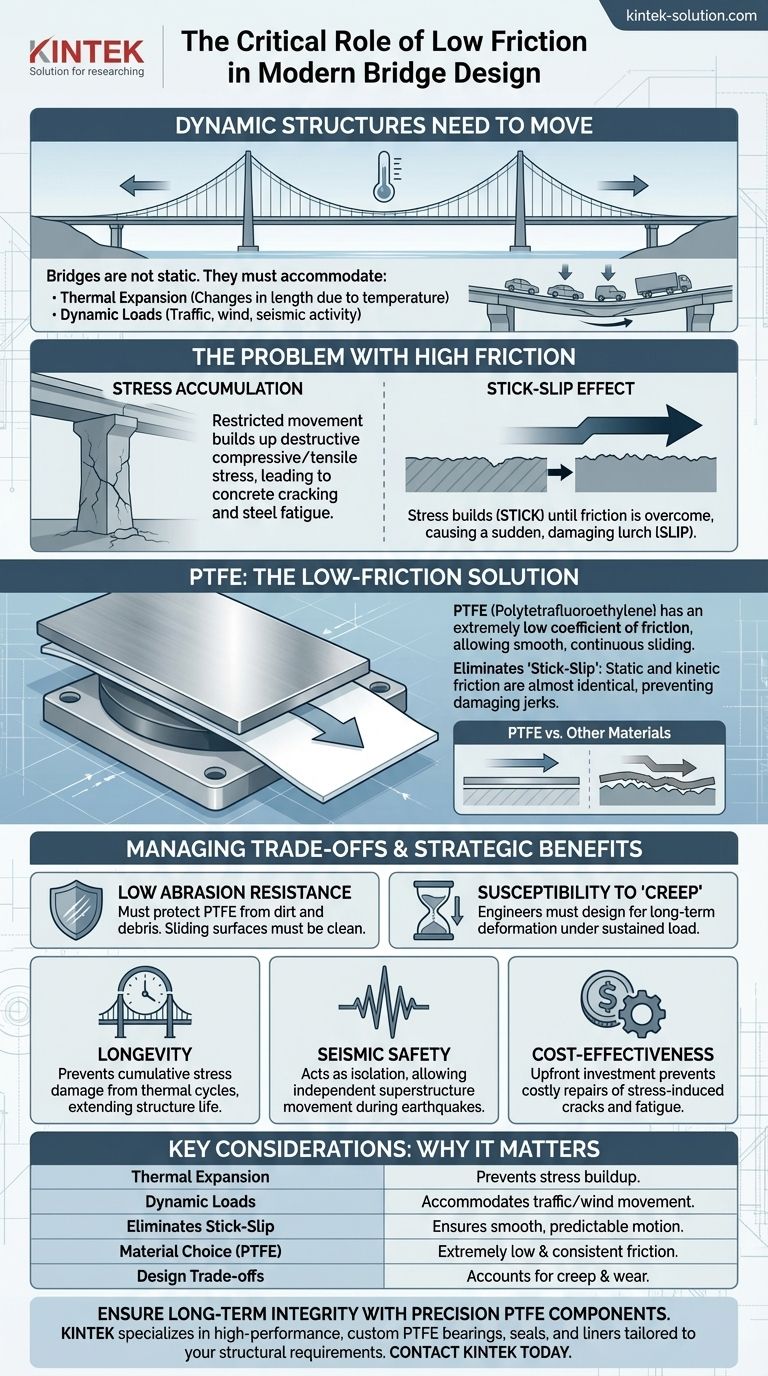
In modern bridge design, a low coefficient of friction is critical for managing the immense, often unseen forces of thermal expansion and contraction. Materials with low friction, such as PTFE, are used in bridge bearings to allow the structure to move smoothly and predictably, preventing the buildup of destructive stress in core components like piers and abutments. This controlled movement is essential for the long-term structural integrity and safety of the bridge.
The central takeaway is this: bridges are not rigid; they are designed to be dynamic structures that must breathe with temperature changes and flex under load. A low coefficient of friction in their bearings is what allows this necessary movement to occur safely, transforming a potentially destructive force into a manageable engineering parameter.

Why a Massive Bridge Needs to Move
What appears to be a static, immovable object is in constant, subtle motion. Acknowledging and managing this movement is a fundamental principle of modern bridge engineering.
The Force of Thermal Expansion
All materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. Over the long span of a bridge, a change in ambient temperature can cause the deck to change in length by several inches or even feet.
Without a mechanism to accommodate this change, the structure would be subjected to enormous internal forces, similar to a vice being tightened with every heat wave.
