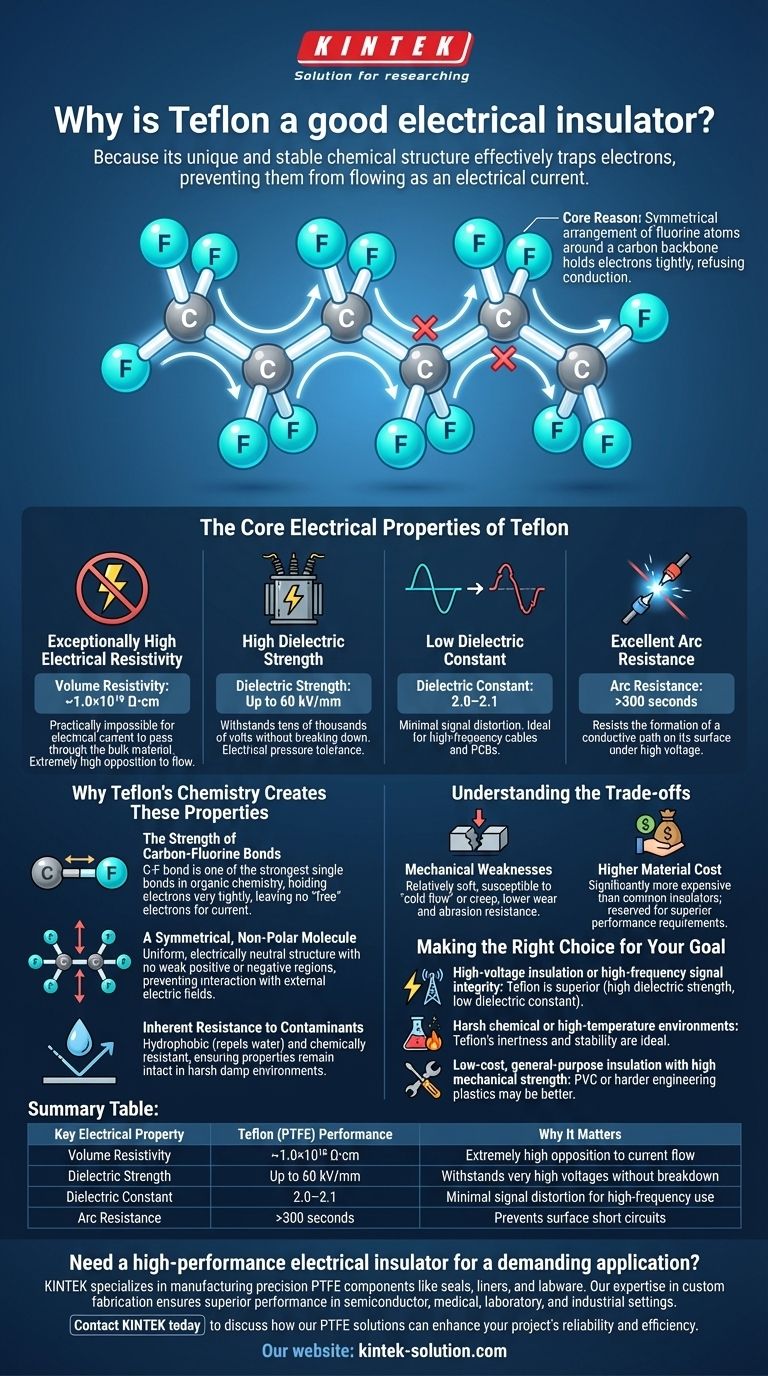
In short, Teflon is an exceptional electrical insulator because its unique and stable chemical structure effectively traps electrons, preventing them from flowing as an electrical current. The strong bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms create a material with extremely high resistance to electricity and an ability to withstand very high voltages without breaking down.
The core reason for Teflon's insulating power lies in its chemistry. The symmetrical arrangement of fluorine atoms around a carbon backbone creates an electrically stable molecule that holds its electrons tightly, refusing to let them move and conduct electricity.

