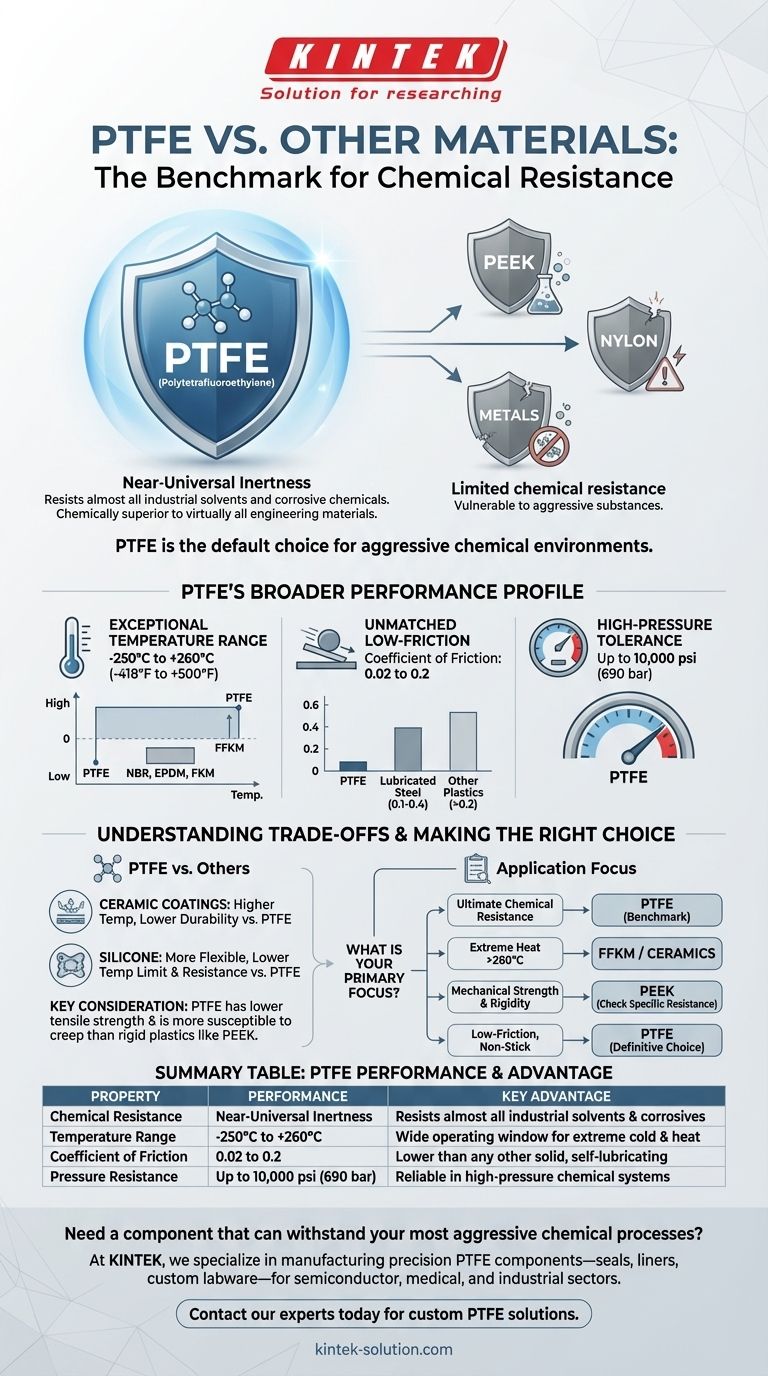
In terms of chemical resistance, PTFE is superior to virtually all other engineering materials. Its unique molecular structure makes it almost completely chemically inert, highly insoluble, and capable of withstanding corrosive substances that degrade even high-performance plastics like PEEK and Nylon.
