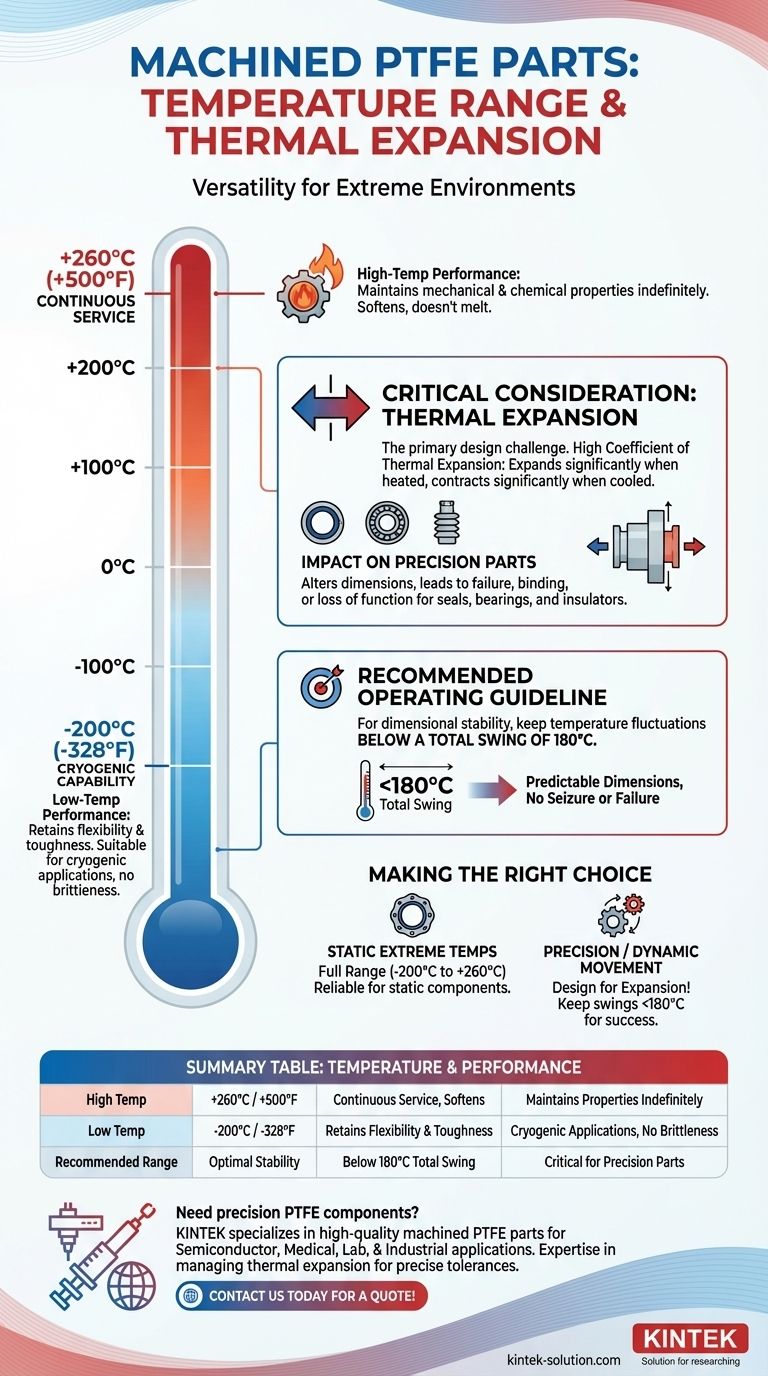
For machined parts, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) can operate within a remarkably wide temperature range, from as low as -200°C (-328°F) up to a continuous service temperature of +260°C (+500°F). This makes it one of the most versatile polymers for extreme thermal environments.
While PTFE's absolute temperature range is impressive, the most critical factor for engineering success is managing its high rate of thermal expansion. This property, more than the temperature limits themselves, dictates how a part must be designed.

The Full Operating Spectrum of PTFE
PTFE's unique molecular structure gives it one of the widest operating temperature ranges of any polymer. It maintains its core properties at temperatures that would cause most other plastics to become brittle or melt.
High-Temperature Performance
The upper limit of +260°C (+500°F) is a continuous service temperature. This means a PTFE component can operate at this temperature indefinitely without significant degradation of its mechanical or chemical properties. It will not melt, but rather softens above this point.
Cryogenic Capabilities
At the low end, PTFE remains functional down to approximately -200°C (-328°F). Unlike many materials that become extremely brittle at such low temperatures, PTFE retains a degree of flexibility and toughness, making it suitable for cryogenic applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Thermal Expansion
The primary challenge when designing with PTFE is not its temperature limit, but its dimensional response to temperature changes. This is a critical consideration for any machined part requiring precise tolerances.
What is Thermal Expansion?
PTFE has a very high coefficient of thermal expansion compared to metals and even other polymers. In simple terms, it expands significantly when heated and contracts significantly when cooled.
The Impact on Machined Parts
This expansion and contraction can alter the dimensions of a machined part beyond its specified tolerances. For components like seals, bearings, or insulators, a change in size can lead to failure, binding, or loss of function.
The "Normal Use" Guideline
For applications where dimensional stability is crucial, it's recommended to keep temperature fluctuations below a total swing of 180°C. This guideline helps ensure the part's dimensions remain predictable and within the functional design tolerance, preventing issues like seizure in bushings or failure in dynamic seals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE requires you to consider not just the absolute temperature, but the operational demands of the part.
- If your primary focus is simple survival in extreme static temperatures: The full -200°C to +260°C range is a reliable guide for components like gaskets or static seals in a thermally stable environment.
- If your primary focus is high precision or dynamic movement: You must design for thermal expansion, making the guideline of keeping temperature swings below 180°C the more critical factor for success.
Understanding PTFE's thermal behavior is the key to successfully leveraging its exceptional temperature resistance in your design.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Performance Characteristics | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| High Temp: +260°C (+500°F) | Continuous service temperature; softens but doesn't melt | Maintains mechanical/chemical properties indefinitely |
| Low Temp: -200°C (-328°F) | Retains flexibility and toughness | Suitable for cryogenic applications without brittleness |
| Recommended Operating Range | Optimal for dimensional stability | Keep temperature swings below 180°C for precision parts |
Need precision PTFE components that perform reliably in extreme temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality machined PTFE parts (seals, liners, labware, and more) for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Our expertise in managing PTFE's thermal expansion ensures your components maintain precise tolerances across their entire operating range.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, delivering the precision and reliability your application demands.
Contact us today to discuss your specific temperature requirements and get a quote for your next PTFE project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















