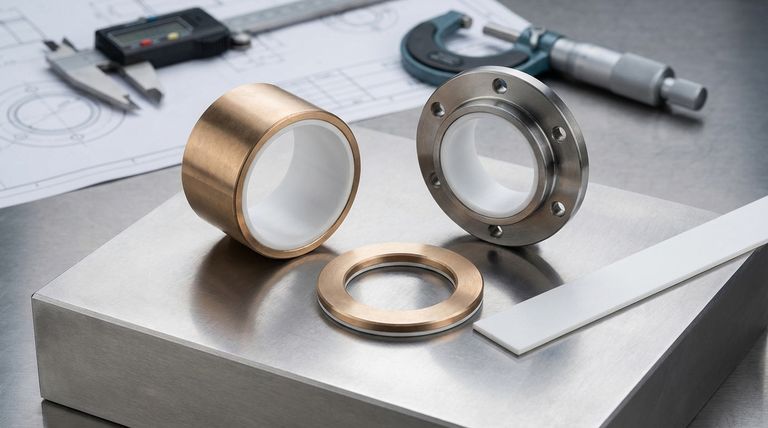
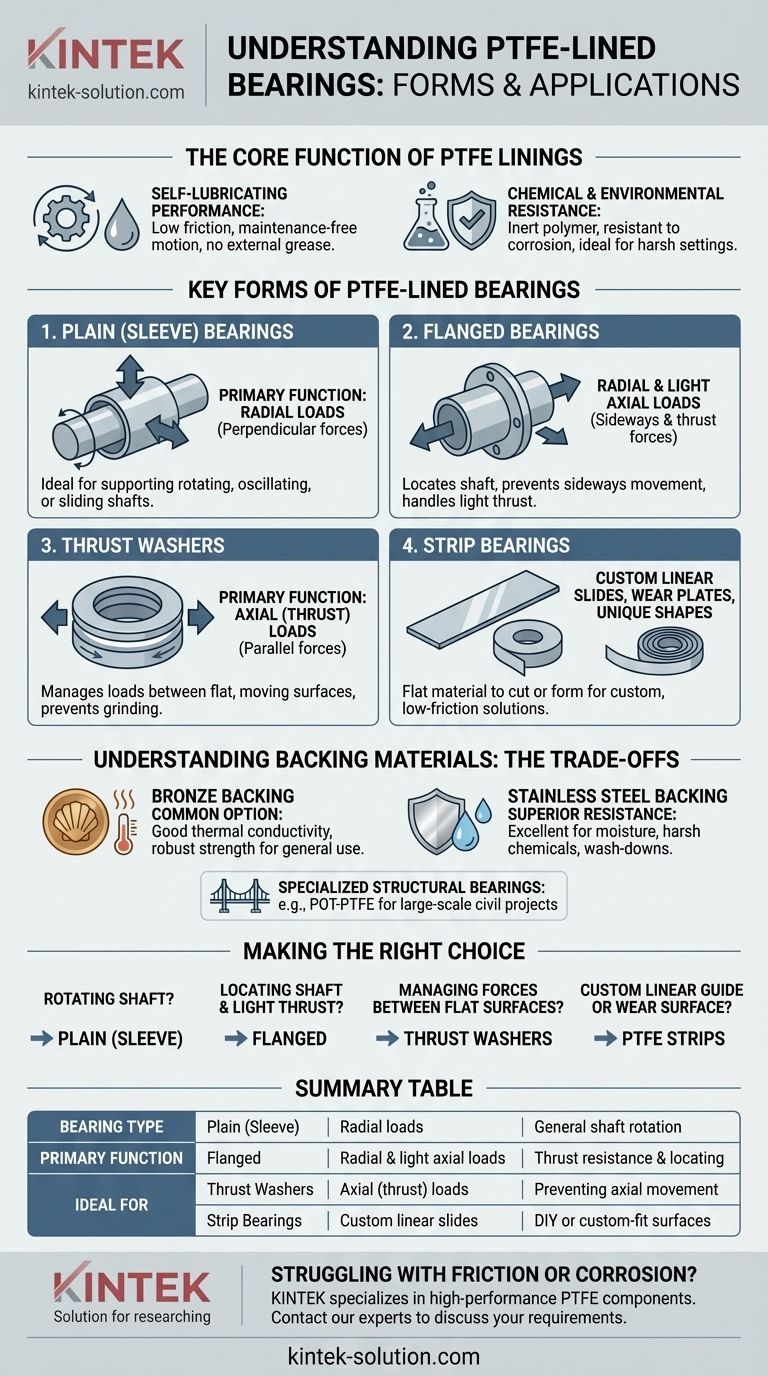
In short, PTFE-lined bearings are available in several standard forms: plain (sleeve) bearings, flanged bearings, thrust washers, and flat strips. These types can come in metric or imperial sizes and often offer a choice of backing material, such as bronze or stainless steel, to suit different environmental and load conditions.
