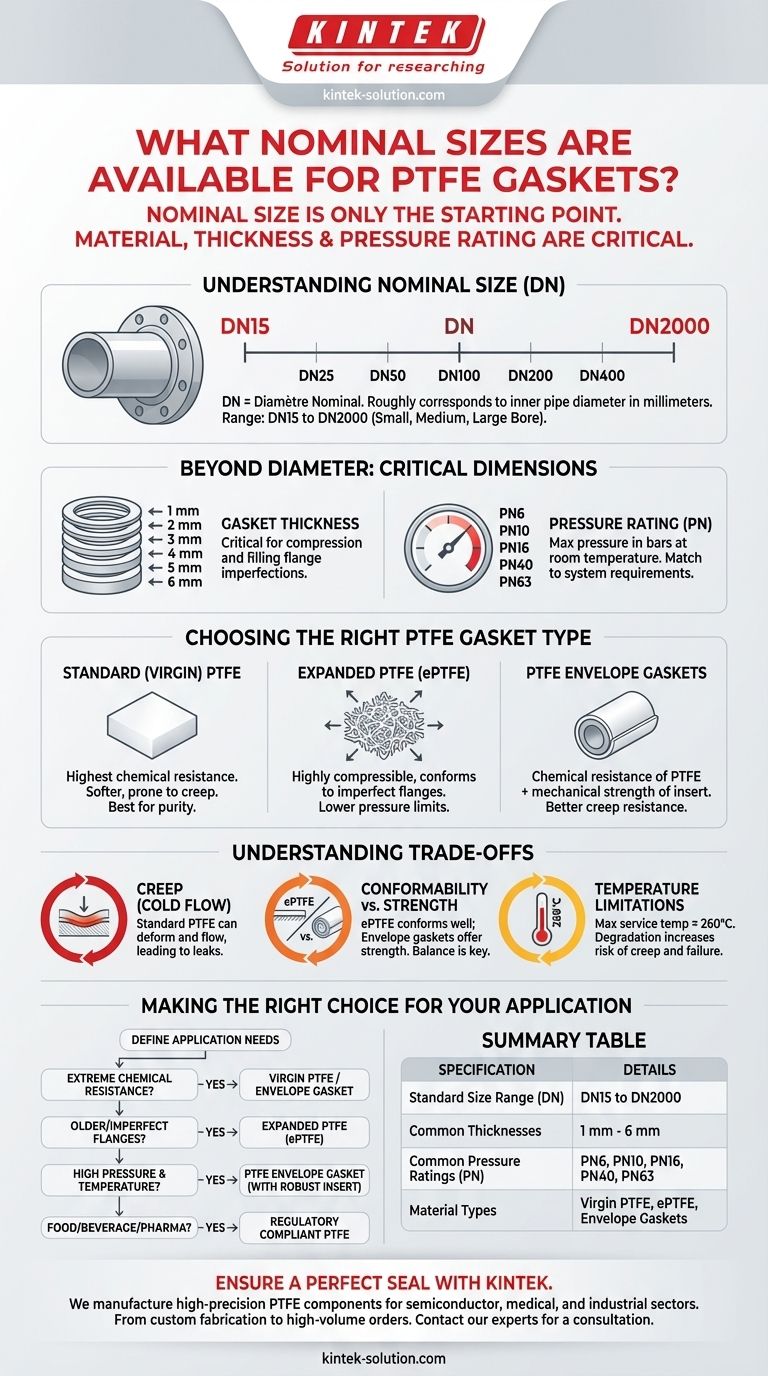
To answer your question directly, PTFE gaskets are available in a wide range of standard nominal sizes, typically from DN15 to DN2000. This includes common increments such as DN25, DN50, DN100, on up to very large diameter piping. However, selecting the right gasket involves more than just its diameter.
The nominal size of a PTFE gasket is only the starting point. A reliable and safe seal depends equally on matching the gasket's material type, thickness, and pressure rating to the specific demands of your application.

Understanding Nominal Size (DN)
The "DN" designation is a European standard that stands for "Diamètre Nominal." It refers to the nominal pipe size and is a convenient, standardized way to match components like pipes, valves, flanges, and gaskets.
