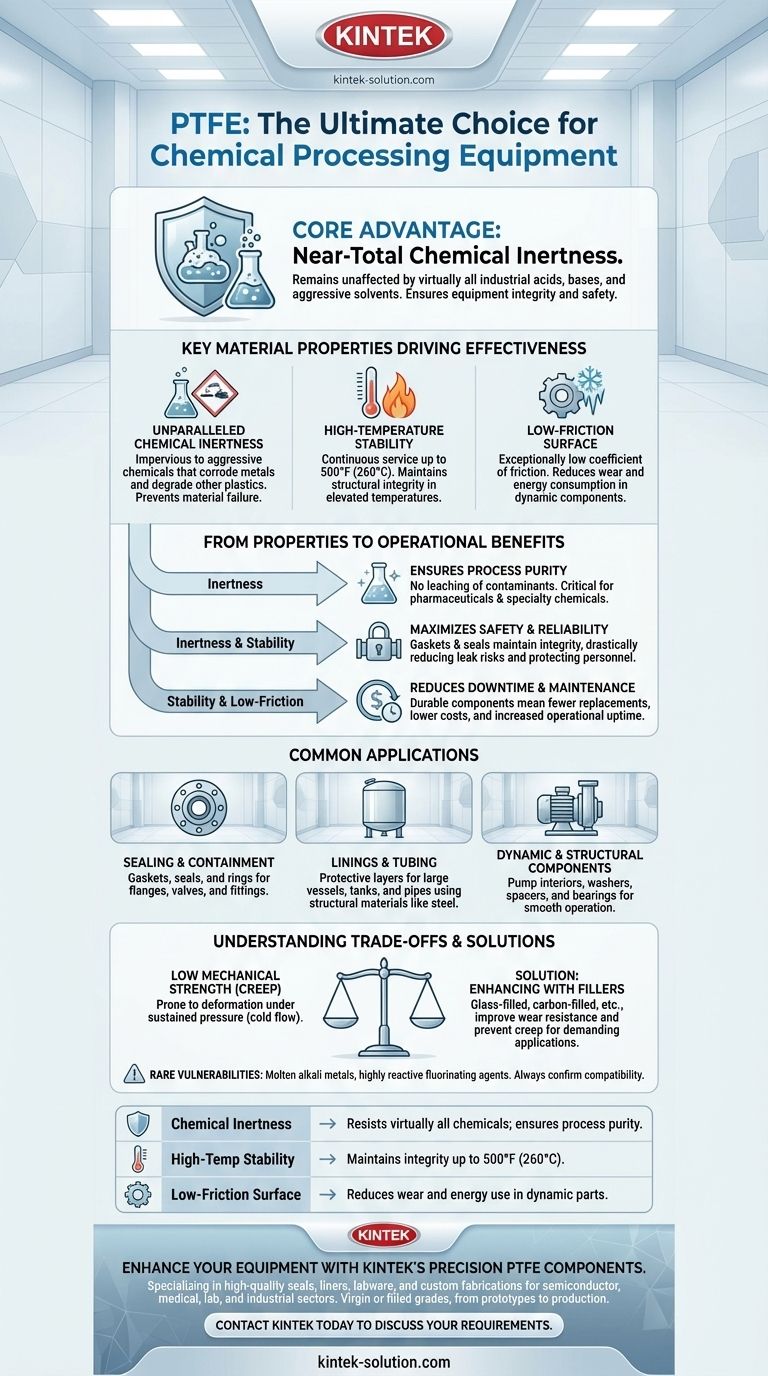
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the material of choice for chemical processing equipment due to its near-total chemical inertness. This means it remains almost completely unaffected when exposed to the vast majority of industrial acids, bases, and aggressive solvents. This unique property prevents the material from degrading, ensuring the integrity and safety of the equipment it's part of.
The suitability of PTFE is not just about surviving harsh chemicals; it's about what that survival enables. Its chemical inertness directly translates to higher process purity, enhanced operational safety, and significantly reduced equipment failure, ensuring long-term reliability in the most demanding environments.

The Fundamental Properties Driving PTFE's Effectiveness
To understand why PTFE is so dominant in this sector, we must look at its three key material characteristics. These properties work in concert to deliver performance that few other materials can match.
Unparalleled Chemical Inertness
PTFE is chemically inert to virtually all industrial chemicals. It is unaffected by aggressive acids, caustics, and solvents that would quickly corrode metals and degrade other plastics.
