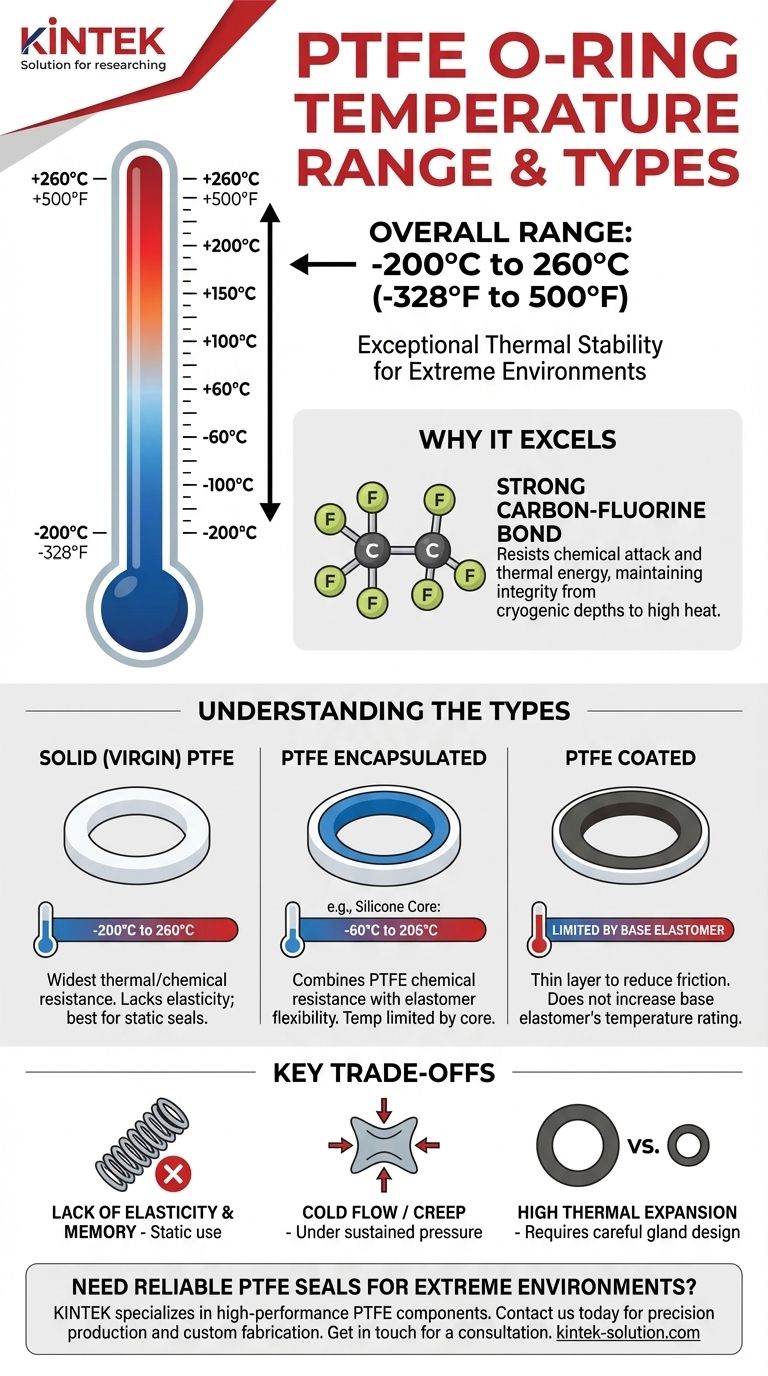
In short, PTFE O-rings operate reliably within an exceptionally wide temperature range, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). This outstanding thermal stability allows them to function in cryogenic conditions and high-heat environments where nearly all standard elastomers would fail. However, the precise operational limit depends heavily on the specific construction of the O-ring.
The critical takeaway is that not all "PTFE" O-rings are the same. The headline temperature range applies to solid PTFE, but the choice between solid, coated, or encapsulated versions dictates the true operational limits and mechanical properties for your specific application.

Why PTFE Excels in Extreme Temperatures
The performance of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is rooted in its fundamental molecular structure. Understanding this provides context for its impressive capabilities.
The Stability of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE consists of a chain of carbon atoms completely surrounded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry.
