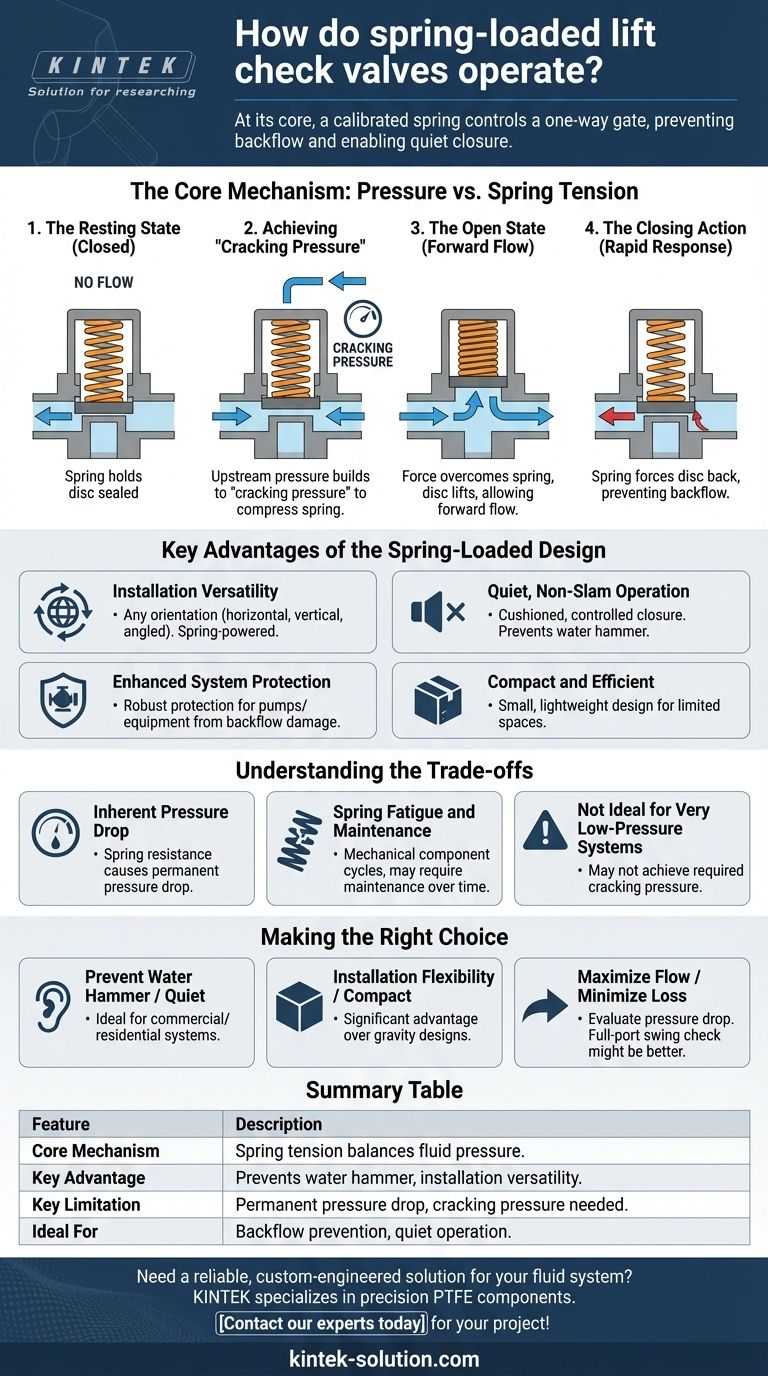
At its core, a spring-loaded lift check valve operates as a one-way gate controlled by a calibrated spring. The valve opens only when the incoming fluid pressure is strong enough to overcome the opposing force of the spring. When the flow stops or reverses, the spring immediately pushes a disc or piston back into place, creating a seal that prevents any backflow.
The spring is the defining feature of this valve. It enables a rapid, quiet closure and allows the valve to be installed in any orientation, unlike gravity-dependent designs. However, this mechanism introduces a required "cracking pressure" that must be overcome, creating a slight pressure drop across the system.
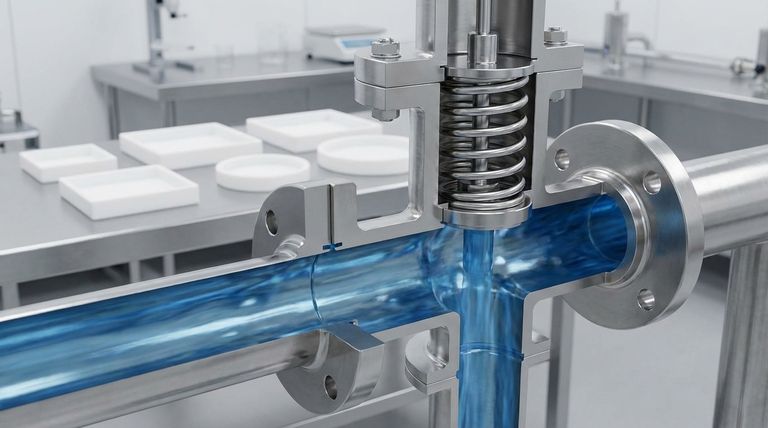

The Core Mechanism: Pressure vs. Spring Tension
The operation of a spring-loaded lift check valve is a simple yet effective balancing act between fluid dynamics and mechanical force.
