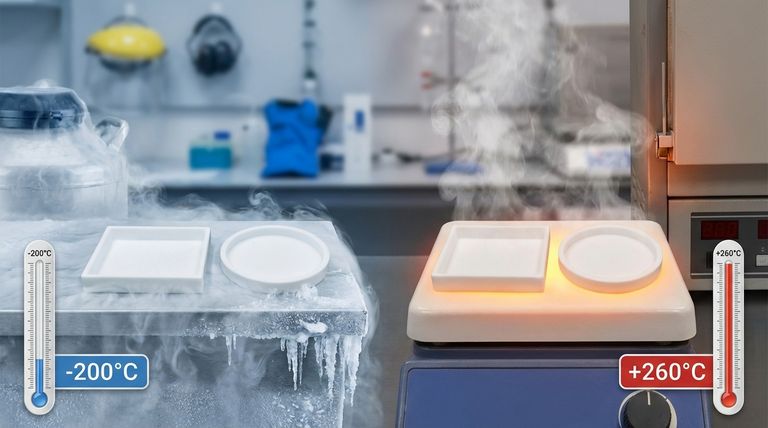
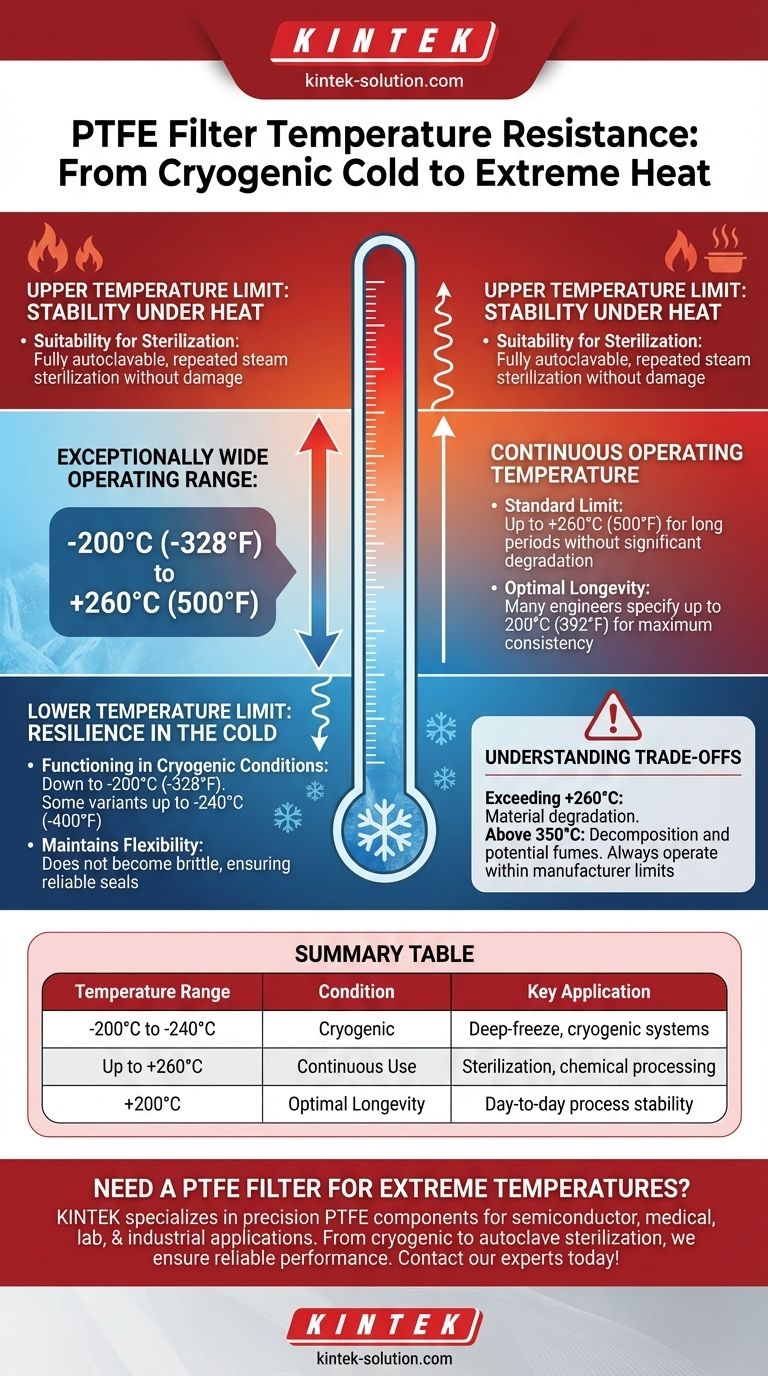
In short, PTFE offers an exceptionally wide operating temperature range. Most PTFE filters are rated for continuous service from approximately -200°C (-328°F) up to +260°C (500°F). This remarkable thermal stability on both ends of the spectrum makes it one of the most versatile materials for extreme temperature applications.