This immense bond strength makes the material exceptionally non-reactive and thermally stable. It simply takes a great deal of energy to disrupt these bonds, whether from chemical attack or thermal vibration.
Performance at Cryogenic Temperatures
Unlike most elastomers that become hard and brittle at low temperatures, PTFE retains a useful degree of flexibility and toughness even at cryogenic levels approaching -200°C (-328°F).
This property makes it a go-to material for sealing applications in aerospace, space exploration, and liquefied natural gas (LNG) processing.
Stability Under High Heat
At the upper end of the spectrum, PTFE maintains its structural integrity and sealing properties up to 260°C (500°F).
While most rubber compounds will begin to degrade, soften, or permanently set well below this temperature, PTFE remains solid and functional, making it ideal for automotive, industrial, and processing environments.
Understanding the Different Formats
The term "PTFE O-ring" can refer to several distinct products, each with a different performance profile. The temperature range is directly affected by this construction.
Solid (Virgin) PTFE O-Rings
These O-rings are machined from 100% pure PTFE stock. They offer the widest possible temperature and chemical resistance attributed to the material.
The typical range of -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) is most accurate for this type. Their primary drawback is a lack of elasticity.
PTFE Encapsulated O-Rings
This design features an elastomer core (typically Silicone or FKM/Viton) inside a seamless jacket of PTFE. The goal is to combine the chemical resistance of PTFE with the flexibility and memory of rubber.
Crucially, the operational temperature range is limited by the elastomer core material. For example, an encapsulated O-ring with a silicone core may only be rated from -60°C to 205°C (-75°F to 400°F).
PTFE Coated O-Rings
These are standard elastomer O-rings that have a thin layer of PTFE applied to the surface. The coating primarily serves to reduce friction and prevent sticking, not to fundamentally increase the temperature rating.
The performance temperature of a coated O-ring is dictated entirely by its elastomer core material.
Key Trade-offs and Application Factors
Temperature is only one part of the equation. The unique physical properties of solid PTFE introduce critical design trade-offs that must be considered.
Lack of Elasticity and "Memory"
Solid PTFE is a rigid material. Unlike rubber, it does not rebound well after being compressed. This means it is generally suitable for static, face-seal applications only.
Once installed and compressed, it holds its shape and may not reseal effectively if disturbed.
Cold Flow or "Creep"
Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can slowly deform over time. This phenomenon, known as creep or cold flow, can lead to a loss of sealing force.
Proper gland design, with tight clearances that fully support the O-ring, is essential to mitigate this effect.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion compared to metals. In applications with wide temperature swings, the O-ring will expand and contract significantly.
The hardware and gland design must account for this dimensional change to ensure a reliable seal is maintained at both the low and high ends of the temperature range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct seal, match the material's properties to your primary operational need.
- If your primary focus is the absolute maximum temperature and chemical range: A solid (virgin) PTFE O-ring offers the best performance, but requires careful hardware design for a static, one-time seal.
- If your primary focus is elasticity and reliable sealing across pressure cycles: A PTFE encapsulated O-ring is a better choice, but you must verify that its temperature range (limited by the elastomer core) meets your needs.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in a dynamic application: A PTFE coated elastomer O-ring is the intended solution, with its temperature limits defined by the base rubber material.
Ultimately, understanding these material differences empowers you to select a seal based not just on a temperature number, but on the true mechanical demands of your system.
Summary Table:
| PTFE O-Ring Type | Typical Temperature Range | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Solid (Virgin) PTFE | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Widest chemical/thermal resistance; lacks elasticity |
| PTFE Encapsulated | Varies by core elastomer (e.g., Silicone: -60°C to 205°C) | Combines PTFE chemical resistance with rubber flexibility |
| PTFE Coated | Limited by base elastomer | Reduces friction; does not increase base temperature rating |
Need a PTFE seal that performs reliably in your extreme environment?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom O-rings, seals, liners, and labware. Whether your application operates in the cryogenic depths of semiconductor manufacturing or the high-heat demands of industrial processing, our precision production and custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get a seal engineered for your exact thermal and mechanical requirements.
Contact us today to discuss your project and let our experts help you select or design the ideal PTFE solution. Get in touch via our contact form for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















