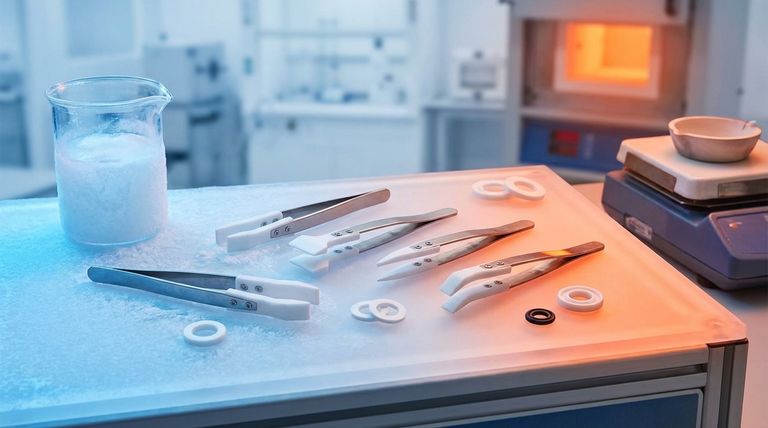
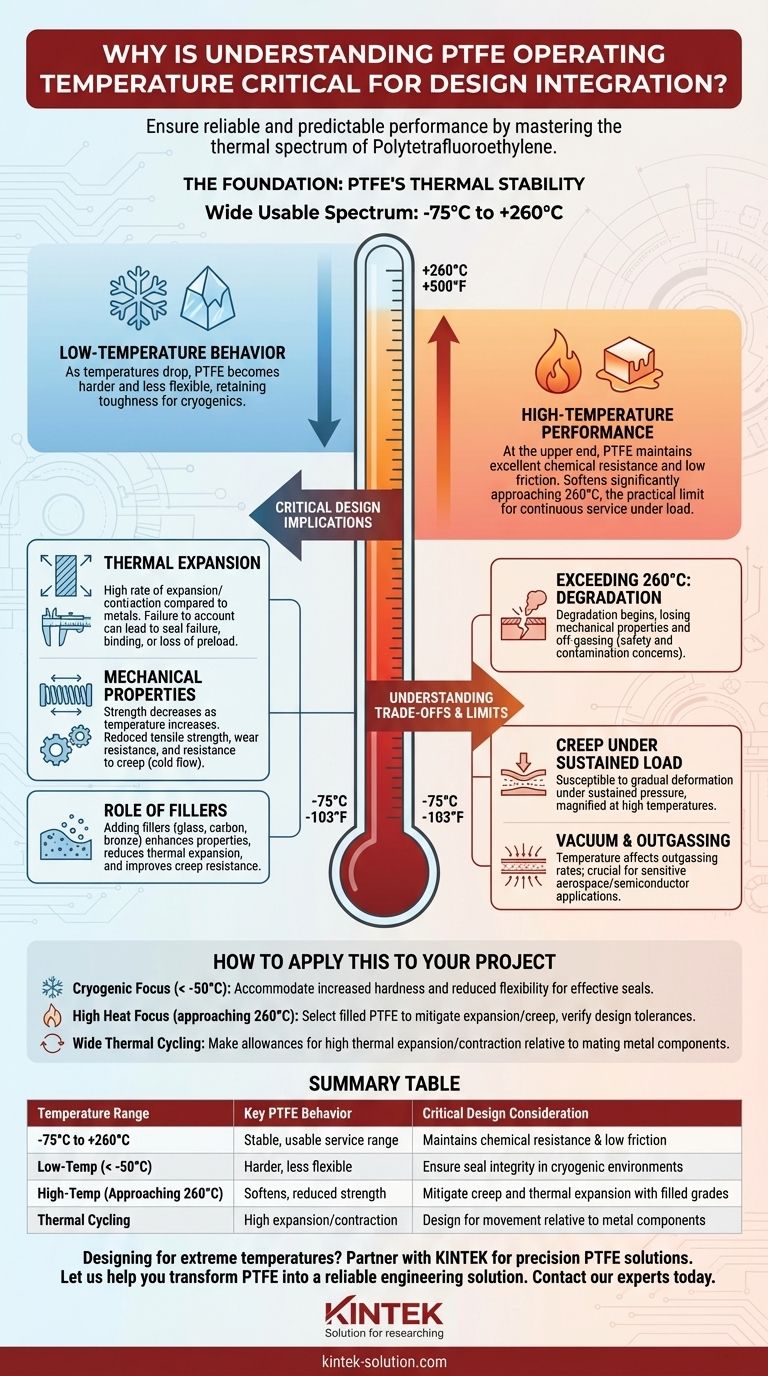
To ensure reliable and predictable performance, understanding the operating temperature range of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a non-negotiable aspect of design integration. PTFE maintains its critical properties across an exceptionally wide thermal spectrum, from approximately -75°C to +260°C (-103°F to +500°F). Operating outside this range can lead to material degradation, loss of sealing integrity, and ultimately, component failure.
