In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a premier sealing material because of its extraordinary combination of properties that no other single material typically offers. It is exceptionally resistant to nearly all chemicals, remains stable across an enormous range of temperatures, and has an extremely low coefficient of friction, making it durable and non-contaminating in the most demanding environments.
The true value of PTFE lies not in a single attribute, but in the synergy of its core features. Its ability to resist chemical attack and extreme temperatures while physically conforming to surfaces creates a uniquely reliable, long-lasting, and non-contaminating seal where other materials would quickly fail.

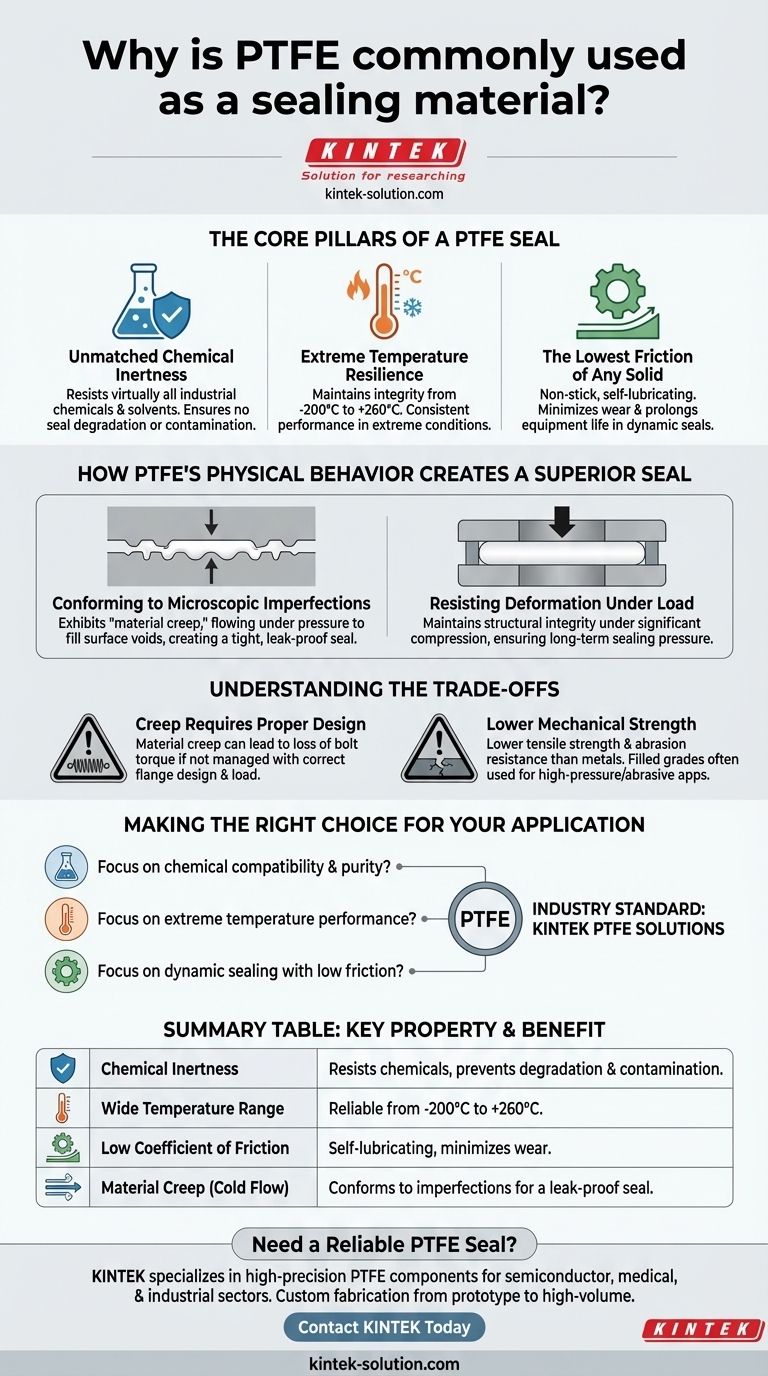
The Core Pillars of a PTFE Seal
PTFE's effectiveness as a sealant stems from three fundamental characteristics that allow it to function in conditions that are hostile to most other materials.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert materials known. It resists attack from virtually all industrial chemicals and solvents.