The core reason for PTFE's broad temperature resistance lies in its stable molecular structure. This allows it to function reliably in environments, from cryogenic freezing to high-heat sterilization, where most other polymers would fail.

The Upper Temperature Limit: Stability Under Heat
The ability of PTFE to withstand high temperatures is one of its most defining characteristics. This makes it a default choice for demanding industrial, chemical, and laboratory processes.
The Continuous Operating Temperature
The most commonly cited upper limit for continuous use of PTFE is +260°C (500°F). At this temperature, the material retains its structural and chemical integrity without significant degradation over long periods.
Optimal Performance vs. Absolute Limit
While PTFE can withstand 260°C, its optimal performance for some applications may be slightly lower. For maximum longevity and consistency, many engineers specify continuous operating temperatures up to 200°C (392°F), using the higher range for intermittent peaks.
Suitability for Sterilization
PTFE's high heat resistance makes it fully autoclavable. This allows PTFE filters and components to be repeatedly steam sterilized for use in sterile filtration, pharmaceutical, and food processing applications without damage.
The Lower Temperature Limit: Resilience in the Cold
Just as impressive as its heat resistance is PTFE's performance in extreme cold. It maintains its properties in conditions that cause many other materials to become brittle and crack.
Functioning in Cryogenic Conditions
PTFE remains functional and durable at temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F). Some specialized variants, such as expanded PTFE, can even withstand temperatures approaching -240°C (-400°F).
Maintaining Flexibility and Integrity
Unlike many plastics that become rigid and fragile when frozen, PTFE retains a significant degree of its flexibility at cryogenic temperatures. This prevents it from shattering under stress, ensuring a reliable seal and filter integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE's temperature range is vast, it is not infinite. Understanding its limitations is critical for ensuring safety and reliability in any application.
Exceeding the Maximum Temperature
Operating above the recommended +260°C (500°F) limit will cause the material to degrade. At extremely high temperatures (e.g., above 350°C), PTFE will begin to decompose, which can compromise the application and release fumes. Always operate within the manufacturer's specified limits.
How Product Form Affects Ratings
The exact temperature rating can vary slightly based on the specific product. For example, a PTFE O-ring or gasket might have a slightly more conservative rating than a thick sheet of PTFE due to the pressures and sealing requirements of its application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a material requires matching its capabilities to the demands of the process. PTFE's thermal stability gives you clear advantages for specific goals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sterilization or industrial processing: Rely on PTFE for its proven stability up to the continuous limit of 260°C (500°F), making it a superior choice for autoclaving and chemical processing.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic work or deep-freeze applications: Choose PTFE for its exceptional performance and lack of brittleness, ensuring system integrity at temperatures down to -200°C (-328°F).
- If your primary focus is maximum longevity and process stability: Design your system to operate within PTFE's optimal range (under 200°C) for day-to-day use, reserving its peak temperature resistance for shorter durations.
Ultimately, PTFE's ability to perform consistently across a vast thermal spectrum makes it an exceptionally reliable choice for the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Condition | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to -240°C | Cryogenic | Deep-freeze, cryogenic systems |
| Up to +260°C | Continuous Use | Sterilization, chemical processing |
| +200°C | Optimal Longevity | Day-to-day process stability |
Need a PTFE filter that withstands your extreme temperature requirements? KINTEK specializes in precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume custom fabrication, we ensure your filters perform reliably from cryogenic conditions to autoclave sterilization. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific thermal challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications



