The core challenge is not simply knowing PTFE's temperature limits, but understanding how its physical and mechanical properties change within those limits. A successful design anticipates these changes to ensure consistent performance under all expected operating conditions.

The Foundation: PTFE's Thermal Stability
PTFE's molecular structure gives it one of the widest operating temperature ranges of any polymer. This stability is the primary reason for its selection in demanding thermal environments, from deep-space cryogenics to high-heat industrial processing.
The Usable Temperature Spectrum
The commonly accepted service range for unfilled PTFE is -75°C to +260°C. Within this window, it remains a highly functional material, retaining its defining characteristics.
Low-Temperature Behavior
As temperatures drop toward its lower limit, PTFE becomes harder and less flexible. Unlike many other plastics that become extremely brittle and fracture, PTFE retains a useful degree of toughness, making it a reliable choice for cryogenic seals and components.
High-Temperature Performance
At the upper end of its range, PTFE maintains its excellent chemical resistance and exceptionally low coefficient of friction. It begins to soften significantly as it approaches 260°C, which represents the practical limit for continuous service under load.
Critical Design Implications
A component's success depends on more than just staying within the material's absolute limits. Designers must account for how temperature fluctuations affect the material's behavior in the final assembly.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a very high rate of thermal expansion and contraction compared to metals. A design that fails to account for this can experience seal failure, component binding, or loss of preload as temperatures change.
Impact on Mechanical Properties
Temperature directly influences PTFE's mechanical strength. As temperature increases, its tensile strength, wear resistance, and resistance to creep (cold flow) decrease. A seal designed for 25°C will deform more easily under the same load at 200°C.
The Role of Fillers
Adding fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze to PTFE creates composite materials that enhance specific properties. These fillers can significantly reduce thermal expansion and improve resistance to creep at high temperatures, though they may alter other characteristics like chemical resistance or the coefficient of friction.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limits
While incredibly capable, PTFE is not without its limitations. Pushing the material to the edge of its performance envelope requires a clear understanding of the associated risks.
Exceeding 260°C: The Degradation Point
Above 260°C, PTFE begins to degrade at a notable rate. This process is not just a loss of mechanical properties; it also involves off-gassing, which can be a critical concern for safety and system contamination.
Creep Under Sustained Load
PTFE is susceptible to "creep" or "cold flow"—a gradual deformation under sustained pressure. This effect is magnified at higher temperatures and is a primary consideration in long-term sealing applications.
Vacuum and Outgassing
Even within its operating range, temperature affects outgassing rates in a vacuum. For sensitive applications like aerospace or semiconductor manufacturing, selecting the right grade of PTFE and understanding its thermal profile is essential to prevent system contamination.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your design choices should be directly informed by the specific thermal environment of your application.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic temperatures (below -50°C): Ensure your design accommodates PTFE's increased hardness and reduced flexibility to maintain an effective seal.
- If your primary focus is high heat (approaching 260°C): Select a filled PTFE grade to mitigate thermal expansion and creep, and verify the design can tolerate the material's lower compressive strength at temperature.
- If your primary focus is wide thermal cycling: Make proper allowances for PTFE's high thermal expansion and contraction relative to mating metal components to prevent failure.
Mastering PTFE's thermal behavior is the key to transforming it from a simple material choice into a reliable engineering solution.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key PTFE Behavior | Critical Design Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| -75°C to +260°C | Stable, usable service range | Maintains chemical resistance & low friction |
| Low-Temp (< -50°C) | Harder, less flexible | Ensure seal integrity in cryogenic environments |
| High-Temp (Approaching 260°C) | Softens, reduced strength | Mitigate creep and thermal expansion with filled grades |
| Thermal Cycling | High expansion/contraction | Design for movement relative to metal components |
Designing for extreme temperatures? Partner with KINTEK for precision PTFE solutions.
Understanding the thermal behavior of PTFE is just the first step. Successfully integrating it into your semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial application requires a partner who masters both the material science and precision manufacturing.
At KINTEK, we don't just supply parts; we provide engineered solutions. We specialize in the custom fabrication of high-performance PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware—ensuring they are optimized for your specific thermal and mechanical requirements, whether for prototypes or high-volume production.
Let us help you transform PTFE into a reliable engineering solution. Contact our experts today to discuss your project's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