The core takeaway is that Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sets the industry benchmark for chemical resistance. Its near-total inertness makes it the default choice for the most aggressive chemical environments, but this singular advantage must be evaluated alongside its distinct thermal and mechanical properties.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Superiority
PTFE's reputation is built on its extraordinary ability to resist chemical attack. This property is not just an incremental improvement over other materials; it represents a fundamental step-change in performance.
Near-Universal Inertness
PTFE is virtually impervious to almost all industrial solvents and corrosive chemicals. It remains stable and unreactive in the presence of substances that would readily destroy other polymers and even metals.
Only a few highly specialized and reactive agents, such as molten alkali metals, fluorine gas, and chlorine trifluoride under extreme conditions, are known to affect it.
How It Outperforms Other Plastics
When compared to other common engineering plastics, PTFE's advantage is clear. Even robust materials like PEEK and Nylon, known for their good chemical resistance in specific applications, cannot match the broad, near-universal resistance offered by PTFE.
This makes PTFE the material of choice for components like seals, gaskets, and linings that will be exposed to a wide or unknown range of aggressive chemicals.
A Broader Material Profile
While its chemical resistance is the headline feature, selecting a material requires a holistic view of its properties. PTFE combines its chemical inertness with other high-performance characteristics.
Exceptional Temperature Range
PTFE offers an incredibly wide service temperature range, typically from -250°C to +260°C (-418°F to +500°F).
While materials like FFKM can exceed its upper limit (up to 340°C), they have poorer low-temperature performance. Conversely, many other elastomers like NBR, EPDM, and FKM have significantly narrower operating windows.
Unmatched Low-Friction Surface
PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, with values ranging from 0.02 to 0.2. This is lower than that of any other solid engineering material, including lubricated steel.
This property makes it ideal for applications requiring non-stick, self-lubricating surfaces, such as bearings and non-stick coatings.
High-Pressure Tolerance
In many applications, chemical exposure occurs under pressure. PTFE demonstrates excellent pressure resistance, capable of withstanding up to 10,000 psi (690 bars) in certain configurations.
This capability makes it a reliable choice for sealing solutions in high-pressure systems found in the oil and gas or chemical processing industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Understanding PTFE's limitations is crucial for making an informed decision.
Comparison with Ceramic Coatings
Against ceramic coatings, PTFE offers superior durability and broader chemical resistance. However, ceramic coatings can typically withstand significantly higher temperatures.
Comparison with Silicone
Silicone is a more flexible material than PTFE. However, PTFE provides better non-stick performance and a higher upper temperature limit, along with its vastly superior chemical resistance.
Key Mechanical Considerations
The primary trade-off for PTFE's elite chemical, thermal, and friction properties is its mechanical performance. It is a relatively soft material with lower tensile strength and higher susceptibility to creep (deformation under load) compared to rigid engineering plastics like PEEK.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the most critical demand of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical resistance: PTFE is the benchmark material, virtually impervious to any chemical you are likely to encounter.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat above 260°C (500°F): Consider materials like FFKM or ceramics, but be aware of their compromises in low-temperature performance or durability.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and rigidity: High-performance plastics like PEEK may be a better choice, provided they offer sufficient resistance to the specific chemicals in your application.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction, non-stick surface: PTFE's coefficient of friction is lower than any other solid, making it the definitive choice.
Ultimately, PTFE is the undisputed leader for chemical inertness, but successful engineering requires balancing this elite trait against the complete thermal and mechanical demands of the application.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Performance | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Near-universal inertness | Resists almost all industrial solvents and corrosives |
| Temperature Range | -250°C to +260°C | Wide operating window for extreme cold and heat |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.02 to 0.2 | Lower than any other solid, self-lubricating |
| Pressure Resistance | Up to 10,000 psi (690 bar) | Reliable in high-pressure chemical systems |
Need a component that can withstand your most aggressive chemical processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get a solution that balances elite chemical resistance with the mechanical and thermal performance your application demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and receive a custom solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions



















