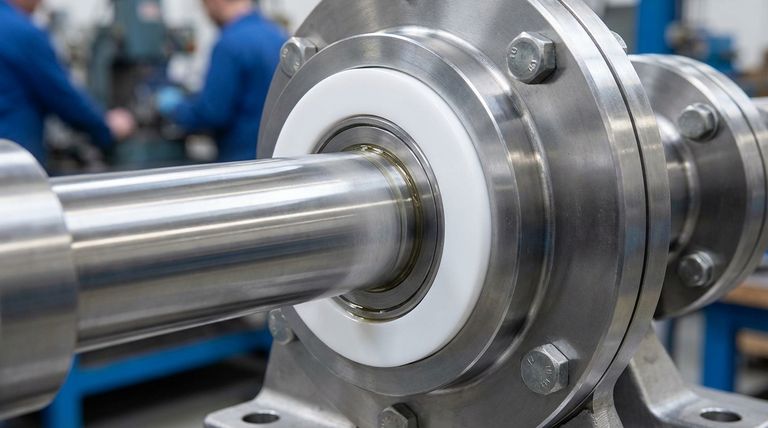
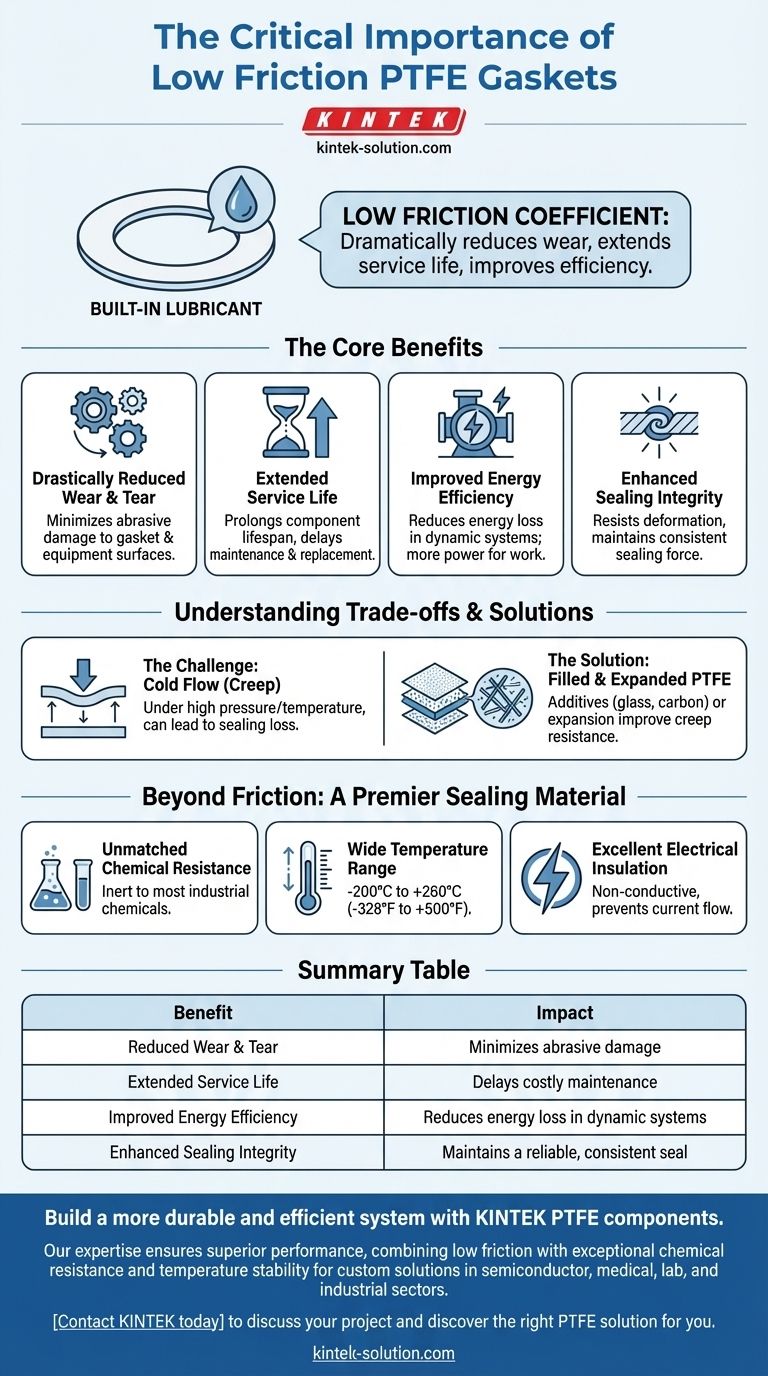
At its core, the low friction coefficient of PTFE gaskets is important because it functions as a built-in lubricant. This property dramatically reduces wear on both the gasket and the equipment components it seals, which extends the service life of the entire assembly and improves overall operational efficiency.
