Yes, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) can be recycled, but the process is not simple or widely available. Its recycling is hindered by the very properties that make it so useful: extreme chemical stability and resistance to heat. Therefore, while technically possible through specialized methods, practical and commercially viable PTFE recycling remains a significant challenge.
The core issue with PTFE is that its exceptional chemical inertness—the quality that makes it invaluable for non-stick surfaces and harsh industrial environments—is also its greatest barrier to being easily broken down and recycled through conventional means.

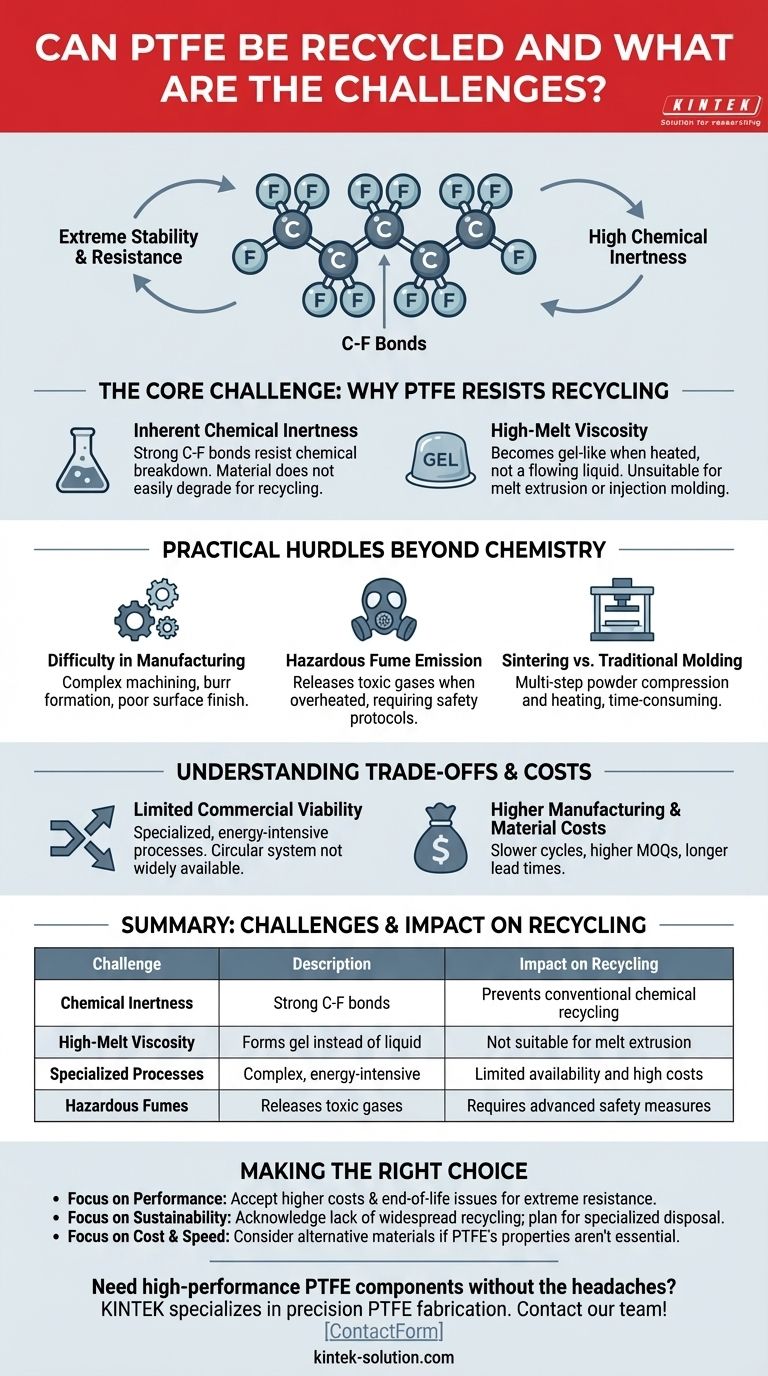
The Core Challenge: PTFE's Extreme Stability
The difficulties in recycling PTFE are not an afterthought; they are intrinsically linked to the material's fundamental chemistry and physical properties. These same properties also make it complex to manufacture with in the first place.