The Resting State (Closed)
In a no-flow or reverse-flow condition, the internal spring is in its natural, expanded state. It exerts constant pressure on a disc or piston, holding it firmly against the valve seat to maintain a tight seal.
Achieving "Cracking Pressure"
For the valve to open, the upstream fluid pressure must build to a specific level known as the cracking pressure. This is the minimum pressure required to compress the spring and lift the disc off its seat, allowing flow to begin.
The Open State (Forward Flow)
Once the cracking pressure is exceeded, the force of the fluid overcomes the spring. The disc lifts, opening a path for the fluid to flow through the valve body.
The Closing Action (Rapid Response)
The moment the forward flow pressure decreases or stops, the spring's stored energy instantly expands. This action forces the disc back onto the valve seat, decisively cutting off flow and preventing backflow.
Key Advantages of the Spring-Loaded Design
This spring-based mechanism provides several distinct advantages that make it ideal for specific applications.
Installation Versatility
Because the closing action is spring-powered and not dependent on gravity, these valves can be installed in any orientation—horizontally, vertically, or at an angle. This offers significant flexibility in system design.
Quiet, Non-Slam Operation
The spring provides a cushioned, controlled closure. This rapid but gentle action prevents the violent slamming effect known as water hammer, reducing noise and mechanical stress on the entire piping system.
Enhanced System Protection
The swift, automatic closure provides robust protection for pumps and other sensitive equipment. It reliably prevents reverse flow that could cause damage, minimizing wear and tear.
Compact and Efficient
Spring-loaded lift check valves typically have a small, lightweight design. This makes them an excellent choice for applications where space is limited.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the spring-loaded design is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper application.
Inherent Pressure Drop
The energy required to overcome the spring and hold the valve open results in a permanent pressure drop across the valve. In systems where maximizing flow efficiency is critical, this loss may be a significant drawback.
Spring Fatigue and Maintenance
The spring is a mechanical component that cycles with every use. Over tens of thousands of cycles, it can fatigue or break, requiring valve maintenance or replacement.
Not Ideal for Very Low-Pressure Systems
If a system operates at extremely low pressures, it may not be able to consistently generate the required cracking pressure to open the valve. This makes it unsuitable for certain gravity-fed or low-flow applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve requires matching its operational characteristics to your primary system goal.
- If your primary focus is preventing water hammer and ensuring quiet operation: The spring-assisted closure makes this valve an excellent choice, particularly in commercial or residential fluid systems.
- If your primary focus is installation flexibility in a compact space: The ability to mount this valve in any orientation gives it a significant advantage over gravity-dependent designs like swing check valves.
- If your primary focus is maximizing flow with minimal pressure loss: You should evaluate if the inherent pressure drop is acceptable or if a valve with less restriction, like a full-port swing check, would be more suitable.
By understanding the spring's central role, you can effectively leverage this valve's unique strengths for a reliable and efficient system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Spring tension balances fluid pressure to control a disc or piston. |
| Key Advantage | Prevents water hammer and can be installed in any orientation. |
| Key Limitation | Introduces a permanent pressure drop and requires cracking pressure. |
| Ideal For | Systems prioritizing backflow prevention and quiet, non-slam operation. |
Need a reliable, custom-engineered solution for your fluid system?
The precise, spring-loaded mechanism described is critical for protecting sensitive equipment. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications.
Let us help you build a more reliable and efficient system. Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Three Neck Flasks for Advanced Chemical Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
People Also Ask
- How does the PTFE layer enhance the functionality of elastomeric bearings? Achieve Superior Load Support and Movement
- What production processes are used to manufacture precision PTFE components? A Guide to CNC Machining & More
- What post-machining treatments are applied to Teflon parts? Stabilize and Clean, Don't Modify.
- What is a Teflon sheet for heat press? Your Essential Guide to Flawless Transfers
- What are the limitations of PTFE gaskets in high-pressure applications? Overcoming Cold Flow & Creep Issues
- How is virgin PTFE processed into sheets? A Guide to Purity, Performance, and Trade-offs
- What are the key properties of PTFE? The Unique Strengths That Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- How do fillers improve the properties of PTFE? Boost Wear Resistance, Creep Resistance & Thermal Conductivity






