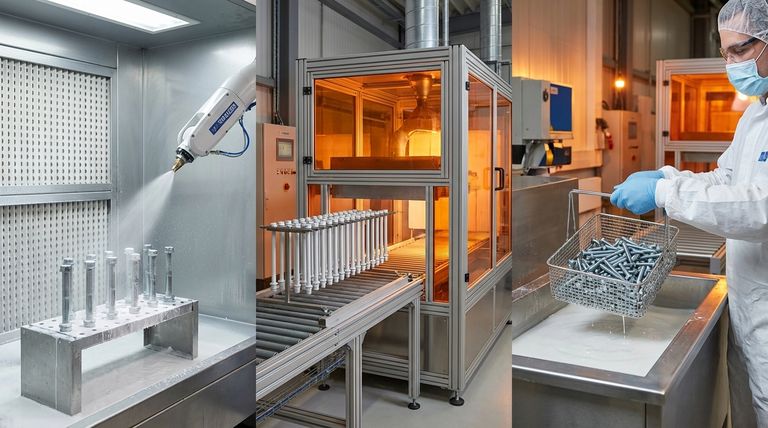
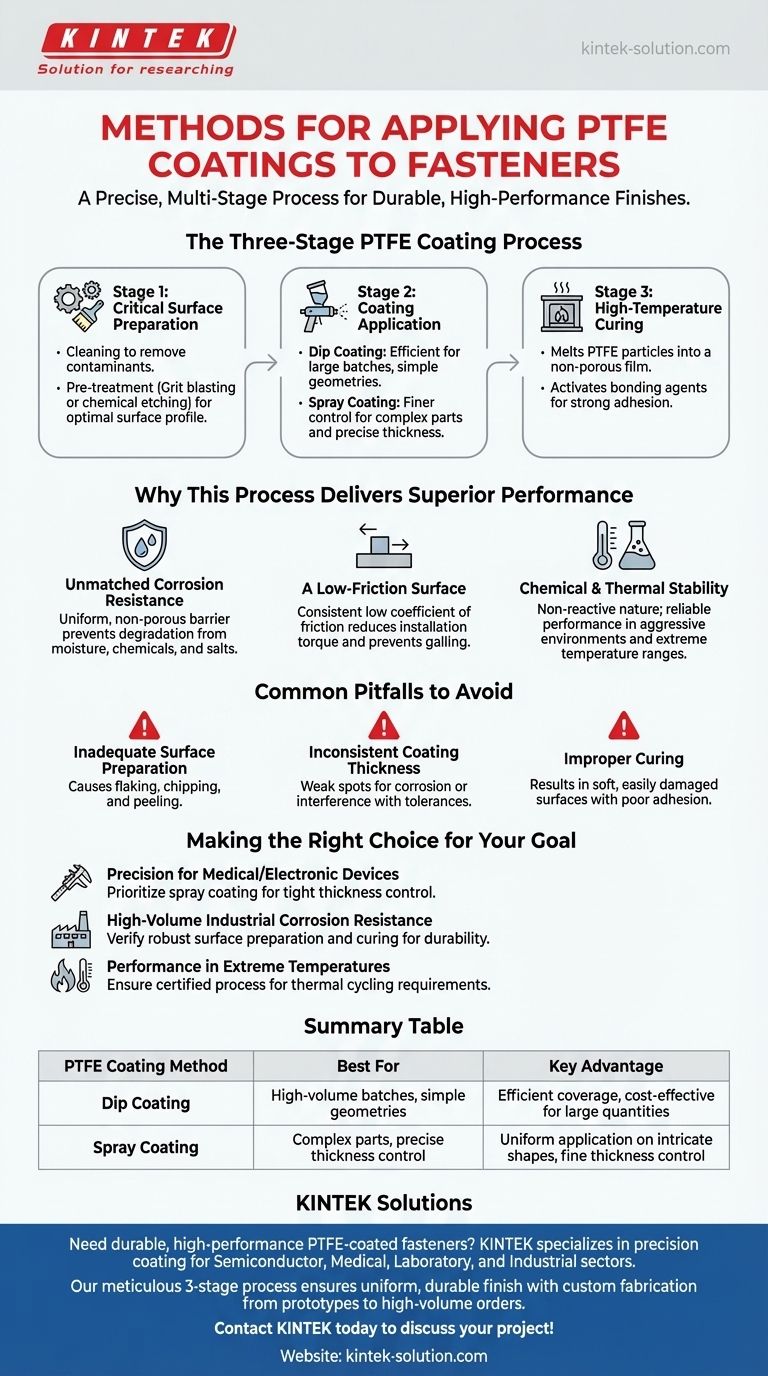
Applying PTFE coatings to fasteners is a precise, multi-stage process designed to create a durable, high-performance finish. The two primary application methods used are dip coating and spray coating, which are chosen based on the fastener's geometry and the required coating specifications. These methods are integrated into a larger manufacturing sequence that includes critical surface preparation and high-temperature curing to ensure the coating fully bonds to the fastener.