What DN Represents
The DN value corresponds roughly to the inner diameter of the pipe in millimeters. For example, a DN50 gasket is designed to fit a flange on a pipe with a nominal bore of 50 mm.
Standard Size Range
PTFE gaskets are manufactured to fit all standard flange sizes. The full range typically includes:
- Small Bore: DN15, DN20, DN25, DN32, DN40, DN50
- Medium Bore: DN65, DN80, DN100, DN125, DN150, DN200
- Large Bore: DN250, DN300, DN350, DN400, up to DN2000
Beyond Diameter: Other Critical Dimensions
Specifying a gasket requires more than just the pipe size. Thickness and pressure rating are essential for performance and safety.
Gasket Thickness
Thickness is critical for the gasket's ability to compress and fill imperfections in the flange faces. Standard thicknesses include 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, and 6 mm, with custom dimensions also available.
Pressure Rating (PN)
The "PN" (Pressure Nominal) rating indicates the maximum pressure in bars that the gasket is designed to withstand at room temperature. It's crucial to match the gasket's PN rating to your system's requirements. Common ratings are PN6, PN10, PN16, PN40, and PN63.
Choosing the Right Type of PTFE Gasket
Not all PTFE is the same. The material construction dictates the gasket's mechanical properties and suitability for a given task.
Standard (Virgin) PTFE
This is pure, unfilled PTFE. It offers the highest chemical resistance but is softer and more prone to deformation under load. It's best for applications where purity and chemical inertness are the top priorities.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
This material is created by expanding virgin PTFE, which introduces a porous, fibrous structure. This makes the gasket much more compressible and conformable, ideal for sealing old, damaged, or irregular flange surfaces.
PTFE Envelope Gaskets
These gaskets feature a core insert material (like compressed fiber) wrapped in a thin "envelope" of PTFE. This construction combines the superior chemical resistance of the PTFE outer layer with the mechanical strength and rigidity of the insert.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is an exceptional sealing material, it's essential to understand its limitations to avoid failures.
The Challenge of Creep
The primary weakness of standard PTFE is creep, or cold flow. Under the compressive load of the flange bolts, the material can slowly deform and "flow" out of the joint, leading to a loss of bolt torque and potential leaks.
Balancing Strength and Conformability
An ePTFE gasket is excellent at conforming to rough surfaces but may not be suitable for extremely high pressures. A stronger PTFE envelope gasket provides better creep resistance but is less forgiving of flange imperfections.
Temperature Limitations
PTFE has an impressive temperature range, but its mechanical properties begin to degrade as it approaches its maximum service temperature of approximately 260°C (500°F). This can increase the risk of creep and sealing failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching its properties to your operational environment.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: A virgin PTFE or PTFE envelope gasket provides the most inert sealing surface.
- If you are dealing with older or imperfect flanges: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) offers the best conformability to ensure a tight seal.
- If your system involves high pressure and temperature: A PTFE envelope gasket with a robust insert provides the necessary mechanical strength and creep resistance.
- If you are in the food, beverage, or pharmaceutical industry: Ensure the PTFE material complies with the necessary regulatory standards for purity.
Ultimately, choosing the right gasket is a critical engineering decision that ensures the safety and integrity of your entire system.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Standard Size Range (DN) | DN15 to DN2000 (e.g., DN25, DN50, DN100, DN200) |
| Common Thicknesses | 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm |
| Common Pressure Ratings (PN) | PN6, PN10, PN16, PN40, PN63 |
| Material Types | Virgin PTFE, Expanded PTFE (ePTFE), PTFE Envelope Gaskets |
| Key Consideration | Nominal size is just the start; material and pressure rating are critical for a safe seal. |
Ensure a Perfect Seal for Your Application
Choosing the right PTFE gasket is critical for the safety and integrity of your system. At KINTEK, we manufacture high-precision PTFE components, including seals, gaskets, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We can help you navigate the complexities of material selection—from chemical-resistant virgin PTFE to conformable ePTFE for imperfect flanges—and provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Get a reliable, high-performance solution tailored to your exact needs. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance



















