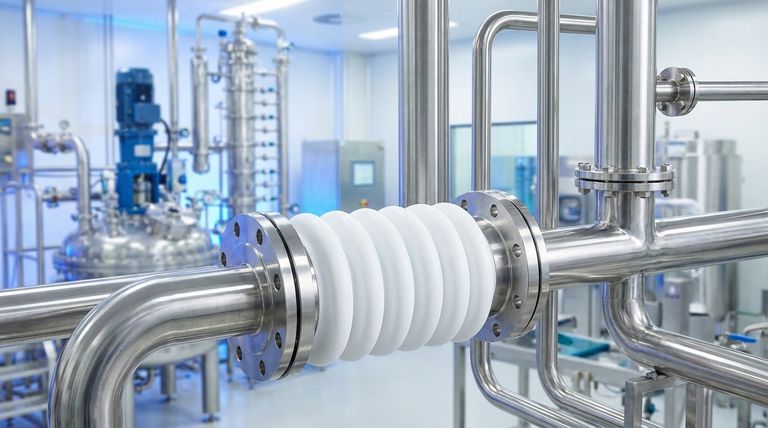
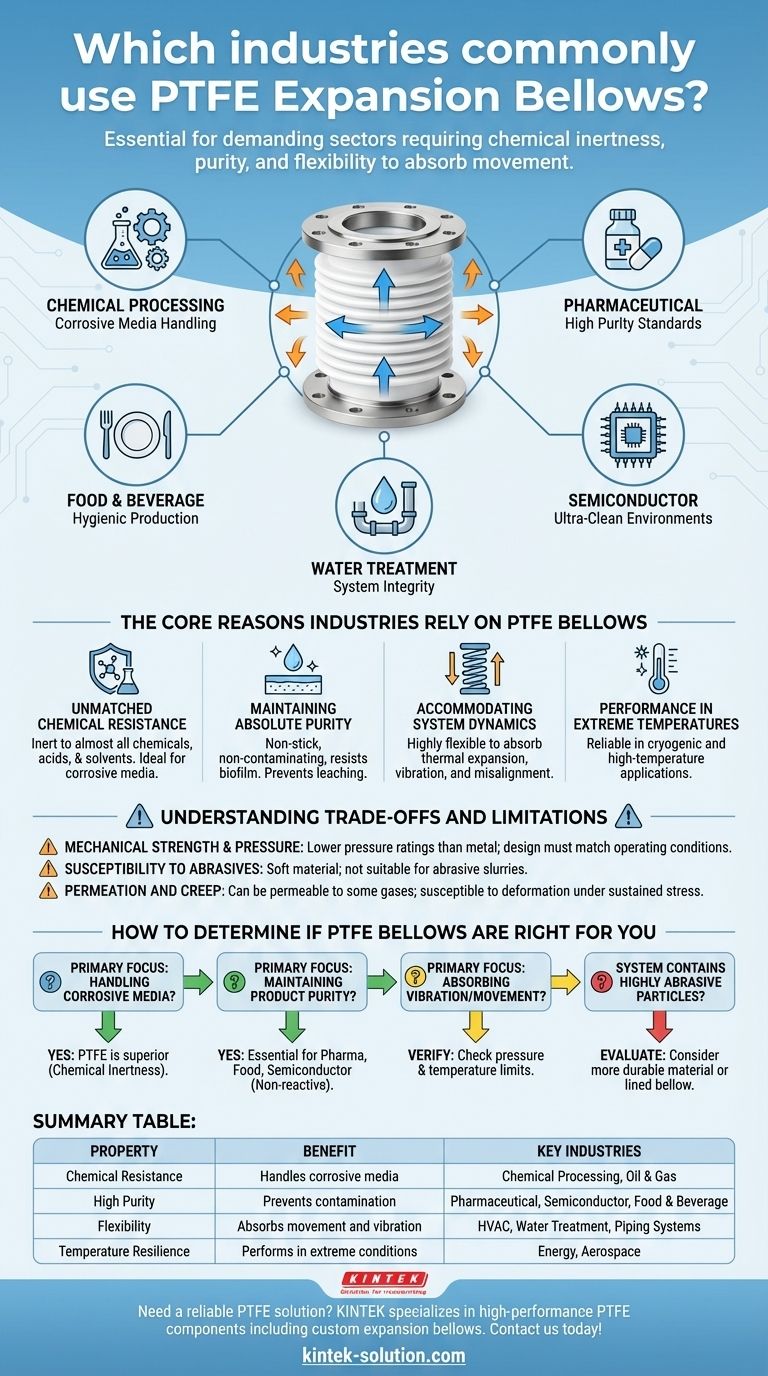
PTFE expansion bellows are essential components in a broad spectrum of demanding industries. They are most commonly utilized in chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, food and beverage production, semiconductor fabrication, and water treatment facilities where material integrity is non-negotiable.