This resistance prevents the material itself from becoming a point of failure, which is the primary reason for its widespread use.
High-Temperature Stability
Many chemical processes operate at elevated temperatures. PTFE maintains its structural integrity and chemical resistance in continuous service up to 500°F (260°C).
This thermal stability allows it to be used in a wide range of applications where other polymers would melt or deform.
Low-Friction Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice.
This property is critical for dynamic components like bearings, pump interiors, and seals, as it reduces wear and energy consumption during operation.
How Properties Translate to Operational Benefits
The material science of PTFE directly creates tangible, high-value benefits in a chemical plant environment. These benefits revolve around safety, purity, and cost-efficiency.
Ensuring Process Purity
Because PTFE does not react with or degrade in the presence of chemicals, it does not leach contaminants into the process stream.
This is absolutely critical in industries like pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, and specialty chemicals, where even trace impurities can ruin a batch.
Maximizing Safety and Reliability
Component failure can lead to catastrophic leaks of hazardous materials. PTFE's resistance to chemical attack means that gaskets, seals, and linings maintain their integrity over time.
This drastically reduces the risk of equipment failure, safeguarding personnel, protecting the environment, and ensuring process stability.
Reducing Downtime and Maintenance
The durability of PTFE components in harsh environments means they need to be replaced far less frequently.
This translates directly to lower maintenance costs and, more importantly, increased operational uptime for the entire processing line.
Common Applications in Chemical Processing
PTFE is not used for just one purpose; its versatility makes it essential for a wide range of components throughout a chemical processing system.
Sealing and Containment
PTFE is the industry standard for gaskets, seals, and rings. They are used to seal flanges, valves, and fittings, providing a reliable and long-lasting barrier against corrosive fluids and preventing leaks.
Linings and Tubing
To protect large vessels, tanks, and pipes from their corrosive contents, they are often lined with a layer of PTFE. This allows for the use of less expensive structural materials like carbon steel while still achieving total chemical resistance on all contact surfaces.
Dynamic and Structural Components
The material is used to manufacture pump interiors, washers, spacers, and bearings. In these applications, its combination of chemical resistance and low friction ensures smooth, reliable operation even when fully submerged in aggressive chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect, and trusting PTFE requires understanding its limitations. Specifying the correct type of PTFE is crucial for success.
Low Mechanical Strength
Standard, or "virgin," PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under sustained pressure, it can be prone to creep, also known as cold flow, where the material slowly deforms.
This can be a problem in high-pressure sealing applications or for structural components.
The Role of Fillers for Enhancement
To overcome its mechanical weaknesses, PTFE is often blended with fillers. Glass-filled PTFE, for example, offers significantly enhanced wear resistance and reduced creep.
Other common fillers include carbon, graphite, and bronze. Specifying a filled grade is essential for mechanically demanding applications like bearings or valve seats.
Rare Chemical Vulnerabilities
While exceptionally resistant, PTFE is not completely invincible. It can be attacked by a few rare substances, such as molten alkali metals and some highly reactive fluorinating agents.
It is always critical to confirm material compatibility, but these exceptions are seldom encountered in typical chemical processing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material specification is key to leveraging PTFE's advantages while mitigating its weaknesses.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and inertness: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is the ideal choice for vessel linings, lab equipment, and dip tubes where contamination is not an option.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance under load: Specify a filled grade of PTFE, such as glass- or carbon-filled, for components like bearings, valve seats, and high-pressure seals to improve wear resistance and prevent creep.
- If your primary focus is reliable sealing in corrosive environments: PTFE gaskets and seals are the proven, industry-standard solution for preventing dangerous leaks in flanges, valves, and pump housings.
By understanding these core properties and their trade-offs, you can confidently specify PTFE to enhance the safety, purity, and longevity of your chemical processing systems.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit in Chemical Processing |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all acids, bases, and solvents; ensures process purity. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains integrity up to 500°F (260°C) for high-heat applications. |
| Low-Friction Surface | Reduces wear and energy use in dynamic parts like seals and bearings. |
Enhance the safety and longevity of your chemical processing equipment with KINTEK's precision PTFE components.
We specialize in manufacturing high-quality PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom fabrications for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need maximum chemical purity with virgin PTFE or enhanced mechanical strength with filled grades, our expertise ensures a solution tailored to your specific operational demands—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our team today to discuss your application requirements and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