While many materials can create a seal, PTFE's uniquely low friction protects the system it's part of. It minimizes the abrasive damage and energy loss that other materials would cause, especially in moving or dynamic applications.

The Core Benefits of Low Friction
The importance of this single property becomes clear when you examine its direct impact on mechanical systems. It is not merely a passive feature but an active contributor to performance and longevity.
Drastically Reduced Wear and Tear
The ultra-smooth, "slippery" surface of a PTFE gasket means that parts moving against it experience minimal resistance. This significantly reduces the abrasive wear that would normally degrade both the gasket and the mating surfaces of the equipment.
Extended Service Life
By minimizing wear, PTFE directly extends the operational lifespan of components. The gasket itself lasts longer because it isn't being abraded away, and the equipment parts are protected from friction-related damage, delaying the need for costly maintenance and replacement.
Improved Energy Efficiency
In dynamic applications like pumps, hydraulics, or pneumatic systems, friction is a direct source of energy loss. A low-friction PTFE gasket ensures that more energy is used for work and less is wasted overcoming resistance, leading to more efficient and economical operation.
Enhanced Sealing Integrity
Friction can cause a gasket to deform, tear, or degrade over time, compromising its ability to hold a seal. Because PTFE resists this friction, it maintains its intended shape and sealing force for longer, ensuring a more reliable and consistent seal throughout its service life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its low friction is a powerful advantage, no material is perfect for every scenario. Understanding the limitations of standard PTFE is crucial for proper application.
The Challenge of Cold Flow (Creep)
Standard, or "virgin," PTFE can be susceptible to creep, also known as cold flow. Under sustained high pressure and temperature, the material can slowly deform and "flow" away from the pressure point, which can lead to a loss of sealing force and potential leakage over time.
Solutions: Filled and Expanded PTFE
To counteract creep in demanding applications, manufacturers have developed modified PTFE. By adding fillers (like glass, carbon, or graphite) or by expanding the material (ePTFE), they create gaskets that retain PTFE's low friction and chemical resistance while significantly improving their resistance to creep.
Beyond Friction: Why PTFE is a Premier Sealing Material
The low friction coefficient is a standout feature, but it works in concert with other elite properties that make PTFE a go-to choice for challenging environments.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert and non-reactive to almost all industrial chemicals. This makes it essential for sealing applications in the chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage industries.
Wide Temperature Range
PTFE gaskets perform reliably across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum, from cryogenic conditions (-200°C) up to high temperatures of 260°C (500°F).
Excellent Electrical Insulation
As a material that does not conduct electricity, virgin PTFE is also highly valuable as an insulator, preventing current from passing through a sealed joint in electrical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right gasket requires matching the material's properties to the operational demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is dynamic systems (pumps, hydraulics): The low friction coefficient is your most critical advantage for reducing energy loss and preventing wear on moving parts.
- If your primary focus is static sealing of aggressive chemicals: The combination of extreme chemical resistance and a reliable seal is key, but be mindful of system pressure to avoid creep.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure or high-temperature applications: Consider a filled or expanded PTFE gasket to gain the benefits of low friction without the risk of cold flow.
Ultimately, viewing PTFE's low friction as a strategic engineering advantage allows you to build more durable, efficient, and reliable systems.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Reduced Wear & Tear | Minimizes abrasive damage to gasket and mating surfaces. |
| Extended Service Life | Delays costly maintenance and component replacement. |
| Improved Energy Efficiency | Reduces energy loss in dynamic systems like pumps. |
| Enhanced Sealing Integrity | Maintains a reliable, consistent seal over time. |
Build a more durable and efficient system with KINTEK PTFE components.
Our expertise in precision manufacturing ensures your PTFE seals, liners, and labware deliver superior performance, combining low friction with exceptional chemical resistance and temperature stability. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors, we provide custom solutions tailored to your application's demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover the right PTFE solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance



















