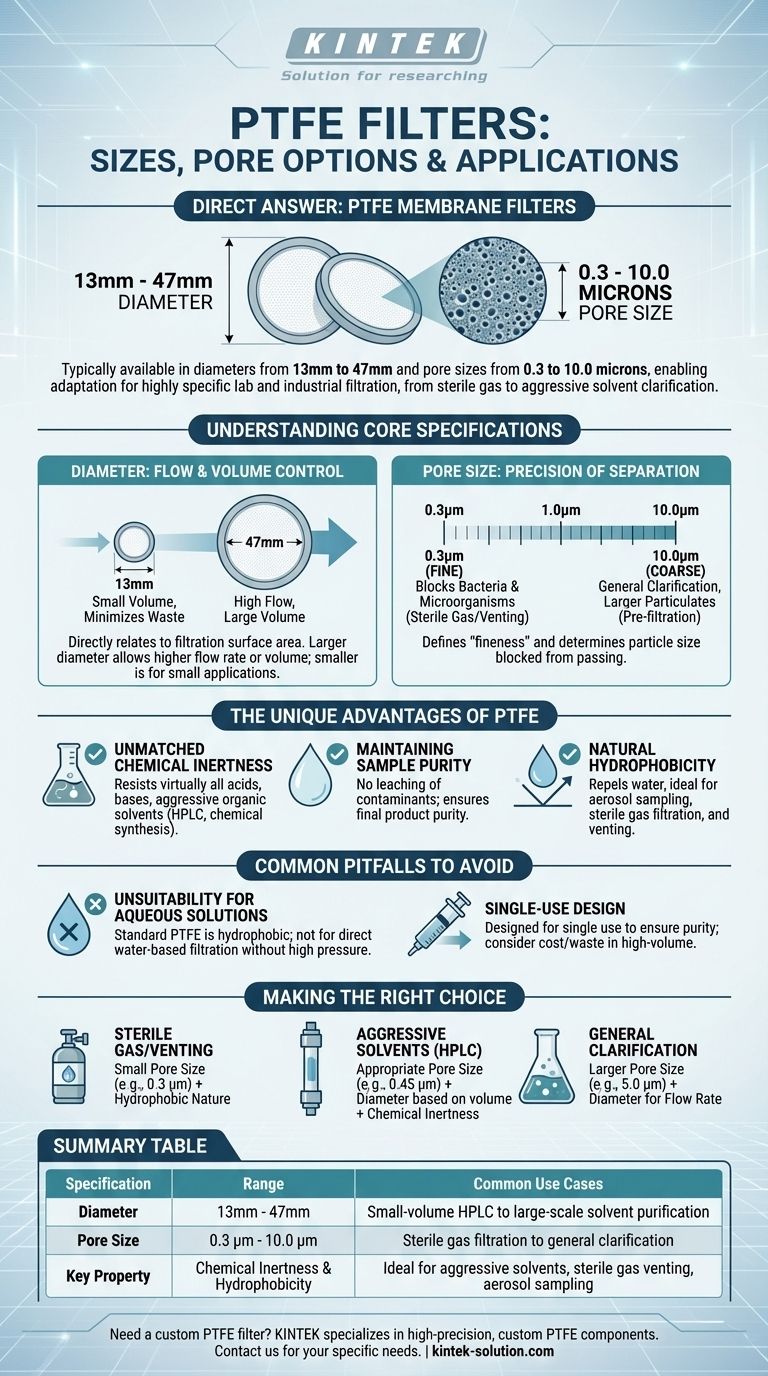
To be direct, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane filters are typically available in diameters ranging from 13mm to 47mm and with pore sizes from 0.3 to 10.0 microns. This range allows them to be adapted for a wide variety of highly specific laboratory and industrial filtration tasks, from sterilizing gases to clarifying aggressive chemical solvents.
The key takeaway is that the selection of a PTFE filter is a deliberate choice balancing physical size against filtration precision. The filter's diameter dictates flow rate and volume capacity, while its pore size determines the specific particles it can capture, all underpinned by PTFE's exceptional chemical resistance.

