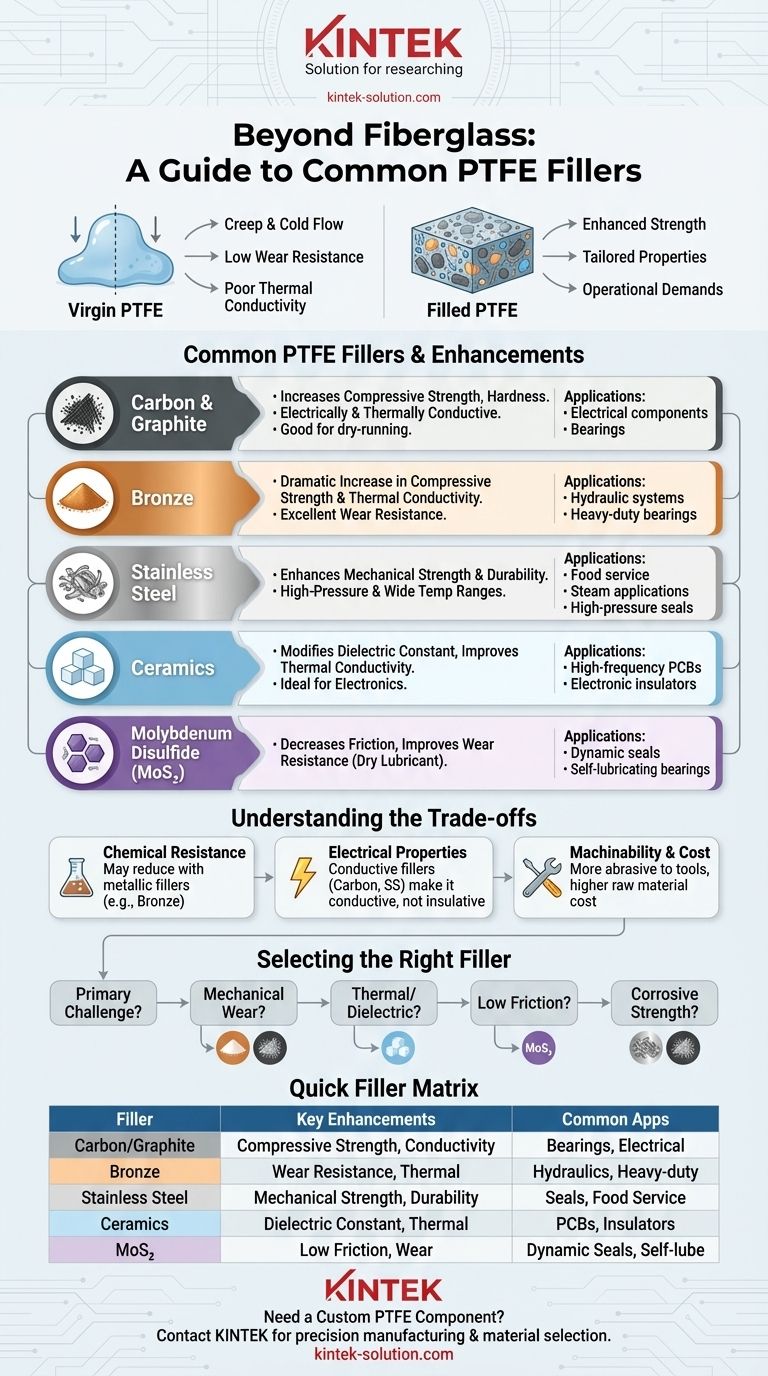
Beyond the commonly used fiberglass, the most prevalent filler materials for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) include carbon, metals like bronze and stainless steel, ceramics, and lubricants such as molybdenum disulfide. These additives are not interchangeable; each one is selected to systematically enhance specific mechanical, thermal, or electrical properties that pure, or "virgin," PTFE lacks on its own.
The choice of a PTFE filler is a deliberate engineering decision to target specific performance weaknesses. While virgin PTFE is chemically inert and has a low coefficient of friction, it is mechanically soft and prone to deformation, making fillers essential for demanding applications.

Why Fill PTFE in the First Place?
The Limitations of Virgin PTFE
Virgin PTFE is an exceptional material known for its extreme chemical resistance and very low friction. However, it is also mechanically soft.
Under load, pure PTFE is susceptible to creep, or cold flow, where the material slowly deformes. It also has poor thermal conductivity and relatively low wear resistance.
