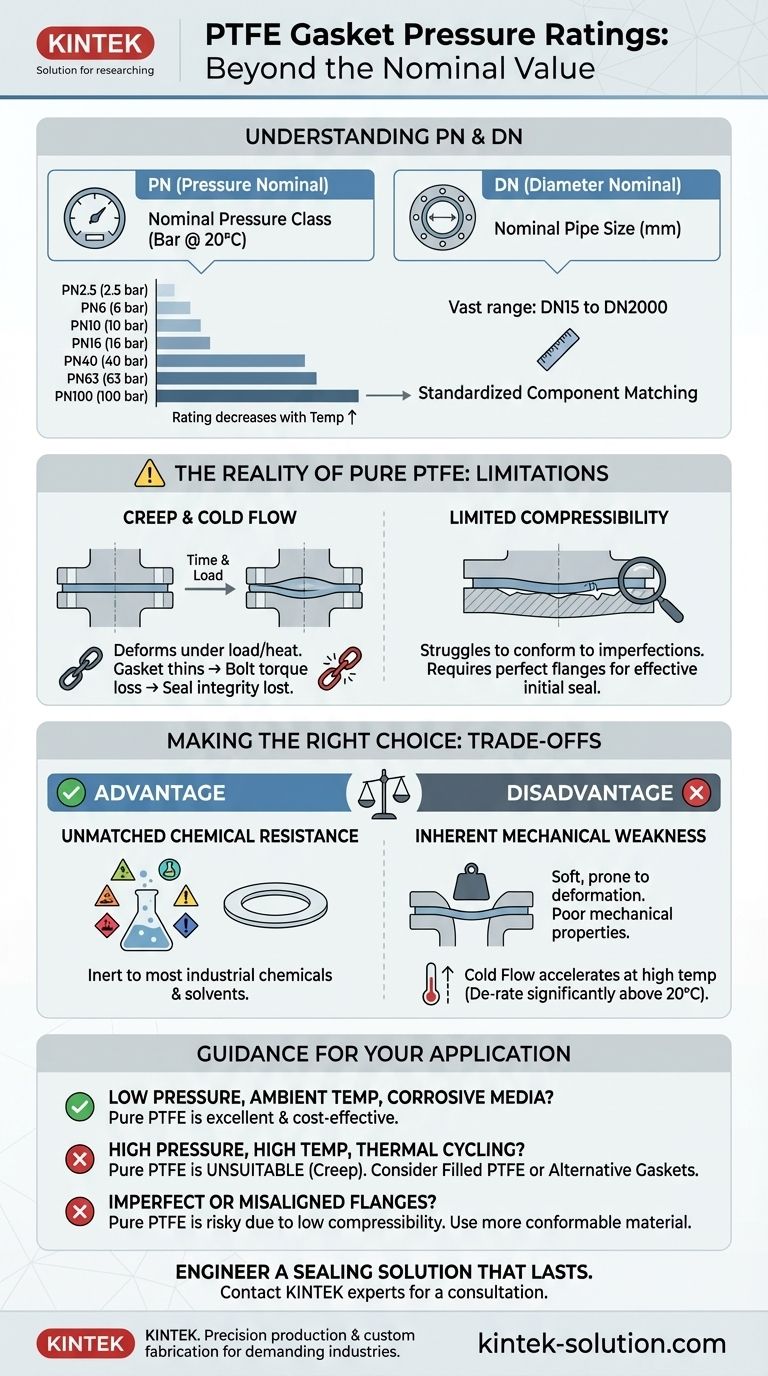
For PTFE gaskets, the most common nominal pressure ratings available are PN2.5, PN6, PN10, PN16, PN40, PN63, and PN100. These ratings, designated by "PN" (Pressure Nominal), indicate the approximate pressure in bars that the gasket can withstand at room temperature.
While standard pressure ratings provide a baseline, the true performance of a pure PTFE gasket is dictated by its significant mechanical weakness. Its tendency to deform under load and heat is the single most important factor to consider for ensuring a reliable, long-term seal.

What Do the Ratings Actually Mean?
To properly select a gasket, it's essential to understand the terminology. The ratings provide a standardized way to match components in a piping system.