The key is to understand that the "type" of PTFE-lined bearing is defined by its physical shape. This shape dictates the kind of motion and load it is designed to support—whether rotational, linear, axial (thrust), or a combination.

The Core Function of PTFE Linings
Before examining the different forms, it's crucial to understand why PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is used as a lining. This material fundamentally defines the bearing's performance.
Self-Lubricating Performance
The primary advantage of a PTFE lining is its extremely low coefficient of friction. This allows for smooth, stick-slip-free motion without the need for external grease or oil, making these bearings ideal for maintenance-free applications.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
PTFE is a highly inert polymer. This gives it excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for use in corrosive environments, food processing equipment, and medical devices.
Key Forms of PTFE-Lined Bearings
Each bearing shape is engineered to solve a specific mechanical problem. The choice depends entirely on the forces and movements in your application.
Plain (Sleeve) Bearings
These are simple cylindrical bushings. They are designed to support a rotating, oscillating, or sliding shaft within a housing. Their primary function is to handle radial loads—forces perpendicular to the shaft's axis.
Flanged Bearings
A flanged bearing is essentially a plain sleeve bearing with a rim, or flange, at one end. This flange provides a thrust surface, allowing the bearing to handle light axial loads (forces parallel to the shaft's axis) in addition to radial loads. They are excellent for preventing a shaft from moving sideways.
Thrust Washers
These are simple, flat, ring-shaped components. Their sole purpose is to manage axial (thrust) loads between two rotating or moving surfaces. They act as a low-friction wear pad, preventing components from grinding against each other.
Strip Bearings
PTFE strips are flat, rectangular pieces of bearing material. They are designed to be cut or formed by the user to create custom linear slide-ways, wear plates, or unique bearing shapes that are not available in standard formats.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Backing Materials
The PTFE lining provides the low-friction surface, but the metal backing provides the structural strength and dimensional stability. The choice of backing material is a critical design decision.
Bronze Backing
This is the most common and cost-effective option. The bronze shell offers good thermal conductivity to dissipate heat and provides robust mechanical strength for a wide range of general-purpose applications.
Stainless Steel Backing
For applications exposed to moisture, harsh chemicals, or wash-down procedures, a stainless steel backing is the superior choice. It provides significantly better corrosion resistance than standard bronze, ensuring the bearing's structural integrity in challenging environments.
Specialized Structural Bearings
Beyond common machine components, highly specialized types like POT-PTFE bearings exist. These are complex assemblies used in large-scale civil engineering projects, such as bridges, to accommodate thermal expansion and structural movement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection should be driven by the specific loads and movements your design requires.
- If your primary focus is supporting a rotating shaft: A standard plain (sleeve) bearing is your most direct solution.
- If your primary focus is locating a shaft and handling light thrust: A flanged bearing provides both radial support and axial location in a single component.
- If your primary focus is managing forces between two flat, rotating surfaces: A thrust washer is designed specifically for this axial load scenario.
- If your primary focus is creating a custom linear guide or wear surface: PTFE strips offer the flexibility to build a solution tailored to your exact needs.
Ultimately, choosing the right PTFE-lined bearing is about matching the component's geometry to the forces at play in your design.
Summary Table:
| Bearing Type | Primary Function | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Plain (Sleeve) | Supports radial loads (rotating/sliding shafts) | General shaft rotation or oscillation |
| Flanged | Handles radial & light axial loads; locates shaft | Applications requiring thrust resistance |
| Thrust Washers | Manages axial (thrust) loads between surfaces | Preventing axial movement in assemblies |
| Strip Bearings | Custom linear slides, wear plates, unique shapes | DIY or custom-fit low-friction surfaces |
Struggling with friction, corrosion, or maintenance in your design? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom PTFE-lined bearings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific bearing requirements and discover a maintenance-free solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability



















