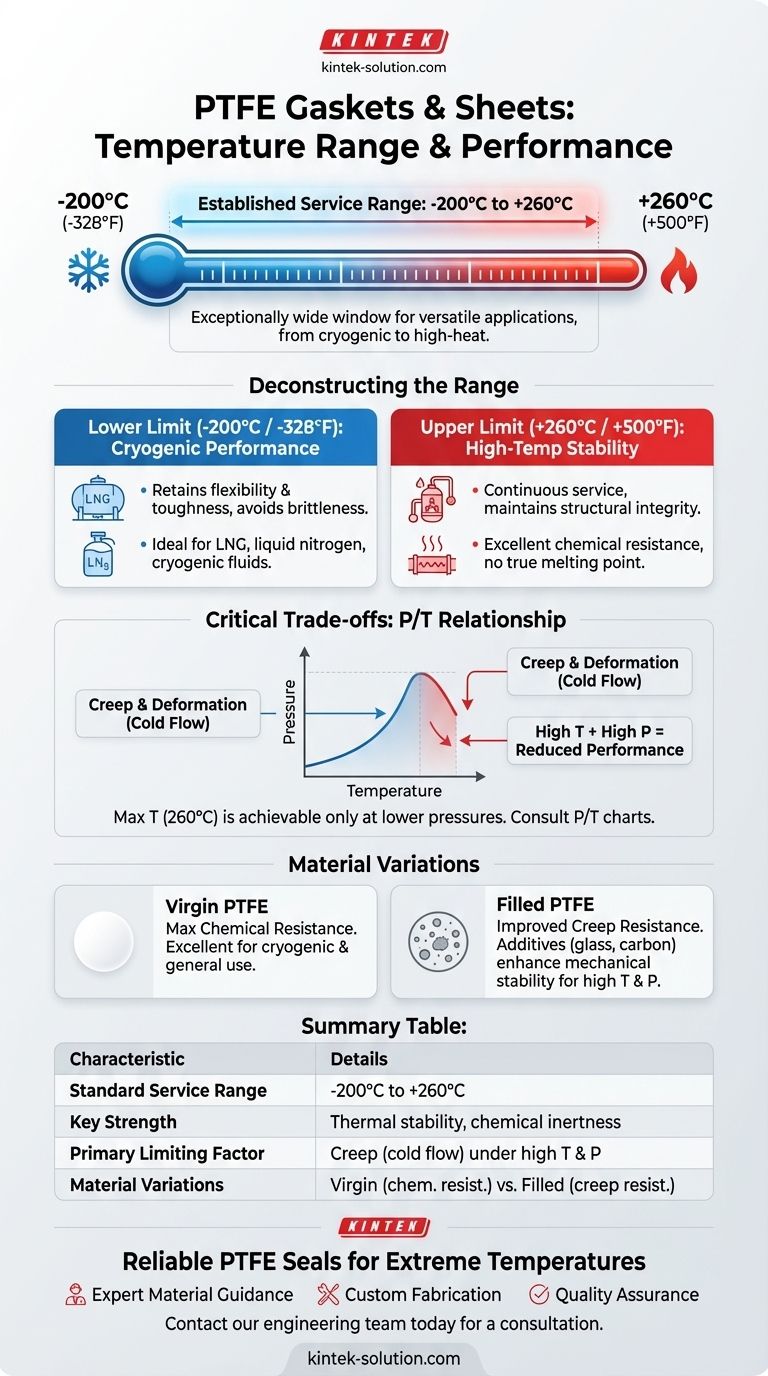
The established service temperature range for PTFE gaskets and sheets is generally between -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). This exceptionally wide operational window makes PTFE a highly versatile material, suitable for both extreme cryogenic applications and high-heat industrial processes where chemical inertness is paramount.
While PTFE's temperature rating is a key strength, its true performance depends on the interplay of heat, pressure, and mechanical stress. The material's usable temperature in a specific application may be lower than its stated maximum, especially under high mechanical loads.

Deconstructing the PTFE Temperature Range
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer known for its remarkable thermal stability. Its molecular structure allows it to function reliably where many other materials would fail.
The Upper Limit: Stability at High Temperatures
PTFE provides continuous service up to +260°C (+500°F).
Unlike many plastics, PTFE does not have a true melting point. At this upper temperature limit, it maintains its structural integrity and exceptional chemical resistance, making it ideal for gaskets in chemical reactors, hot fluid lines, and other demanding environments.
The Lower Limit: Performance in Cryogenic Conditions
PTFE remains functional at temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F).
While many materials become extremely brittle and fracture at such low temperatures, PTFE retains a degree of flexibility and toughness. This makes it a reliable choice for sealing applications involving liquefied natural gas (LNG), liquid nitrogen, and other cryogenic fluids.
Why This Range Matters for Industry
The ability to operate across a nearly 500°C spectrum makes PTFE a problem-solving material in numerous sectors.
It is specified for applications with extreme temperature fluctuations, from food processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing to metallurgy and chemical processing, where it must withstand aggressive fluids at various temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Limits
A material's datasheet temperature range is an ideal figure. In practice, operational conditions introduce critical trade-offs that must be considered for a successful and safe seal.
Creep and Deformation Under Load
PTFE is a relatively soft material, and its primary mechanical weakness is creep, or cold flow.
As temperature increases toward the upper limit, PTFE softens further, making it more susceptible to deforming under the compressive load of a flange. This can lead to a loss of sealing pressure and potential leaks over time.
The Impact of Pressure
The combination of high temperature and high pressure is the most significant limiting factor.
A gasket's ability to withstand high temperatures is reduced as system pressure increases. This relationship, often illustrated in a P/T diagram, is crucial for engineering safe and reliable sealed joints. The maximum service temperature of 260°C is only achievable at lower pressures.
Variations in PTFE Materials
Not all PTFE is the same. The +260°C figure applies to virgin PTFE.
Many gaskets use filled PTFE, where materials like glass, carbon, or graphite are added to improve properties like creep resistance and dimensional stability. While these fillers enhance mechanical performance, they can sometimes slightly alter the material's chemical resistance or absolute temperature ceiling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To ensure reliability, evaluate your specific operational conditions against the material's properties.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sealing: Select a filled PTFE for superior creep resistance and always consult a P/T chart to ensure the material is suitable for your specific combination of pressure and temperature.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance: Virgin PTFE is an excellent choice, but ensure your flange design accounts for the material's increased stiffness and thermal contraction at extreme cold.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical resistance with moderate temperatures: Standard virgin PTFE provides an unmatched balance of chemical inertness and a wide, reliable service temperature range for general industrial use.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's performance beyond a single number is the key to leveraging its full potential in your design.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Standard Service Range | -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F) |
| Key Strength | Exceptional thermal stability and chemical inertness across a wide range |
| Primary Limiting Factor | Creep (cold flow) under high temperature and pressure |
| Material Variations | Virgin PTFE for maximum chemical resistance; Filled PTFE for improved creep resistance |
Need a Reliable PTFE Seal for Extreme Temperatures?
Selecting the right PTFE component is critical for safety and performance in demanding environments. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, gaskets, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Expert Material Guidance: Help you choose between virgin or filled PTFE based on your specific temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure requirements.
- Custom Fabrication: From rapid prototypes to high-volume production runs, ensuring a perfect fit and function.
- Quality Assurance: Precision production that you can rely on for your most critical applications.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