Understanding PN (Pressure Nominal)
PN is a European standard designation that refers to the nominal pressure class. The number following "PN" indicates the maximum allowable pressure in bars at a reference temperature, typically 20°C (room temperature).
For example, a PN16 rated gasket is designed for a system with a maximum pressure of 16 bar at ambient temperature. It's critical to remember that this pressure rating decreases as the operating temperature increases.
Understanding DN (Diameter Nominal)
While your question focuses on pressure, you will always see a corresponding size rating. DN (Diameter Nominal) refers to the nominal pipe size in millimeters.
These gaskets are available in a vast range of sizes, from DN15 to DN2000, ensuring compatibility with standard pipe flanges.
Why Pressure Ratings Don't Tell the Whole Story
Relying solely on a PN rating for a pure PTFE gasket is a common and costly mistake. The material's inherent properties create significant limitations that are not captured by a simple pressure class.
The Problem of Creep and Cold Flow
Pure PTFE is a relatively soft material. When subjected to the compressive load of a bolted flange, it begins to slowly deform over time. This phenomenon is known as creep or cold flow.
This gradual deformation causes the gasket to thin out, leading to a loss of the initial bolt torque. As the clamping force diminishes, the seal's integrity is compromised.
Impact on Sealing Integrity
The loss of sealing stress due to cold flow is the primary failure mode for PTFE gaskets. It can eventually lead to leaks, especially in applications with pressure or temperature fluctuations.
This makes pure PTFE a poor choice for high-pressure scenarios or critical applications where a long-term, maintenance-free seal is required.
Limited Compressibility
Unlike more resilient materials, PTFE has limited compressibility. This means it struggles to conform to and fill in minor imperfections on flange surfaces.
If the flanges are not perfectly flat, smooth, and parallel, a pure PTFE gasket may not be able to create an effective initial seal, regardless of the pressure rating.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PTFE Gaskets
Choosing any gasket material involves balancing its strengths and weaknesses against the demands of the application.
The Advantage: Unmatched Chemical Resistance
The primary reason for selecting PTFE is its extraordinary resistance to chemical attack. It is inert to almost all industrial chemicals and solvents, making it the default choice for highly corrosive media.
The Disadvantage: Inherent Mechanical Weakness
This chemical inertness comes at a significant cost: poor mechanical properties. The same molecular structure that makes PTFE non-reactive also makes it soft and prone to deformation under physical stress.
The Critical Temperature Factor
The tendency for cold flow accelerates dramatically with increasing temperature. A PN rating established at 20°C is not a reliable indicator of performance at 100°C. You must always de-rate the gasket's pressure-holding capability as service temperature rises.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use the operating conditions of your system as the ultimate guide for material selection.
- If your primary focus is containing highly corrosive media at low pressure and ambient temperature: A pure PTFE gasket is often an excellent and cost-effective choice.
- If your system involves high pressures, high temperatures, or significant thermal cycling: Pure PTFE is likely unsuitable and will fail due to creep. You should strongly consider filled PTFE (e.g., glass- or carbon-filled) or alternative materials like spiral wound gaskets.
- If your flanges have minor imperfections or are difficult to align: The low compressibility of pure PTFE makes it a risky option; a more conformable gasket material is recommended.
Ultimately, selecting the right gasket requires matching the material's capabilities to the specific mechanical and chemical demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Common PTFE Gasket Pressure Ratings (PN) | Approx. Pressure (bar at 20°C) |
|---|---|
| PN2.5 | 2.5 bar |
| PN6 | 6 bar |
| PN10 | 10 bar |
| PN16 | 16 bar |
| PN40 | 40 bar |
| PN63 | 63 bar |
| PN100 | 100 bar |
Don't let gasket failure compromise your system. The nominal pressure rating is just the starting point. For a truly reliable seal, you need a partner who understands the mechanical limitations of PTFE and can provide a solution tailored to your specific pressure, temperature, and chemical requirements.
At KINTEK, we manufacture high-performance PTFE components—including seals, gaskets, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your gaskets perform reliably under your exact operating conditions.
Contact our experts today for a consultation on your specific application. Let's engineer a sealing solution that lasts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