The Core Electrical Properties of Teflon
To understand why Teflon (PTFE) is a top-tier insulator, we need to look at four key electrical properties. These metrics quantify a material's ability to resist the flow of electricity.
Exceptionally High Electrical Resistivity
Resistivity measures how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A higher number means better insulation.
Teflon exhibits a volume resistivity of around 1.0×10¹⁸ Ω⋅cm, one of the highest known. This astronomically high value means it is practically impossible for an electrical current to pass through the bulk of the material.
High Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength is the maximum electric field a material can withstand without "breaking down" and conducting electricity. Think of it as electrical pressure tolerance.
With a dielectric strength of up to 60 kV/mm, a thin sheet of Teflon can insulate against tens of thousands of volts. This makes it invaluable for high-voltage applications where other materials would fail.
Low Dielectric Constant
The dielectric constant indicates a material's ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. For pure insulation, a lower number is better because it means the material won't interfere with the signal it's insulating.
Teflon's low dielectric constant of 2.0–2.1 ensures minimal signal distortion, making it ideal for high-frequency cables and printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Excellent Arc Resistance
Arc resistance is the time in seconds that a material can resist the formation of a conductive path on its surface when exposed to a high-voltage arc.
Teflon can withstand this arcing for over 300 seconds, preventing dangerous short circuits on its surface.
Why Teflon's Chemistry Creates These Properties
The impressive electrical ratings are a direct result of Teflon's molecular structure. The way its atoms are bonded and arranged dictates its performance.
The Strength of Carbon-Fluorine Bonds
The fundamental building block of Teflon is a chain of carbon atoms, each bonded to two fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
These powerful bonds hold the electrons very tightly, leaving no "free" electrons to move and carry a current. This is the primary reason for Teflon's high resistivity.
A Symmetrical, Non-Polar Molecule
The fluorine atoms are arranged symmetrically around the carbon chain. This uniform structure creates an electrically neutral, or non-polar, molecule.
Because the molecule has no weak positive or negative regions, it does not interact with external electric fields. This contributes to its low dielectric constant and overall electrical stability.
Inherent Resistance to Contaminants
Teflon is famously hydrophobic, meaning it repels water. It is also highly resistant to chemicals.
Since water and other contaminants can create conductive paths on an insulator's surface, Teflon's ability to repel them ensures its insulating properties remain intact even in harsh or damp environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While Teflon's electrical properties are world-class, no material is perfect for every situation. Its primary limitations are mechanical and financial.
Mechanical Weaknesses
Teflon is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to "cold flow" or creep, where the material slowly deforms under sustained pressure. It also has lower wear and abrasion resistance compared to harder plastics.
Higher Material Cost
Compared to common insulators like PVC or polyethylene, PTFE is significantly more expensive. Its use is typically reserved for applications where its superior electrical, thermal, and chemical performance is a critical requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right insulator requires matching the material's properties to the application's demands.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation or high-frequency signal integrity: Teflon is a superior choice due to its high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant.
- If your primary focus is performance in harsh chemical or high-temperature environments: Teflon's chemical inertness and stability make it an ideal candidate.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, general-purpose insulation with high mechanical strength: A different material, such as PVC or a harder engineering plastic, may be more appropriate.
Ultimately, understanding the link between Teflon's molecular structure and its electrical performance empowers you to leverage its capabilities where they matter most.
Summary Table:
| Key Electrical Property | Teflon (PTFE) Performance | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Volume Resistivity | ~1.0×10¹⁸ Ω⋅cm | Extremely high opposition to current flow |
| Dielectric Strength | Up to 60 kV/mm | Withstands very high voltages without breakdown |
| Dielectric Constant | 2.0–2.1 | Minimal signal distortion for high-frequency use |
| Arc Resistance | >300 seconds | Prevents surface short circuits |
Need a high-performance electrical insulator for a demanding application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components like seals, liners, and labware. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get the exact Teflon part you need for superior performance in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial settings.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your project's reliability and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