This property is critical for two reasons. First, it ensures the seal itself will not degrade, even in highly corrosive environments. Second, its high intrinsic purity prevents it from contaminating sensitive mediums, a vital requirement in the food, medical, and pharmaceutical industries.
Extreme Temperature Resilience
PTFE maintains its integrity and mechanical properties over a vast temperature range, typically from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
This allows it to be used in everything from cryogenic applications to high-temperature processing plants without becoming brittle or melting. Its performance remains consistent and predictable across these extremes.
The Lowest Friction of Any Solid
Known for its non-stick, self-lubricating properties, PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction.
In dynamic sealing applications with moving parts, this minimizes wear and tear on both the seal and the equipment. This "gliding ability" ensures smoother operation and significantly prolongs the service life of the components.
How PTFE's Physical Behavior Creates a Superior Seal
Beyond its core resistances, the unique physical way PTFE behaves under pressure is what makes it an excellent gasket and seal material.
Conforming to Microscopic Imperfections
A critical feature of PTFE is its tendency to exhibit material creep, or cold flow. While often seen as a negative, in sealing it is a distinct advantage.
When compressed between two surfaces (flanges), the PTFE material flows just enough to fill the microscopic voids and irregularities of the mating surfaces. This creates an exceptionally tight, leak-proof seal that conforms perfectly to the hardware.
Resisting Deformation Under Load
While PTFE conforms to surfaces, it also maintains its structural integrity under significant compressive loads.
This ability to resist excessive deformation ensures that the seal maintains the necessary pressure to prevent leaks over a long period. This is crucial in high-pressure systems found in chemical plants and oil refineries, where a seal failure can be catastrophic.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and understanding PTFE's limitations is key to using it effectively. Its unique properties can present challenges if not accounted for in the design.
Creep Requires Proper Design
The same material creep that helps PTFE conform to surfaces can become a liability if not managed. In improperly designed joints, PTFE can continue to flow under load, leading to a loss of bolt torque and sealing pressure over time.
This is why the design of the flange and the compressive load are critical factors for ensuring a long-lasting PTFE seal.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals or certain high-performance elastomers, pure PTFE has lower tensile strength and resistance to abrasion.
For applications involving very high pressures or significant abrasive wear, designers often use filled grades of PTFE, where materials like glass, carbon, or graphite are added to enhance its mechanical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a sealing material always depends on the specific demands of the environment.
- If your primary focus is chemical compatibility and purity: PTFE is an industry standard due to its near-total inertness, making it essential for food, medical, or aggressive chemical processing.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: PTFE's ability to maintain its sealing properties from cryogenic levels to over 260°C offers reliability where other materials would degrade.
- If your primary focus is dynamic sealing with low friction: PTFE's self-lubricating nature minimizes wear and energy loss in applications involving rotating shafts or moving pistons.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique molecular structure gives it a combination of defensive properties that allow it to create and maintain a reliable seal under the most demanding conditions.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Sealing Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all chemicals; prevents seal degradation and contamination. |
| Wide Temperature Range | Performs reliably from -200°C to +260°C, suitable for cryogenic to high-heat uses. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Self-lubricating; minimizes wear in dynamic seals for longer service life. |
| Material Creep (Cold Flow) | Conforms to surface imperfections under compression, creating a leak-proof seal. |
Need a Reliable PTFE Seal for Your Demanding Application?
PTFE's unique properties make it the ideal choice for sealing solutions in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—that deliver unmatched performance in extreme environments.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication services, from initial prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get the exact seal you need.
Let us provide a sealing solution that guarantees purity, durability, and reliability. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















