In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is used in electrical components because it is one of the most effective and reliable electrical insulators available. Its unique combination of properties ensures that electrical current is contained, components are protected from environmental factors, and performance remains stable even under extreme operational stress.
The core reason for PTFE's prevalence in electronics is not just its ability to insulate, but its capacity to maintain that high level of insulation reliably across a vast range of temperatures, frequencies, and harsh chemical environments where lesser materials would fail.
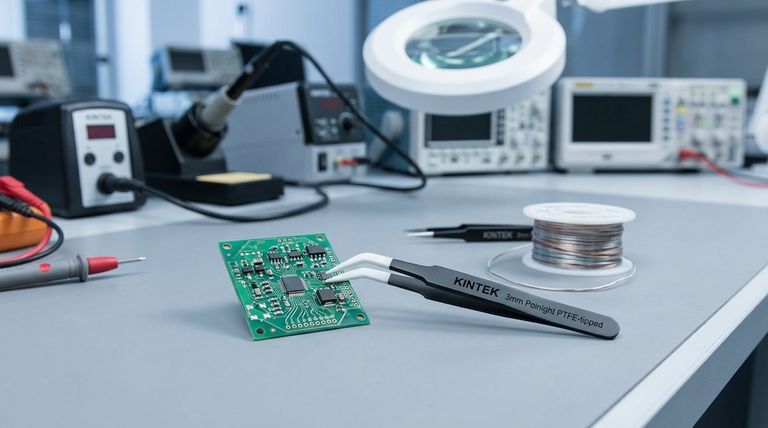
The Core Electrical Properties of PTFE
The primary function of an insulator is to prevent the flow of electricity where it isn't wanted. PTFE excels at this due to a few fundamental characteristics that set it apart.
Exceptional Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength is the measure of a material's ability to withstand a strong electric field without breaking down and conducting electricity.
PTFE possesses excellent dielectric properties, making it a highly effective barrier against electrical current. This is the foundational reason it is used for insulating wires, contacts, and other critical parts.
Stable Dielectric Constant
The dielectric constant affects how a material influences an electric field, which is critical in high-frequency applications like data cables and connectors.
A key advantage of PTFE is that its dielectric constant remains stable regardless of temperature changes. This ensures consistent, predictable performance in components that heat up during operation.
Resistance to Arcing
Arcing occurs when electricity jumps across a gap, which can damage an insulator and create a conductive path for future failures.
PTFE does not form carbon tracks when subjected to arcing. This means a single electrical fault is less likely to create a permanent failure path, significantly improving the safety and long-term reliability of the component.
Why Environmental Resilience Matters for Electronics
Electrical components rarely operate in perfect conditions. They are exposed to heat, moisture, and mechanical stress. PTFE's robust physical properties ensure it protects components throughout their operational life.
High-Temperature Stability
Many electrical parts, such as transformers and motors, generate significant heat. An insulator must not melt or degrade under these conditions.
PTFE functions exceptionally well at temperature extremes, maintaining its structural integrity and insulating properties where other plastics would fail.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Moisture and chemicals can cause short circuits and corrosion, leading to component failure.
PTFE is not wetted by water and is highly resistant to corrosive chemicals. This makes it an ideal material for gaskets and external insulators that protect sensitive internal electronics from the environment.
Low Friction and Wear Resistance
Components like electrical connectors must endure repeated use without degrading.
With its low coefficient of friction and excellent wear properties (especially when glass-filled), PTFE is used for connector insulators and housings that must withstand high mating cycles. This ensures a long and reliable mechanical life.
Common Applications in Electrical Systems
The unique properties of PTFE make it the material of choice for a range of demanding electrical and electronic applications.
Wire and Cable Insulation
Extruded PTFE rods and tapes are commonly used as the primary insulator for high-performance wiring where signal integrity and safety are paramount.
Connectors, Insulators, and Housings
In complex connectors, PTFE provides both the electrical insulation between contacts and the dimensional stability needed for a reliable mechanical connection.
Gaskets and Seals
In transformers and electric motors, PTFE gaskets are used to seal enclosures. Their ability to withstand heat and chemical exposure (like cooling oils) prevents leaks and protects the internal workings.
Insulating Fasteners
For certain medical and electronic devices, complete electrical isolation is necessary. Fasteners made from PTFE ensure that there is no conductive path through the mounting hardware itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE offers exceptional performance, it is not a universal solution. Its primary trade-off is cost and manufacturability.
PTFE is a premium-performance polymer, making it significantly more expensive than common insulators like PVC or polyethylene. It also requires specialized processing techniques, which can add to the final component cost.
Therefore, PTFE is typically reserved for applications where its high reliability and resilience to extreme conditions justify the higher investment. It is chosen when the cost of failure is much greater than the cost of the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right insulator depends entirely on the operational demands of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability in harsh environments: PTFE is the superior choice due to its unmatched thermal, chemical, and moisture resistance.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency signal integrity: PTFE's stable dielectric constant ensures consistent performance where other materials would cause signal loss or distortion.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose insulation in a stable environment: A more cost-effective polymer may be sufficient for your needs.
Ultimately, PTFE is the definitive material for critical applications where electrical insulation cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Electrical Components |
|---|---|
| Exceptional Dielectric Strength | Withstands high electric fields without breaking down, ensuring safety and reliability. |
| Stable Dielectric Constant | Provides consistent performance in high-frequency applications, even with temperature fluctuations. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains integrity and insulating properties in extreme heat where other plastics fail. |
| Moisture & Chemical Resistance | Protects components from short circuits and corrosion caused by harsh environments. |
| Resistance to Arcing | Does not form carbon tracks, improving long-term safety and preventing permanent failure paths. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical electrical applications?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, insulators, connectors, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure your components deliver unmatched reliability in extreme conditions through our custom fabrication services, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance the safety and performance of your electrical systems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