The Inherent Chemical Inertness
PTFE is built on incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bonds. This structure makes it resistant to almost all chemicals and high temperatures.
While ideal for performance, this stability means the material does not easily break down, which is the first step in most recycling processes.
The Problem of High-Melt Viscosity
Unlike common plastics that melt into a flowing liquid, PTFE has an extremely high melt viscosity. When heated, it becomes a gel-like substance rather than a liquid.
This property makes it unsuitable for traditional recycling methods like melt extrusion or injection molding, which rely on the material being able to flow easily.
The Need for Specialized Processes
Because conventional methods fail, recycling PTFE requires specialized techniques. These often involve breaking the material down into smaller particles or back into its chemical precursors.
These processes are complex, energy-intensive, and not widely available on a commercial scale, limiting practical recycling options.
Practical Hurdles Beyond Chemistry
The challenges with PTFE extend beyond its chemical makeup and affect its entire lifecycle, from initial manufacturing to final disposal.
Difficulty in Manufacturing and Machining
PTFE's unique properties make it notoriously difficult to work with. It is a soft material, which can lead to burr formation and poor surface finishes if not machined with perfect settings and extremely sharp tools.
Its slick surface makes it hard to secure for processing, and its thermal properties can cause tools to dull or break if not managed with proper coolants and cutting speeds.
Hazardous Fume Emission
When heated or machined improperly, PTFE can release hazardous fumes. This necessitates specialized ventilation and safety protocols, adding complexity and cost to both manufacturing and any potential high-temperature recycling process.
Sintering vs. Traditional Molding
Due to its high viscosity, PTFE cannot be injection molded. Instead, it is typically processed using techniques similar to powder metallurgy: the powder is compressed into a shape and then heated (sintered) to fuse the particles together.
This multi-step process is more time-consuming and less efficient than the methods used for most other polymers.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Costs
Choosing PTFE has direct consequences for project timelines, budgets, and sustainability goals. These are not minor points but central trade-offs to consider.
Limited Commercial Viability of Recycling
The primary takeaway is that a circular, closed-loop recycling system for PTFE is not a current reality for most applications. While technically feasible, the infrastructure is simply not in place.
Higher Manufacturing and Material Costs
The specialized equipment, slow cycle times, and safety precautions required to process PTFE result in significantly higher manufacturing costs compared to more conventional polymers.
In certain forms, like PTFE laminates for electronics, this can also lead to higher minimum order quantities (MOQs) and longer lead times from suppliers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Evaluating PTFE requires balancing its unparalleled performance against its significant processing and end-of-life challenges.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme environments: PTFE's chemical and thermal resistance may be non-negotiable, but you must factor in its higher costs and end-of-life limitations.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and circularity: You must acknowledge that widespread, simple recycling for PTFE is not currently available and plan for its disposal or seek out rare, specialized recycling partners.
- If your primary focus is cost and manufacturing speed: Carefully assess if PTFE's specific properties are essential, as alternative materials may offer simpler processing and a more favorable cost structure.
Understanding PTFE's full lifecycle, from its complex processing to its recycling limitations, is the key to leveraging its remarkable properties responsibly.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Description | Impact on Recycling |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Strong C-F bonds resist breakdown | Prevents conventional chemical recycling |
| High-Melt Viscosity | Forms gel instead of liquid when heated | Not suitable for melt extrusion or injection molding |
| Specialized Processes | Requires complex, energy-intensive methods | Limited commercial availability and high costs |
| Hazardous Fumes | Releases toxic gases when overheated | Requires advanced safety measures and ventilation |
Need high-performance PTFE components without the manufacturing headaches? KINTEK specializes in precision PTFE fabrication for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Our expertise in machining and sintering PTFE ensures superior quality while managing the material's unique challenges. Let us handle the complexity—from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















