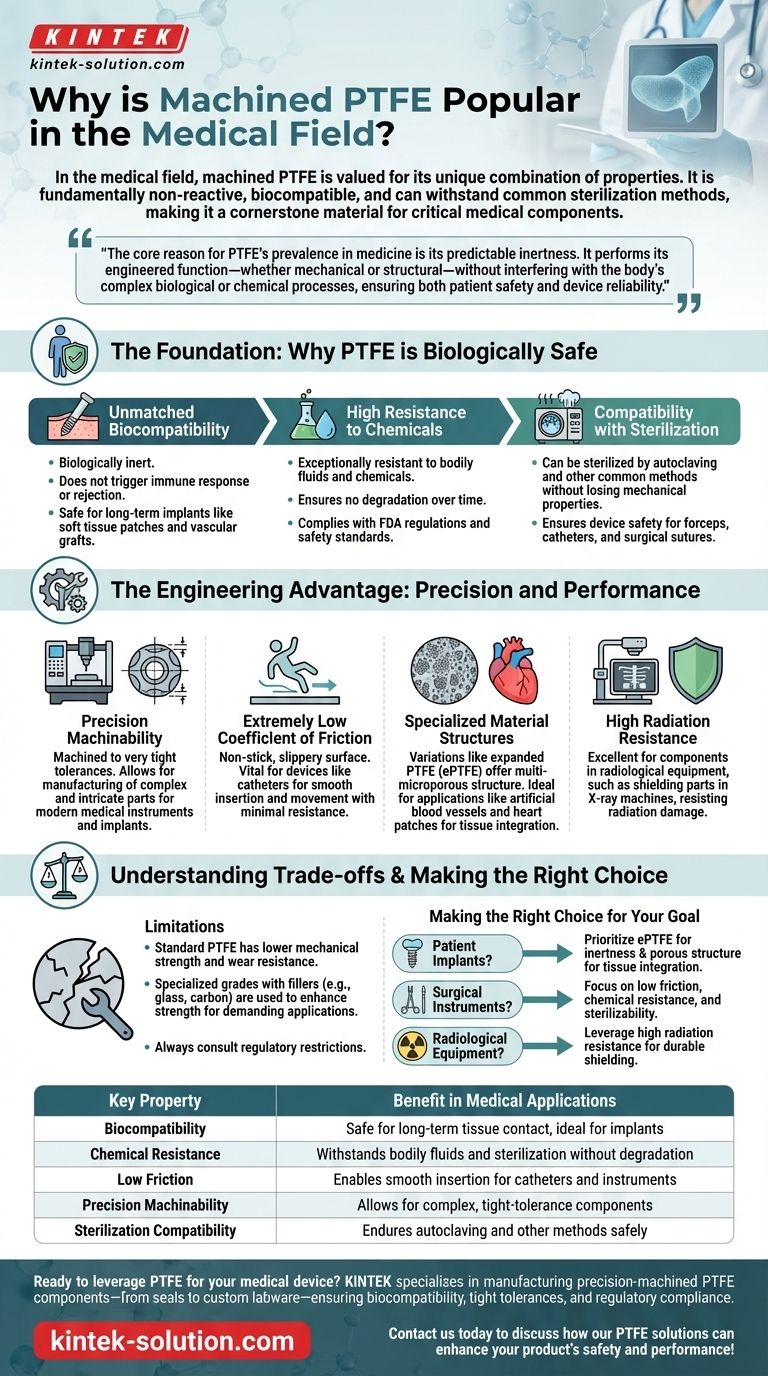
In the medical field, machined PTFE is valued for its unique combination of properties. It is fundamentally non-reactive and biocompatible, meaning it can safely contact human tissue without causing adverse effects. This, combined with its ability to withstand common sterilization methods and be machined to incredibly high precision, makes it a cornerstone material for a wide range of critical medical components.
The core reason for PTFE's prevalence in medicine is its predictable inertness. It performs its engineered function—whether mechanical or structural—without interfering with the body's complex biological or chemical processes, ensuring both patient safety and device reliability.