The Role of Fillers
Fillers are added to the PTFE matrix to create a composite material with enhanced properties. They act as a reinforcement that improves hardness, compressive strength, and wear resistance.
By selecting the right filler, an engineer can tailor a PTFE compound to a precise set of operational demands, such as high pressure, thermal cycling, or electrical performance.
A Guide to Common PTFE Fillers
Each filler imparts a unique set of characteristics to the base PTFE material. The percentage of filler used, typically between 5% and 40% by weight, also plays a critical role in the final properties.
Carbon & Graphite
Carbon, often in the form of powder or fiber, significantly increases compressive strength and hardness. It provides good thermal conductivity and is electrically conductive.
Graphite, a form of carbon, is often added alongside carbon to lower the coefficient of friction and improve wear characteristics, particularly in dry-running applications.
Metallic Fillers (Bronze & Stainless Steel)
Bronze is a popular filler that dramatically increases compressive strength and thermal conductivity, making it excellent for heat dissipation. It provides exceptional wear resistance, making it a common choice for hydraulic systems.
Stainless steel powder enhances the mechanical strength and durability of PTFE. It is particularly useful for applications requiring high-pressure and wide temperature ranges, such as in food service or steam applications.
Ceramic Fillers
Ceramics are primarily used to modify electrical properties, specifically the dielectric constant. They also provide higher thermal conductivity compared to virgin PTFE.
This makes ceramic-filled PTFE a foundational material for high-frequency printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other electronic insulators where signal integrity and heat management are critical.
Lubricants (Molybdenum Disulfide - MoS₂)
Often called "Moly," molybdenum disulfide is a dry lubricant. It is added to PTFE to decrease friction and improve wear resistance.
MoS₂ is often used in combination with other fillers to create a material with excellent self-lubricating properties for dynamic seals and bearings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is not without compromise. Enhancing one property often comes at the expense of another, a crucial consideration for any design.
Impact on Chemical Resistance
One of virgin PTFE's most valued traits is its near-universal chemical inertness. Adding metallic fillers like bronze can reduce this resistance, making the compound unsuitable for certain corrosive environments.
Altered Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. The addition of conductive fillers like carbon or stainless steel fundamentally changes this property, making the material electrically conductive and unsuitable for insulation purposes.
Machinability and Cost
Filled PTFE grades can be more abrasive than virgin PTFE, leading to faster tool wear during machining. The fillers themselves also add to the raw material cost.
Selecting the Right Filler for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated entirely by the primary challenge you need the material to overcome.
- If your primary focus is mechanical wear and load-bearing: Bronze or carbon-filled grades offer the best combination of compressive strength and durability.
- If your primary focus is thermal management and dielectric control: Ceramic-filled PTFE is the industry standard for high-frequency electronics.
- If your primary focus is low friction in dynamic seals: Molybdenum Disulfide (often combined with other fillers) provides essential self-lubricating properties.
- If your primary focus is strength in corrosive or pure environments: Stainless steel or carbon are superior choices over fillers like bronze.
By understanding the specific function of each filler, you can select a PTFE compound engineered precisely for your application's demands.
Summary Table:
| Filler Material | Key Properties Enhanced | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon/Graphite | Compressive strength, hardness, thermal & electrical conductivity | Electrical components, bearings |
| Bronze | Compressive strength, wear resistance, thermal conductivity | Hydraulic systems, heavy-duty bearings |
| Stainless Steel | Mechanical strength, durability, corrosion resistance | Food service, steam applications, high-pressure seals |
| Ceramics | Dielectric constant, thermal conductivity | High-frequency PCBs, electronic insulators |
| Molybdenum Disulfide | Lower friction, improved wear resistance | Dynamic seals, self-lubricating bearings |
Need a Custom PTFE Component for Your Specific Application?
Selecting the right filler is critical for performance. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We work with you to select the optimal filled PTFE compound and provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your component meets exact mechanical, thermal, and chemical requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What temperature range can Teflon (PTFE) balls withstand? -200°C to +260°C Performance Guide
- What factors determine the different grades of PTFE balls available? Select the Right Grade for Your Application
- What are the key chemical properties of PTFE balls? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability
- Why are PTFE balls particularly suitable for high-performance applications? Key Properties & Selection Guide
- What are the overall advantages of using PTFE balls in fluid management systems? Enhance Reliability & Efficiency



















