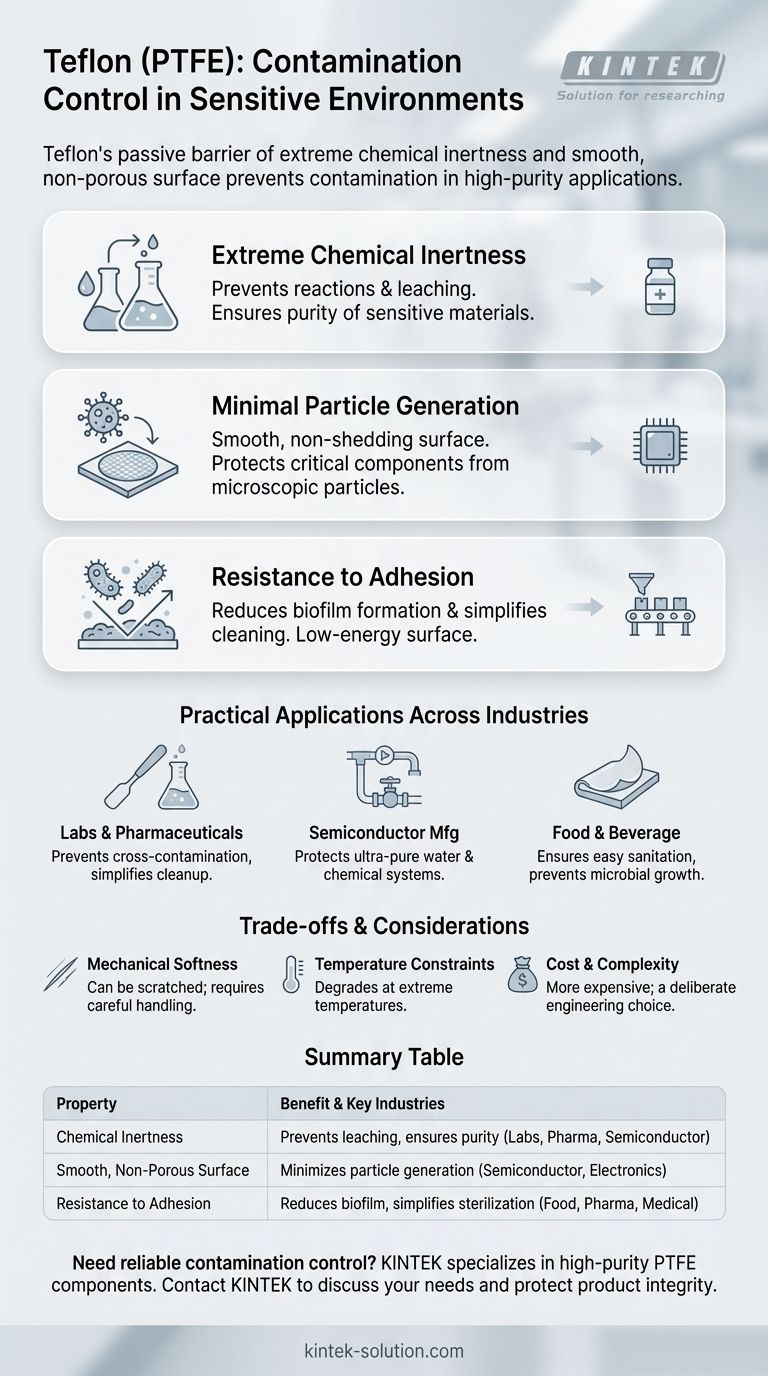
In sensitive environments, Teflon controls contamination primarily through its extreme chemical inertness and exceptionally smooth, non-porous surface. This unique combination prevents it from reacting with chemicals it contacts, minimizes the generation of microscopic particles, and offers no place for bacteria or other contaminants to adhere and multiply.
Teflon's value in contamination control isn't about an active process, but a passive one. It doesn't react, doesn't shed particles, and doesn't give contaminants a place to hide, making it an invisible but powerful barrier in high-purity applications.

