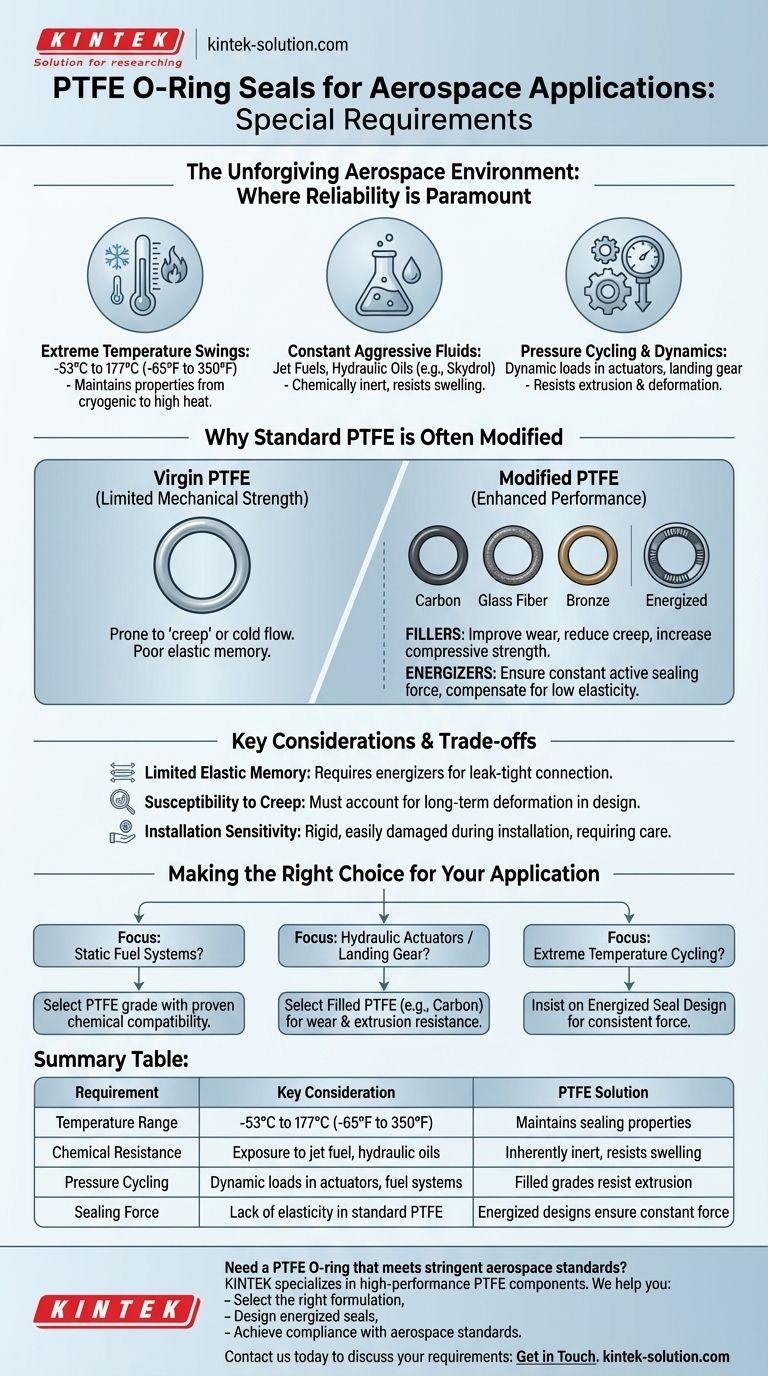
To be considered for aerospace applications, PTFE O-rings must meet a set of exceptionally stringent requirements that go far beyond standard industrial use. They must provide unwavering performance across extreme temperature ranges, from cryogenic cold to high engine heat, while resisting aggressive fluids like jet fuel and hydraulic oils. Above all, they must deliver absolute reliability, as seal failure in an aerospace context can have catastrophic consequences.
The core challenge for aerospace seals is not just enduring a single harsh condition, but performing flawlessly across a vast and rapidly changing spectrum of temperatures, pressures, and chemical exposures. Therefore, the special requirements for PTFE O-rings are less about the material itself and more about ensuring its integrity and sealing force are maintained under these volatile operational cycles.

The Unforgiving Environment of Aerospace
The unique demands placed on PTFE seals in aerospace are a direct result of the operational environment. A component must function perfectly on a hot runway, at a cruising altitude of -53°C, and within high-temperature engine or hydraulic systems.