Accommodating Dynamic Loads
Beyond temperature, bridges must also handle movement from the constant load of traffic, high winds, and, in some areas, seismic activity.
These forces cause the structure to vibrate, sway, and shift. Bridge bearings provide a controlled interface that helps absorb and dissipate this energy safely.
The Problem with High Friction
If a bridge's components cannot slide past one another smoothly, the consequences can be severe. High friction turns predictable movement into a structural threat.
Stress Accumulation
When movement is restricted by friction, the energy from thermal expansion has nowhere to go. It builds up as compressive or tensile stress within the bridge deck, piers, and foundations.
Over time, this cyclical stress can lead to concrete cracking, steel fatigue, and ultimately, a shortened lifespan for the entire structure.
The "Stick-Slip" Effect
High-friction surfaces often exhibit a "stick-slip" phenomenon. Stress builds up while the surfaces are "stuck" by static friction. When the force finally overcomes this friction, the component lurches forward in a sudden "slip."
This jerky, uncontrolled movement sends a damaging shockwave through the bridge, causing far more wear than smooth, continuous sliding.
Why Modern Steel Structures Amplify the Issue
Modern bridges often use steel superstructures, which have a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion.
This means they expand and contract more significantly than older stone or concrete structures, making the need for effective, low-friction movement even more critical.
PTFE: The Low-Friction Solution
To solve the friction problem, engineers turn to advanced materials, most notably Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), often known by its brand name, Teflon.
A Uniquely Slippery Material
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. Its molecular structure results in very weak forces between it and other surfaces, allowing for exceptionally smooth sliding.
The Key Property: Eliminating "Stick-Slip"
Crucially, the difference between PTFE's static coefficient of friction (the force to start moving) and its kinetic coefficient of friction (the force to keep moving) is almost zero.
This property is the direct antidote to the damaging "stick-slip" effect. It ensures that movement begins smoothly at a predictable force, eliminating the sudden, jarring slips that damage the structure.
How It Works in a Bridge Bearing
A typical modern bridge bearing consists of a sheet of PTFE sliding against a highly polished stainless steel plate. This assembly is placed between the bridge deck and the pier cap.
As the bridge expands or contracts, the PTFE layer allows the deck to glide effortlessly over the pier, dissipating the energy of movement without transferring stress into the substructure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is an exceptional material for this application, it is not without limitations that must be engineered around.
Low Abrasion Resistance
As a consequence of its molecular structure, PTFE is a relatively soft material with low resistance to wear and abrasion.
Bridge bearing designs must therefore protect the PTFE surface from dirt, debris, and water, which could compromise its performance. The sliding surfaces must be kept perfectly clean and smooth.
Susceptibility to "Creep"
Under a sustained, heavy load, PTFE can slowly deform over time in a process known as "creep."
Engineers must account for this property in the bearing's design, often by using dimpled or woven PTFE, or by ensuring the load is distributed over a large enough area to keep pressure within acceptable limits for the bridge's multi-decade lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The use of low-friction bearings is a strategic decision that directly impacts the bridge's health, safety, and economic viability.
- If your primary focus is longevity: Low-friction bearings are the most effective way to prevent the cumulative stress damage from thermal cycles that leads to premature aging and costly structural repairs.
- If your primary focus is seismic safety: These bearings can be part of an isolation system, allowing the superstructure to move independently from the ground during an earthquake, dissipating energy and protecting the piers from catastrophic failure.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness: While specialized bearings represent an upfront investment, they prevent far more expensive lifecycle costs associated with repairing stress-induced cracks and fatigue damage.
Ultimately, managing these microscopic movements with low-friction materials is the key to ensuring the macroscopic stability and endurance of our most critical infrastructure.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | Why It Matters for Bridge Bearings |
|---|---|
| Thermal Expansion | Prevents stress buildup in piers and deck from temperature changes. |
| Dynamic Loads | Accommodates movement from traffic, wind, and seismic activity. |
| Eliminates Stick-Slip | PTFE ensures smooth, predictable movement, not damaging jerks. |
| Material Choice | PTFE offers an extremely low and consistent coefficient of friction. |
| Design Trade-offs | Engineers must account for PTFE's susceptibility to creep and wear. |
Ensure the Long-Term Integrity of Your Infrastructure Projects with Precision PTFE Components
For bridge engineers and designers, the right material choice is critical for safety and longevity. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and specialized bearings—that deliver the reliable, low-friction performance demanded by modern bridge design.
Our expertise in custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensures you get components tailored to your specific structural and environmental requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our precision PTFE solutions can enhance the durability and safety of your next project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