The Core Properties Driving Contamination Control
The effectiveness of Teflon, a brand name for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), stems from a few fundamental material characteristics that are highly desirable in controlled environments.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
Teflon is renowned for its resistance to nearly all chemicals, acids, and bases. This non-reactive quality is critical for preventing contamination.
It ensures that the material itself does not leach impurities into a high-purity chemical, alter a pharmaceutical compound, or affect the taste and safety of food products.
Minimal Particle Generation
The surface of Teflon is exceptionally smooth and non-friable, meaning it does not easily break down or shed its own particles.
In environments like semiconductor cleanrooms, where a single microscopic particle can ruin a microchip, using Teflon for components ensures the equipment itself does not become a source of contamination.
Resistance to Adhesion
Teflon's famous non-stick property extends to microorganisms. Its low-energy surface makes it very difficult for bacteria and other microbes to attach and form biofilms.
This is a crucial advantage in pharmaceutical and food processing, as it simplifies cleaning and sterilization, thereby reducing the risk of biological contamination between batches.
Practical Applications Across Industries
These properties translate directly into how Teflon is used to maintain purity and safety in various critical fields.
In Laboratories and Pharmaceuticals
Teflon is frequently used for lab utensils like spatulas and beakers, as well as for lining work surfaces and fume hoods.
Its non-reactive nature prevents cross-contamination between experiments, and its non-stick surface makes cleanup simple and thorough, ensuring no residue is left behind to corrupt the next process.
In Semiconductor Manufacturing
The production of microelectronics requires ultra-pure water and harsh chemicals. Teflon is used for tubing, valves, and containers that handle these fluids.
Because Teflon will not degrade or release ions or particles into these systems, it protects the integrity of the manufacturing process and the final product.
In Food and Beverage Processing
In food processing, the primary concern is preventing microbial growth. Teflon-coated surfaces are used where easy cleaning and the prevention of bacterial adhesion are paramount.
This ensures that equipment can be reliably sanitized, meeting strict hygiene standards and enhancing food safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective for contamination control, Teflon is not a universal solution. Its limitations must be considered for proper application.
Mechanical Softness
Teflon is a relatively soft material. In high-wear applications, it can be scratched or abraded.
A compromised surface could potentially create microscopic crevices where contaminants might lodge, defeating its primary purpose. Careful handling and design are essential.
Temperature Constraints
While it has a wide operating temperature range, Teflon does have its limits. Exposing it to extreme heat can cause it to degrade, which would compromise its integrity and inertness.
Cost and Complexity
Teflon is often more expensive than other polymers. Its selection is a deliberate engineering choice where the cost is justified by the absolute need for purity and non-reactivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use Teflon should be based on the specific type of contamination you need to control.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity: Teflon's non-reactive nature ensures it will not leach into or react with your sensitive materials, making it the superior choice for handling high-purity chemicals.
- If your primary focus is microbiological control: Its anti-adhesion surface minimizes biofilm formation and drastically simplifies the cleaning and sterilization processes required in pharma or food production.
- If your primary focus is particulate control: Its smooth, non-shedding surface makes it ideal for cleanroom components where minimizing airborne particles is the most critical factor.
Ultimately, selecting Teflon is a strategic decision to engineer a passive, reliable, and highly effective barrier against contamination.
Summary Table:
| Property | Contamination Control Benefit | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents leaching, ensures purity of sensitive materials | Laboratories, Pharmaceuticals, Semiconductor |
| Smooth, Non-Porous Surface | Minimizes particle generation and shedding | Semiconductor, Electronics Manufacturing |
| Resistance to Adhesion | Reduces biofilm formation, simplifies sterilization | Food & Beverage, Pharmaceutical, Medical |
Need reliable contamination control for your sensitive processes?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-purity PTFE (Teflon) components—including seals, liners, tubing, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and custom fabrication services, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensure you get the exact passive barrier your application requires.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and learn how our PTFE solutions can protect your product integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