From Ground to Altitude: Extreme Temperature Swings
An aircraft experiences dramatic temperature shifts, from ambient ground temperatures to the extreme cold of high altitudes. PTFE is specified for its incredible thermal stability.
A critical requirement is the ability to maintain sealing properties across a typical range of -53°C to 177°C (-65°F to 350°F). Unlike many elastomers that can become brittle and fail in deep cold, PTFE remains functional, preventing leaks in critical systems.
Constant Exposure to Aggressive Fluids
Aerospace systems rely on fluids that are often chemically aggressive, including various jet fuels, synthetic lubricating oils, and hydraulic fluids like Skydrol.
A primary requirement for any seal in these systems is chemical inertness. PTFE's molecular structure makes it resistant to swelling, degradation, or chemical attack, ensuring the purity of the fluid and the long-term integrity of the seal.
Pressure Cycling and System Dynamics
Seals in hydraulic actuators, landing gear, and fuel systems must endure constant pressure cycling as systems are activated and deactivated.
While PTFE has excellent compressive strength, the seal design must resist extrusion and deformation under repeated pressure loads. This ensures a consistent, leak-free seal throughout thousands of operational hours in components like flap actuators and brake systems.
Why Standard PTFE is Often Modified
While virgin PTFE provides the necessary thermal stability and chemical resistance, it often requires modification to meet the mechanical demands of aerospace applications.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength with Fillers
Standard PTFE can be prone to "creep" or "cold flow," where the material slowly deforms under sustained pressure. This is a significant risk in a critical sealing application.
To counteract this, PTFE is often blended with fillers like carbon, glass fiber, or bronze. These additives significantly improve wear resistance, reduce creep, and increase compressive strength, making the O-ring more robust for dynamic or high-pressure applications.
Compensating for Low Elasticity with Energizers
PTFE is a plastic, not an elastomer like rubber. It has poor elastic memory, meaning it does not spring back to its original shape effectively after being compressed.
To ensure a constant, active sealing force, especially at low temperatures where materials contract, PTFE seals are often energized. This is typically achieved with an internal component, such as a metal spring or a standard elastomer O-ring, that pushes the PTFE "jacket" firmly against the sealing surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Choosing PTFE involves recognizing its inherent properties and designing around its limitations. This objective understanding is key to successful implementation.
Limited Elastic Memory
The primary trade-off is PTFE's lack of elasticity. A PTFE O-ring will not provide a strong sealing force on its own, which is why energizers are so critical for ensuring a leak-tight connection across all operating conditions.
Susceptibility to Creep
Even in filled grades, creep remains a design consideration. Engineers must account for this long-term deformation in gland design and under sustained loads to prevent eventual leaks.
Installation Sensitivity
Compared to a flexible rubber O-ring, PTFE seals are relatively rigid. They can be damaged (nicked or scratched) during installation if proper care is not taken. A damaged seal surface can create a leak path, compromising the entire system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The selection of a PTFE O-ring in an aerospace context is a decision based on the specific demands of the subsystem.
- If your primary focus is static fuel systems: Prioritize a PTFE grade with proven chemical compatibility for long-term exposure to specific fuels and their additives.
- If your primary focus is hydraulic actuators or landing gear: Select a filled PTFE composition (e.g., carbon-filled) for superior wear resistance, low friction, and high extrusion resistance.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature cycling (e.g., APUs or engine components): Insist on an energized seal design to guarantee a consistent sealing force is maintained from cold start to peak operating temperature.
Ultimately, specifying a PTFE seal for aerospace is about ensuring predictable, reliable performance in an environment where there is no margin for error.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Key Consideration | PTFE Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -53°C to 177°C (-65°F to 350°F) | Maintains sealing properties from cryogenic cold to high heat |
| Chemical Resistance | Exposure to jet fuel, hydraulic oils (e.g., Skydrol) | Inherently inert, resists swelling and degradation |
| Pressure Cycling | Dynamic loads in actuators, landing gear, and fuel systems | Filled grades (carbon, glass) resist extrusion and deformation |
| Sealing Force | Lack of elasticity in standard PTFE | Energized designs (springs, elastomers) ensure constant sealing force |
Need a PTFE O-ring that meets stringent aerospace standards?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom O-ring seals, for the aerospace, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures your seals deliver absolute reliability in extreme environments.
We help you:
- Select the right PTFE formulation (virgin or filled) for chemical compatibility and mechanical strength.
- Design energized seals to maintain consistent sealing force across vast temperature swings.
- Achieve compliance with aerospace industry standards for safety and performance.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application requirements: Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