The specific industry is less important than the underlying operational challenge. PTFE bellows are chosen wherever an application demands extreme chemical inertness, high purity, and the flexibility to absorb movement and vibration in a system.

The Core Reasons Industries Rely on PTFE Bellows
The widespread adoption of PTFE bellows isn't based on industry trends, but on the fundamental material properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) that solve critical engineering problems.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents. This makes it the default choice for components that will be in direct contact with corrosive or aggressive media.
This property is indispensable in chemical processing plants, oil refineries, and pulp and paper mills where harsh substances are a constant.
Maintaining Absolute Purity
The material is inherently non-stick, non-contaminating, and resists biofilm growth. This ensures that the material of the bellow itself does not leach into or contaminate the process media.
This is a critical requirement in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and semiconductor manufacturing industries, where even trace amounts of contamination can ruin a batch or compromise product safety.
Accommodating System Dynamics
Piping systems are rarely static. They experience thermal expansion and contraction, equipment vibration, and minor misalignments. PTFE bellows are highly flexible, designed to absorb these movements.
This protects sensitive equipment like pumps and reactors, prevents stress fractures in rigid pipes, and dampens vibration, making them vital in any intricate piping network, from HVAC systems to chemical reactors.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
PTFE maintains its properties over a wide temperature range, performing reliably in both cryogenic and high-temperature applications where many other polymers would fail.
This resilience is crucial for applications in the energy and aerospace sectors, as well as for various chemical processes that operate under extreme thermal conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly versatile, PTFE bellows are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to successful implementation.
Mechanical Strength and Pressure
Compared to metal expansion joints, PTFE bellows have lower tensile strength and pressure ratings. The design, including wall thickness and the number of convolutions, must be carefully matched to the system's operating pressure and temperature to prevent failure.
Susceptibility to Abrasives
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is not well-suited for applications involving abrasive slurries, as sharp particles can score the surface and lead to premature wear and failure.
Permeation and Creep
While highly resistant, PTFE is not completely impermeable to all gases, and this can be a factor in high-purity vacuum systems. Additionally, like all fluoropolymers, it can experience "creep" or cold flow—a slow deformation under sustained mechanical stress, especially at elevated temperatures.
How to Determine if PTFE Bellows Are Right for You
Focus on your specific operational requirements to make the correct choice for your system.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive media: PTFE is almost always the superior choice due to its near-universal chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is maintaining product purity: The non-reactive and non-stick surface of PTFE makes it essential for pharmaceutical, food, and semiconductor applications.
- If your primary focus is absorbing vibration or thermal movement: PTFE bellows provide excellent flexibility, but you must verify your system's pressure and temperature are within the bellow's design limits.
- If your system contains highly abrasive particles: Carefully evaluate whether a more durable material or a specially lined bellow is a more appropriate and reliable solution.
Ultimately, matching the unique properties of PTFE to the specific demands of your application is the key to ensuring system safety, reliability, and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Handles corrosive media | Chemical Processing, Oil & Gas |
| High Purity | Prevents contamination | Pharmaceutical, Semiconductor, Food & Beverage |
| Flexibility | Absorbs movement and vibration | HVAC, Water Treatment, Piping Systems |
| Temperature Resilience | Performs in extreme conditions | Energy, Aerospace |
Need a reliable PTFE solution for your demanding application? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including custom expansion bellows, seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE expertise can enhance your system's safety, purity, and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