The Foundation: Why PTFE is Biologically Safe
The primary concern for any material used in medicine is its interaction with the human body. PTFE excels in this area due to its fundamental chemical structure, making it one of the most trusted polymers for medical applications.
Unmatched Biocompatibility
PTFE is biologically inert. This means it does not trigger an immune response, cause rejection, or produce any other negative physiological side effects when used for implants or instruments.
This inertness allows for its use in applications like soft tissue regeneration patches and vascular grafts, where direct, long-term contact with the body is required.
High Resistance to Chemicals
The material is exceptionally resistant to nearly all chemicals and bodily fluids. This ensures that a PTFE component will not degrade over time when implanted or used within the body.
This chemical stability is a key reason it complies with stringent FDA regulations and safety standards for medical devices.
Compatibility with Sterilization
Medical components must be sterilized to prevent infection. PTFE can be sterilized by any common method, including autoclaving, without losing its crucial mechanical properties.
This reliability ensures that devices like forceps, catheters, and surgical sutures remain safe and effective after sterilization, a critical requirement for both single-use and reusable instruments.
The Engineering Advantage: Precision and Performance
Beyond its safety profile, PTFE offers distinct engineering benefits that allow for the creation of sophisticated and high-performing medical devices.
Precision Machinability
One of the key advantages of PTFE is that it can be machined to very tight tolerances. This allows for the manufacturing of complex and intricate parts required for modern medical instruments and implants.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, giving it a characteristic non-stick, slippery surface. This property is vital for devices like catheters that must be inserted and moved with minimal resistance.
Specialized Material Structures
Beyond solid PTFE, variations like expanded PTFE (ePTFE) offer unique benefits. ePTFE has a multi-microporous structure that is ideal for applications like artificial blood vessels and heart patches, where tissue integration is desirable.
High Radiation Resistance
The material's ability to resist radiation damage makes it an excellent choice for components used in radiological equipment, such as shielding parts in X-ray machines.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While PTFE is exceptionally useful, it is not a universal solution. A clear understanding of its limitations is crucial for proper application.
Mechanical Strength Considerations
Standard PTFE is a relatively soft material with lower mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to other engineering plastics.
To counteract this, manufacturers often create specialized grades of PTFE with fillers (like glass or carbon) to enhance specific properties like strength or thermal conductivity for more demanding applications.
Regulatory and Application-Specific Hurdles
Despite its general biocompatibility, there are restrictions on its use in certain medical devices. Engineers and designers must always consult the specific regulatory requirements for their intended application.
Choosing the right grade of PTFE and ensuring it meets all safety standards for a particular use case is a critical step in the design process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct material is about matching its properties to the primary function of the device. PTFE's versatility allows it to serve multiple, distinct roles within the medical industry.
- If your primary focus is patient implants: Prioritize medical-grade, expanded PTFE (ePTFE) for its inertness and porous structure that can encourage tissue integration in grafts and patches.
- If your primary focus is surgical instruments: Focus on the material's low friction, chemical resistance, and sterilizability for creating high-performance tools like catheters or forceps.
- If your primary focus is radiological equipment: Leverage PTFE's high radiation resistance for durable and effective shielding components that will not degrade under exposure.
Understanding these core attributes allows you to leverage PTFE not just as a material, but as a strategic component in modern medical innovation.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Medical Applications |
|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Safe for long-term tissue contact, ideal for implants |
| Chemical Resistance | Withstands bodily fluids and sterilization without degradation |
| Low Friction | Enables smooth insertion for catheters and instruments |
| Precision Machinability | Allows for complex, tight-tolerance components |
| Sterilization Compatibility | Endures autoclaving and other methods safely |
Ready to leverage PTFE for your medical device? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision-machined PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure biocompatibility, tight tolerances, and regulatory compliance, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's safety and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















