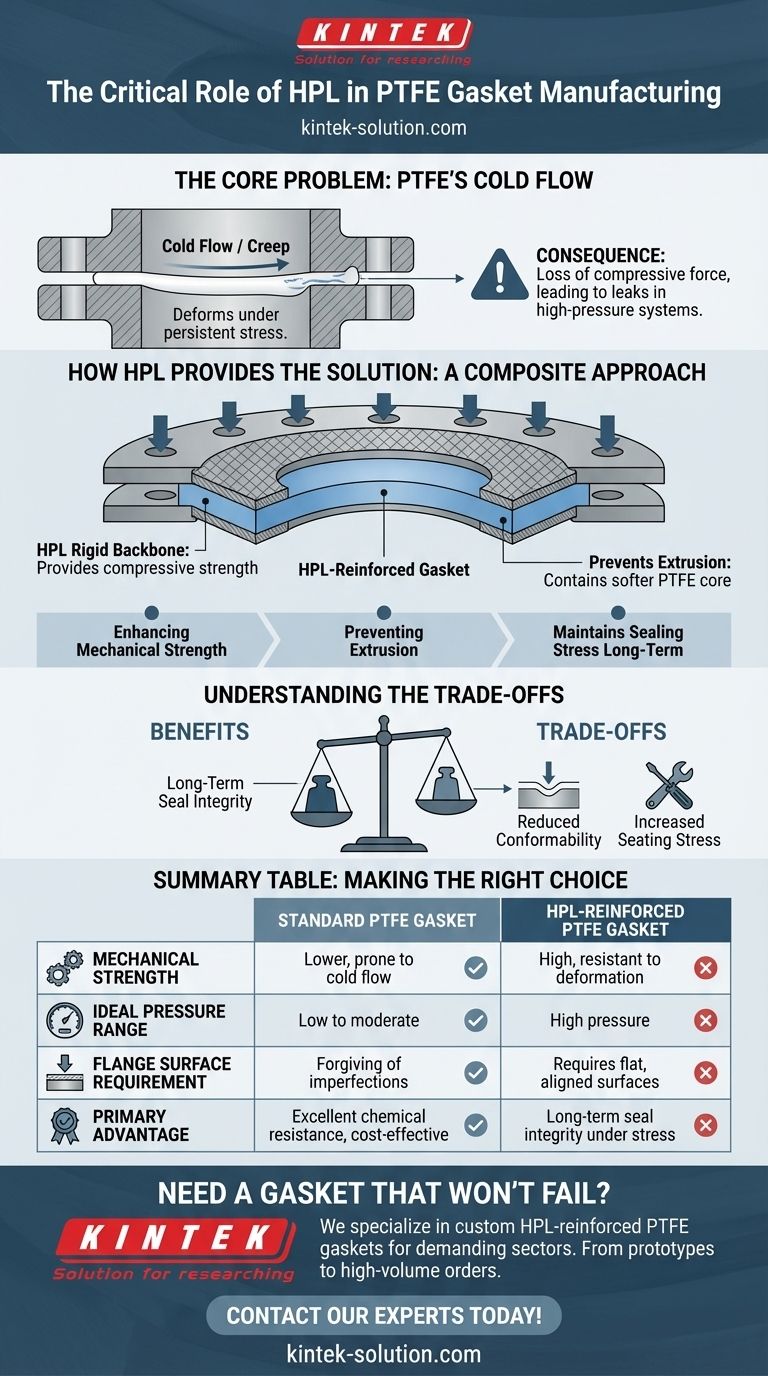
In PTFE gasket manufacturing, high-pressure laminate (HPL) serves as a critical reinforcing component applied to the gasket's surface. Its function is to enhance the gasket's mechanical strength, significantly improving its ability to create and maintain a reliable seal in high-pressure applications where standard PTFE might fail.
The fundamental role of HPL is to counteract PTFE's natural tendency to deform (or "cold flow") under load. By adding a rigid HPL layer, manufacturers create a composite gasket that combines PTFE's superior chemical resistance with the mechanical stability required for demanding sealing conditions.

The Core Problem: PTFE's Inherent Limitation
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is an exceptional sealing material due to its nearly universal chemical inertness and low-friction surface. However, it possesses one significant mechanical weakness that can compromise its performance under pressure.
Understanding Cold Flow (Creep)
Cold flow, also known as creep, is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under persistent mechanical stress. For PTFE, this means that when compressed between two flanges, it can slowly "flow" or squeeze out from its intended position over time.
The Consequence in High-Pressure Sealing
This deformation is a major problem in gasket applications. As the PTFE flows, the gasket thins, leading to a loss of compressive force (bolt load). This reduction in stress is the primary cause of eventual leaks in high-pressure or high-temperature systems.
How HPL Provides the Solution
Applying a high-pressure laminate layer to a PTFE gasket is a classic example of creating a composite material that leverages the strengths of its individual components to overcome their weaknesses.
A Composite Approach
The HPL-enhanced gasket is not a single material but a structured combination. It uses the PTFE core for its chemical resistance and conformability, while relying on the HPL for its structural integrity.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength
HPL is a dense, hard, and rigid material made from resin-impregnated paper fused under intense heat and pressure. When bonded to PTFE, it acts as a rigid backbone, providing the compressive strength that pure PTFE lacks.
Preventing Extrusion
The HPL layer serves as a physical barrier. It effectively contains the softer PTFE core, preventing it from extruding or flowing out of the flange gap, even under high bolt loads and system pressures. This preserves the gasket's thickness and ensures the sealing stress is maintained long-term.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While HPL enhancement offers a significant performance boost, it's important to recognize the trade-offs that come with creating a more rigid gasket.
Reduced Conformability
A stiffer gasket is less forgiving of flange imperfections. It may not seal as effectively on slightly warped, scratched, or misaligned flange surfaces compared to a softer, pure PTFE gasket.
Increased Seating Stress
The added rigidity often means that higher initial bolt torque is required to properly compress the gasket and create an effective seal. The system must be capable of providing this higher seating stress.
Environmental Considerations
While the PTFE core provides the primary chemical barrier to the fluid being sealed, the exposed outer edge of the HPL must be compatible with the external operating environment, which could include atmospheric chemicals or wash-down solutions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the material's properties to the system's demands.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals in low-pressure systems: A standard or filled PTFE gasket without HPL is likely sufficient, more cost-effective, and more forgiving of flange imperfections.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a long-term, leak-free seal in a high-pressure or fluctuating-temperature system: An HPL-enhanced PTFE gasket provides the necessary mechanical stability to prevent cold flow and ensure operational reliability.
Ultimately, integrating HPL transforms a standard PTFE gasket into a high-performance sealing solution engineered for the most demanding industrial environments.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Standard PTFE Gasket | HPL-Reinforced PTFE Gasket |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Lower, prone to cold flow | High, resistant to deformation |
| Ideal Pressure Range | Low to moderate | High pressure |
| Flange Surface Requirement | Forgiving of imperfections | Requires flat, aligned surfaces |
| Primary Advantage | Excellent chemical resistance, cost-effective | Long-term seal integrity under stress |
Need a gasket that won't fail under pressure?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom HPL-reinforced gaskets for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production ensures your gaskets deliver reliable sealing, preventing costly downtime and leaks in critical applications.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution engineered for your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















