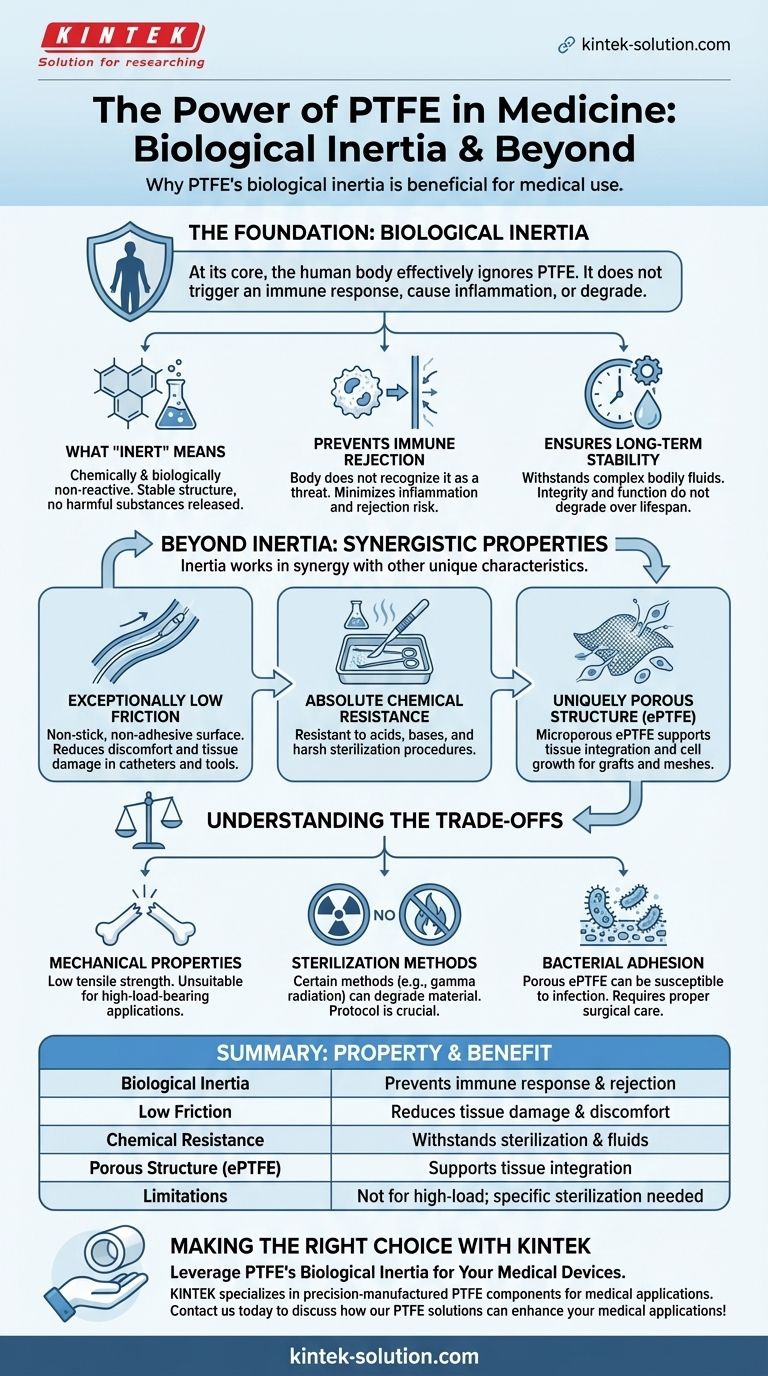
At its core, PTFE's biological inertia is beneficial because the human body effectively ignores it. This fundamental property means Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) does not trigger an immune response, cause inflammation, or degrade when exposed to bodily fluids. This lack of reaction makes it an exceptionally safe and reliable material for devices used inside the human body.
The true value of PTFE in medicine isn't just its biological inertness, but how this fundamental stability works in synergy with its other unique characteristics—like low friction and chemical resistance—to solve critical challenges in both implants and external devices.
