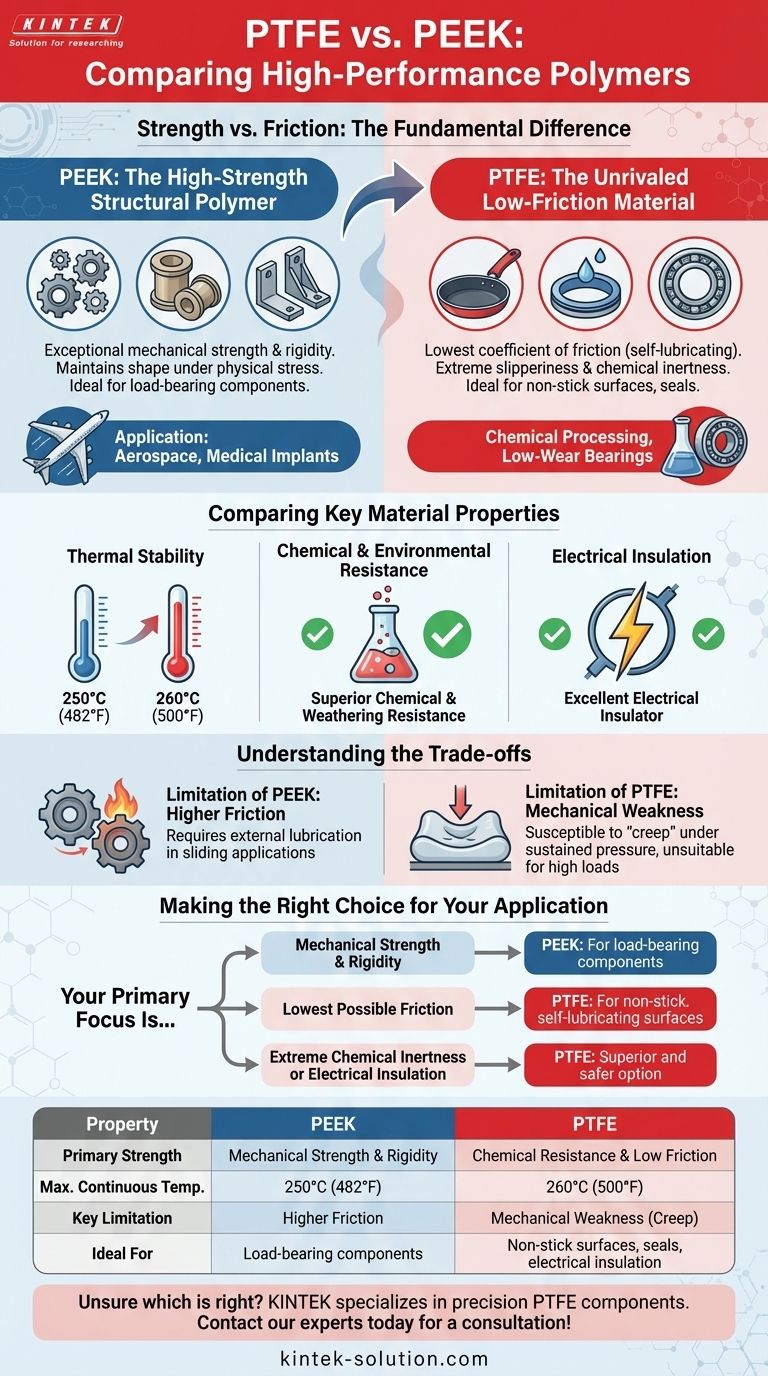
At their core, PEEK and PTFE are high-performance polymers chosen for demanding environments, but they solve fundamentally different problems. PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is selected for its exceptional mechanical strength and rigidity, making it a replacement for metal in structural components. In contrast, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is chosen for its unparalleled low friction and chemical inertness, making it the ideal material for non-stick surfaces and seals.
The choice between PEEK and PTFE is not about which is superior overall, but which specific property is non-negotiable for your application. You choose PEEK for strength and load-bearing capability; you choose PTFE for its extreme slipperiness and chemical resistance.

The Fundamental Difference: Strength vs. Friction
The most critical distinction between these two materials lies in their mechanical properties. They occupy opposite ends of the polymer spectrum.
PEEK: The High-Strength Structural Polymer
PEEK is known for its exceptional mechanical strength and high rigidity. This allows it to maintain its shape and resist deformation under significant physical stress and high temperatures.
It is often used for components that must bear a load, such as gears, bushings, and structural brackets in aerospace and medical implants.
PTFE: The Unrivaled Low-Friction Material
PTFE is a soft fluoropolymer famous for having one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This self-lubricating property gives it a uniquely slippery, non-stick surface.
Its primary applications are those that require minimal friction, like non-stick coatings, chemical-resistant seals, and low-wear bearings.
Comparing Key Material Properties
While the strength-vs-friction trade-off is central, other properties often guide the final selection.
Thermal Stability
Both materials demonstrate excellent performance at high temperatures. PTFE has a slightly higher maximum continuous operating temperature at 260°C (500°F).
PEEK is very close behind, with a maximum operating temperature of 250°C (482°F). For most applications, this difference is negligible.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
PTFE is renowned for its superior chemical resistance. It is inert to nearly all chemicals and solvents, making it a first choice for harsh chemical processing environments.
It also exhibits excellent weathering and UV resistance, preventing degradation from environmental exposure.
Electrical Insulation
PTFE is one of the best known electrical insulators. Its high dielectric strength and low dissipation factor make it an essential material for high-frequency cables and circuit boards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing one material means accepting the inherent limitations of the other. Understanding these trade-offs is key to successful design.
The Limitation of PEEK: Higher Friction
While incredibly strong, PEEK does not have the self-lubricating properties of PTFE. In applications requiring sliding contact, PEEK components will generate more friction and may require external lubrication to prevent wear.
The Limitation of PTFE: Mechanical Weakness
The softness that gives PTFE its useful properties is also its main drawback. It is not a structural material.
Under sustained pressure, PTFE is susceptible to "creep," a tendency to deform permanently over time. It is unsuitable for applications that require high load-bearing capacity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the single most important requirement of your project.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and rigidity: PEEK is the clear choice for load-bearing components that cannot deform under stress.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction: PTFE is unrivaled for creating non-stick, self-lubricating surfaces or seals.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical inertness or electrical insulation: PTFE's unique properties often make it the superior and safer option.
A successful design depends on matching the unique strengths of each material to the specific demands of the task.
Summary Table:
| Property | PEEK | PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Mechanical Strength & Rigidity | Chemical Resistance & Low Friction |
| Max. Continuous Temp. | 250°C (482°F) | 260°C (500°F) |
| Key Limitation | Higher Friction | Mechanical Weakness (Creep) |
| Ideal For | Load-bearing components (gears, bushings) | Non-stick surfaces, seals, electrical insulation |
Unsure which high-performance polymer is right for your component?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get the optimal material solution, from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today for a consultation on your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















