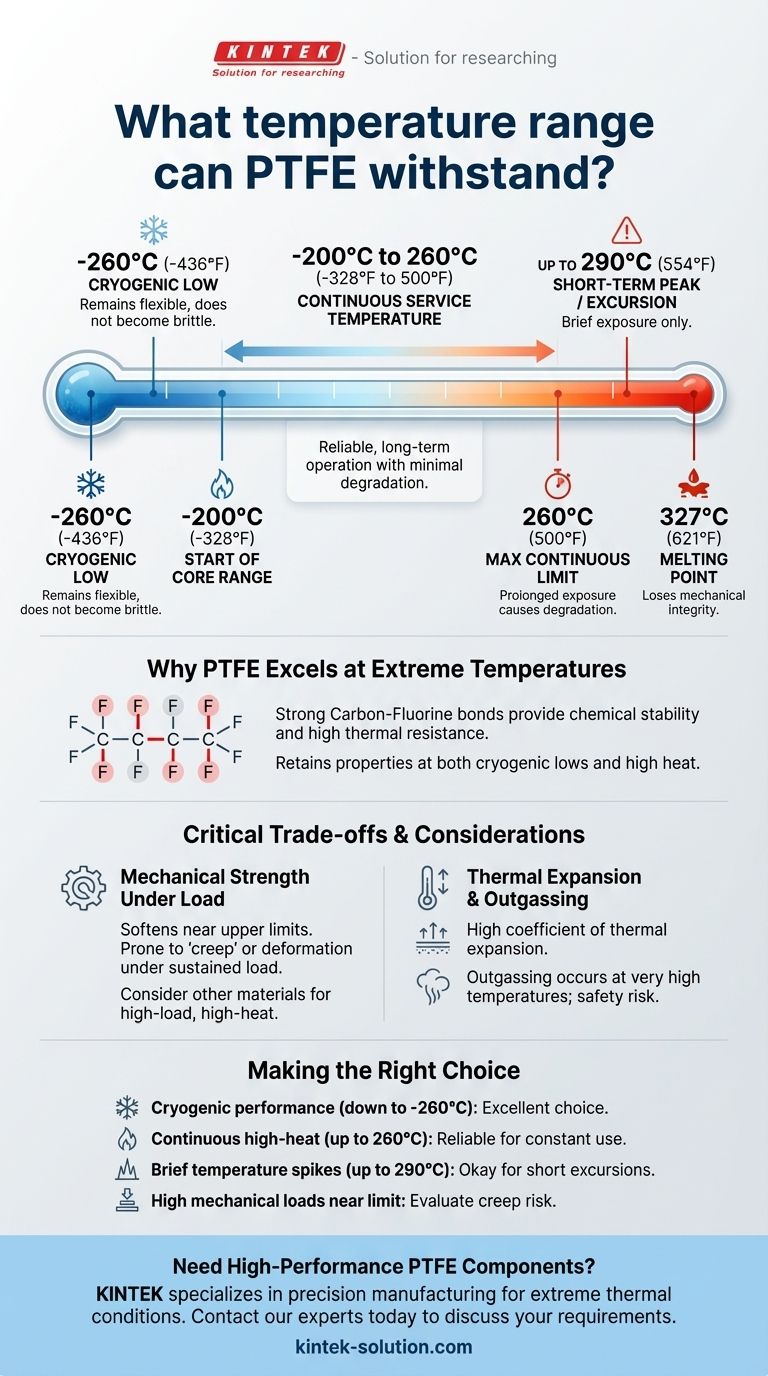
The definitive temperature range for PTFE is from approximately -200°C (-328°F) up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F). While some grades can handle cryogenic temperatures as low as -260°C (-436°F) and brief excursions to 290°C (554°F), its practical, reliable operating window resides within this core range.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) possesses one of the widest temperature operating ranges among plastics, but its utility is defined by understanding the difference between its continuous service limit, its short-term peak temperature, and its ultimate melting point.

Why PTFE Excels at Extreme Temperatures
PTFE, commonly known by the brand name Teflon, is a fluoropolymer with unique properties derived from its molecular structure. The strong carbon-fluorine bonds are exceptionally stable.
The Role of Chemical Bonds
This chemical stability is the direct reason for PTFE's high thermal resistance. The bonds do not easily break down when exposed to thermal energy, allowing the material to maintain its integrity at temperatures that would degrade most other plastics and elastomers.
Performance at Cryogenic Lows
PTFE maintains a high degree of flexibility and strength even at extremely low, or cryogenic, temperatures. Unlike many materials that become brittle and fracture in deep cold, PTFE remains functional, making it a go-to choice for applications like seals and components in liquified gas systems.
Stability at High Temperatures
As temperatures rise, PTFE retains its key characteristics without softening or deforming significantly until it approaches its upper service limit. This makes it ideal for high-temperature industrial machinery, aerospace components, and non-stick cookware coatings.
Understanding the Temperature Limits
Simply knowing the range isn't enough; you must understand what happens at the extremes to use the material effectively and safely.
The Upper Limit: Continuous vs. Peak
The most critical number for high-temperature applications is 260°C (500°F). This is the maximum continuous service temperature where PTFE can operate indefinitely without significant degradation of its mechanical properties.
For very short durations, PTFE can withstand temperatures up to 290°C (554°F). However, prolonged exposure above 260°C will begin to compromise the material's structural integrity.
The Melting Point
PTFE has a high melting point of approximately 327°C (621°F). It is crucial to note that well before it reaches this temperature, the material will have lost most of its useful mechanical properties. Operating near the melting point is not recommended.
Critical Trade-offs and Considerations
While its thermal range is impressive, PTFE is not the solution for every problem. Understanding its limitations is key to successful implementation.
Mechanical Strength Under Load
PTFE is a relatively soft material. As it approaches its upper temperature limit, it will soften further and can be prone to "creep" or deforming under a sustained load. For high-load, high-temperature mechanical parts, other high-performance polymers or metals may be more suitable.
Thermal Expansion
Like all materials, PTFE expands when heated and contracts when cooled. It has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion, which must be accounted for in designs with tight tolerances that will experience wide temperature swings.
Outgassing at Extreme Heat
When heated to very high temperatures (well above the recommended service limit), PTFE can begin to break down and release fumes. This is a critical safety consideration, particularly in food-grade or enclosed applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE's thermal profile meets the demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance: PTFE is an excellent choice, as it retains its properties and does not become brittle at temperatures down to -260°C.
- If your primary focus is continuous high-heat operations: PTFE is reliable for constant use up to 260°C (500°F), making it ideal for industrial ovens, seals, and bearings.
- If you need to handle brief temperature spikes: You can rely on PTFE for short excursions up to 290°C (554°F), but this should not be the normal operating condition.
- If your application involves high mechanical loads near the temperature limit: You must carefully evaluate the risk of material creep and consider a more rigid high-performance material.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE's remarkable thermal stability requires respecting its operational boundaries.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Condition | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| -260°C to -200°C (-436°F to -328°F) | Cryogenic / Short-term | Remains flexible, does not become brittle. |
| -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Continuous Service | Reliable, long-term operation with minimal degradation. |
| Up to 290°C (554°F) | Short-term Peak / Excursion | Brief exposure only; prolonged heat causes degradation. |
| 327°C (621°F) | Melting Point | Material loses mechanical integrity; not for operation. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Environments?
KINTEK specializes in precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components that excel in extreme thermal conditions. Whether your application is in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise ensures your parts perform reliably from deep cryogenics to high heat.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing the material integrity and dimensional stability your critical processes demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific temperature and performance requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss



