Understanding the Core Specifications
Choosing the correct PTFE filter requires understanding how its two primary specifications—diameter and pore size—directly impact your work. Each dimension serves a distinct purpose.
Diameter: The Flow and Volume Control
The diameter of the filter disc, typically between 13mm and 47mm, is directly related to the surface area available for filtration.
A larger diameter allows for a higher flow rate or the processing of a larger sample volume before the filter clogs. This is critical in applications like industrial water treatment or large-scale solvent purification.
A smaller diameter is suitable for small-volume applications, such as preparing individual HPLC samples, where minimizing waste and dead volume is a priority.
Pore Size: The Precision of Separation
Pore size, measured in microns (µm), defines the "fineness" of the filter. It determines the size of the particles that will be blocked from passing through the membrane.
Pore sizes in the 0.3 to 0.5 µm range are often used for sterile filtration of gases or venting applications, as they are small enough to block bacteria and other microorganisms.
Larger pore sizes, such as 5.0 to 10.0 µm, are used for general clarification or pre-filtration to remove larger particulates from a solution without significantly impeding flow.
The Unique Advantage of PTFE
The specifications are only part of the story. The reason PTFE is chosen for demanding applications is its inherent chemical nature.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is chemically inert and highly resistant to virtually all acids, bases, and aggressive organic solvents.
This makes it the ideal choice for filtering samples that would corrode or dissolve other types of membranes, such as those used in organic-based HPLC, chemical synthesis, and pharmaceutical processing.
Maintaining Sample Purity
Because PTFE is so unreactive, it will not leach contaminants into the filtrate. This ensures the purity of the final product, which is a non-negotiable requirement in food, beverage, and high-purity chemical industries.
Natural Hydrophobicity
PTFE membranes are naturally hydrophobic, meaning they repel water. This property is highly advantageous for applications like aerosol sampling, sterile gas filtration, and venting for fermentation tanks, as it allows air and gases to pass through while blocking aqueous moisture and contaminants.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While powerful, PTFE filters are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is crucial for successful application.
Unsuitability for Aqueous Solutions
The inherent hydrophobicity of standard PTFE makes it unsuitable for filtering water-based solutions directly. The high surface tension of water prevents it from passing through the small pores without applying extremely high pressure.
Single-Use Design
PTFE filters are typically designed for single use. While this ensures purity and prevents cross-contamination, it can be a factor in high-volume processes where cost and waste generation are significant concerns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application dictates the ideal combination of diameter and pore size.
- If your primary focus is sterile gas filtration or venting: Opt for a small pore size (e.g., 0.3 µm) to effectively block microbial contaminants, taking advantage of PTFE's hydrophobic nature.
- If your primary focus is filtering aggressive solvents for HPLC: Select a pore size appropriate for your column (often around 0.45 µm) and a diameter based on your sample volume, relying on PTFE's chemical inertness to prevent filter failure.
- If your primary focus is general clarification of a chemical: A larger pore size (e.g., 5.0 µm) may be sufficient, with the diameter chosen to achieve the desired flow rate for your process.
Ultimately, aligning the filter's specifications with your specific scientific or industrial goal is the key to achieving reliable and accurate results.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Range | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | 13mm - 47mm | Small-volume HPLC (13mm) to large-scale solvent purification (47mm) |
| Pore Size | 0.3 µm - 10.0 µm | Sterile gas filtration (0.3µm) to general clarification (5.0-10.0µm) |
| Key Property | Chemical Inertness & Hydrophobicity | Ideal for aggressive solvents, sterile gas venting, and aerosol sampling |
Need a custom PTFE filter for your specific chemical or process requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom membrane filters. Whether you need a unique diameter, a specific pore size, or a modified membrane for challenging applications, our team can fabricate a solution from prototype to high-volume production.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, ensuring every component meets the highest standards of chemical resistance and purity.
Contact us today to discuss your filtration needs and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