The Foundation: Understanding Biological Inertia
Biological inertia is the single most important reason PTFE is trusted for medical applications. It is the bedrock upon which its other useful properties are built.
What "Inert" Really Means
In a medical context, "inert" means a material does not react chemically or biologically when it comes into contact with living tissue.
PTFE's molecular structure is incredibly stable. This prevents it from breaking down or releasing harmful substances into the body over time.
Preventing Immune System Rejection
The human body's immune system is designed to attack foreign objects. Because PTFE is inert, the body does not recognize it as a threat.
This minimizes the risk of inflammation, allergic reaction, or outright rejection of the medical implant, which is critical for long-term success.
Ensuring Long-Term Stability
Devices intended to remain in the body for years must withstand the complex chemical environment of bodily fluids.
PTFE’s resistance to these fluids ensures that the material's integrity and function do not degrade over the device's entire lifespan.
Beyond Inertia: The Synergistic Properties of PTFE
While biological inertia makes PTFE safe, its combination with other properties makes it uniquely functional for a wide range of medical uses.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. Its non-stick, non-adhesive surface is invaluable.
This property reduces discomfort and tissue damage in applications like catheters or as a coating on surgical tools.
Absolute Chemical Resistance
PTFE is resistant to nearly all chemicals, acids, and bases.
This allows it to be used in devices that handle aggressive substances or that must endure repeated, harsh sterilization procedures without degrading.
A Uniquely Porous Structure
PTFE can be manufactured into a microporous material (known as ePTFE) with a structure that supports and encourages cell growth.
This allows for tissue integration, helping the body accept and anchor implants like cardiovascular grafts or surgical meshes more effectively.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. While PTFE's properties are highly beneficial, it is crucial to understand its limitations for proper application.
Mechanical Properties
PTFE is a relatively soft polymer with low tensile strength compared to metals or other high-performance plastics.
This makes it unsuitable for high-load-bearing applications like joint replacements unless it is reinforced or used as a component in a larger assembly.
Sterilization Methods
While PTFE is resistant to high temperatures and chemicals, certain sterilization methods, like gamma radiation, can degrade the material.
Careful consideration of the sterilization protocol is required to ensure the material's properties are not compromised before use.
Bacterial Adhesion
While its non-stick surface is an advantage, under certain conditions, the porous versions of PTFE (ePTFE) can be susceptible to bacterial colonization if an infection is present.
This risk must be managed through proper surgical technique and patient care, especially in permanent implants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is about matching its unique combination of properties to a specific medical challenge.
- If your primary focus is long-term implantation: PTFE's biological inertia and porous structure for tissue integration make it a premier choice for vascular grafts and surgical patches.
- If your primary focus is minimizing tissue friction: The unparalleled low-friction surface of PTFE is ideal for catheters, guidewires, and coatings on surgical instruments.
- If your primary focus is chemical durability: PTFE's resistance to aggressive chemicals and sterilization methods makes it perfect for seals, gaskets, and components in medical equipment.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's complete profile—from its foundational inertness to its practical limitations—empowers you to use it effectively and safely.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Medical Use |
|---|---|
| Biological Inertia | Prevents immune response, inflammation, and rejection in implants |
| Low Friction | Reduces tissue damage and discomfort in catheters and surgical tools |
| Chemical Resistance | Withstands harsh sterilization and bodily fluids without degrading |
| Porous Structure (ePTFE) | Supports tissue integration in grafts and meshes |
| Limitations | Not for high-load-bearing applications; requires specific sterilization protocols |
Leverage PTFE's Biological Inertia for Your Medical Devices
KINTEK specializes in precision-manufactured PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and custom implants) for the medical, semiconductor, and laboratory industries. Our expertise ensures your devices meet stringent safety and performance standards, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your medical applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance



