The effectiveness of a PTFE-coated fastener is determined not just by the application method, but by the quality of the entire process. Meticulous surface preparation and proper high-temperature curing are just as crucial as the coating application itself for achieving the desired corrosion resistance and low-friction properties.

The Three-Stage PTFE Coating Process
Achieving a uniform and durable PTFE coating involves more than simply applying the material. It is a controlled, three-part process where each stage is essential for the final performance of the fastener.
Stage 1: Critical Surface Preparation
Before any coating is applied, the fastener's surface must be impeccably clean and properly prepared. This involves cleaning to remove oils, grease, and other contaminants.
This is often followed by a pre-treatment step, such as grit blasting or chemical etching, which creates an optimal surface profile for the coating to mechanically adhere to.
Stage 2: Coating Application
Once the surface is prepared, the PTFE is applied using one of two primary industrial methods.
The choice between dip coating and spray coating depends on factors like the fastener's complexity, the required thickness, and production volume. Spraying allows for finer control over thickness, while dipping is efficient for coating large batches of parts.
Stage 3: High-Temperature Curing
After the coating is applied, the fasteners are cured in an oven at elevated temperatures. This critical step melts the PTFE particles, causing them to flow together and form a non-porous film.
More importantly, the heat activates bonding agents in the coating, creating a strong, permanent bond between the PTFE layer and the metal substrate of the fastener.
Why This Process Delivers Superior Performance
The structured application process is what unlocks the unique properties of PTFE, making these fasteners suitable for the most challenging environments.
Unmatched Corrosion Resistance
The uniform, non-porous layer created during curing acts as a complete barrier. This shields the underlying metal from corrosive agents like moisture, chemicals, and salts, preventing degradation and extending the fastener's service life.
A Low-Friction Surface
PTFE is known for its extremely low coefficient of friction. A properly applied coating ensures this property is consistent across all surfaces, reducing the torque needed for installation and preventing galling or seizing of threads.
Chemical and Thermal Stability
The non-reactive nature of PTFE means the coating remains stable when exposed to aggressive chemicals, solvents, and even bodily fluids in medical applications.
Furthermore, the curing process ensures the coating can perform reliably across a broad temperature range, making it ideal for applications with frequent or extreme temperature fluctuations.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While highly effective, the value of a PTFE coating is entirely dependent on the quality of its application. Poor process control can lead to premature failure.
Inadequate Surface Preparation
This is the most common point of failure. If the fastener surface is not properly cleaned and pre-treated, the coating will not adhere correctly, leading to flaking, chipping, or peeling under stress.
Inconsistent Coating Thickness
An uneven coating, often a result of poor application technique, can create weak spots where corrosion can begin. For threaded fasteners, excessive thickness can interfere with tolerances and prevent proper mating of nuts and bolts.
Improper Curing
If the fasteners are not cured at the correct temperature or for the required duration, the coating will not achieve full hardness or proper adhesion. This results in a soft, easily damaged surface that fails to provide the expected protection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When specifying or purchasing PTFE-coated fasteners, focus on the integrity of the entire process, not just the material itself.
- If your primary focus is precision for medical or electronic devices: Confirm the supplier uses a method, typically spray coating, that guarantees tight control over coating thickness to avoid interfering with thread tolerances.
- If your primary focus is high-volume corrosion resistance for industrial use: Verify that the manufacturer has robust quality controls for their surface preparation and curing stages, as these are critical for long-term durability in harsh environments.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: Ensure the coating process is certified to create a fully bonded and stable layer capable of withstanding your specific thermal cycling requirements.
Understanding the complete application process empowers you to specify and select fasteners that deliver true reliability in demanding conditions.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Coating Method | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Dip Coating | High-volume batches, simple geometries | Efficient coverage, cost-effective for large quantities |
| Spray Coating | Complex parts, precise thickness control | Uniform application on intricate shapes, fine thickness control |
Need durable, high-performance PTFE-coated fasteners?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision PTFE coating application for fasteners used in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our meticulous 3-stage process—including critical surface preparation, precise dip or spray coating, and high-temperature curing—ensures a uniform, durable finish that delivers unmatched corrosion resistance and a low-friction surface.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your fasteners meet exact specifications for performance and reliability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some other miscellaneous uses of Teflon? From Aerospace to Medical Devices
- Why might PTFE gaskets fail in sanitary applications? The Hidden Mechanical Flaws in a Chemically Perfect Material
- What size range do PTFE balls come in? A Guide from 3mm to 100mm
- What are the key properties of PTFE Teflon washers? Unlock Superior Chemical & Temperature Resistance
- How can the creep formation issue in PTFE gaskets be addressed? Ensure a Long-Term, Leak-Free Seal
- How do the non-stick properties of PTFE benefit impeller applications? Prevent Clogging & Boost Efficiency
- Which industries commonly use Teflon bushes? Solve Critical Engineering Challenges in Harsh Environments
- In what industries are PTFE balls commonly used for chemical applications? Ensure Purity and Chemical Resistance



















