
The genius of the PTFE sliding pad lies in how it decouples different forces, allowing each component to do its job without interference.
Accommodating Linear Movement
As a structure like a bridge expands and contracts due to temperature changes, the PTFE pad glides effortlessly across the stainless steel plate.
This smooth, horizontal movement prevents immense thermal stresses from building up within the structure, which could otherwise cause cracking and failure.
Absorbing Vertical Load and Vibration
Simultaneously, the vertical weight of the structure is transferred down through the PTFE and steel plates into the rubber pad below.
The rubber pad compresses slightly under this load, providing constant support while isolating the substructure from vibrations and impacts occurring on the deck above. This combination of sliding and shock absorption is what makes the system so versatile.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While robust, the effectiveness of a PTFE sliding pad is contingent on proper design, installation, and protection.
Surface Contamination
The single greatest threat to smooth function is contamination. Dirt, sand, or construction debris caught between the PTFE and steel plates will act as an abrasive.
This can score and damage the surfaces, dramatically increasing friction and potentially seizing the bearing. This is why protective dust covers are often integrated into the assembly.
Improper Installation
The sliding surfaces must be installed perfectly level and parallel.
Any misalignment can lead to uneven pressure distribution, causing edge loading on the PTFE pad. This results in accelerated wear, binding, and a failure of the pad to slide smoothly.
Lubricant Degradation
Over a long service life, the silicone grease can dry out or become contaminated. While the bearing will still function due to PTFE's natural properties, the friction coefficient will be higher. This can lead to less predictable movement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this system allows you to focus on the details that matter most for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is structural design: Concentrate on how the complete assembly accommodates both thermal expansion (sliding) and vertical load transfer (compression of the rubber pad).
- If your primary focus is material specification: The critical detail is the synergy between the low-friction PTFE, the polished and corrosion-resistant stainless steel, and the specific grade of silicone lubricant.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and inspection: Your chief concern should be protecting the sliding interface from debris and monitoring for any signs of lubricant degradation or surface scoring.
Ultimately, the smooth function of a PTFE sliding pad is a testament to elegant engineering that manages immense forces with simple, reliable principles.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE Pad | Provides the sliding surface | Extremely low coefficient of friction |
| Stainless Steel Plate | Acts as the counter-surface | High strength, smooth polish, corrosion resistance |
| Elastomeric Pad | Absorbs load and vibration | Flexibility and compressibility |
| Silicone Grease | Reduces friction further | Lubrication, minimizes stick-slip |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Project?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom seals, liners, and labware. Our expertise in material science and custom fabrication ensures you get reliable, low-friction solutions tailored for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Let us help you achieve smooth, reliable performance. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your requirements from prototype to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















