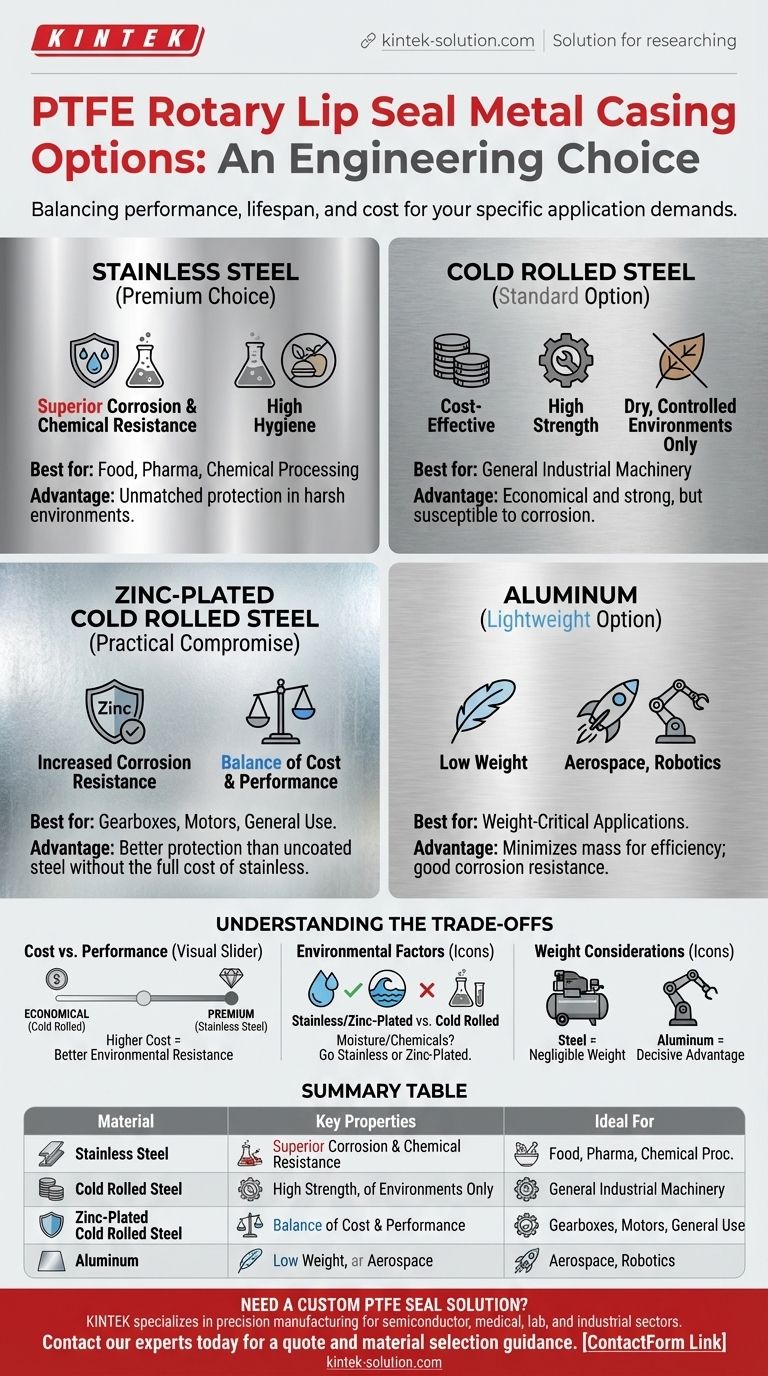
For PTFE rotary lip seals, the standard metal casing options available to a design engineer are stainless steel, cold rolled steel, zinc-plated cold rolled steel, and aluminum. The seal itself consists of a PTFE lip element, but the selection of the metal case that houses it is a critical design choice based on the specific application's demands.
The choice of a casing material is not arbitrary; it is a fundamental engineering decision that directly impacts the seal's performance, lifespan, and cost by balancing the need for corrosion resistance, weight, and budget within a specific operating environment.
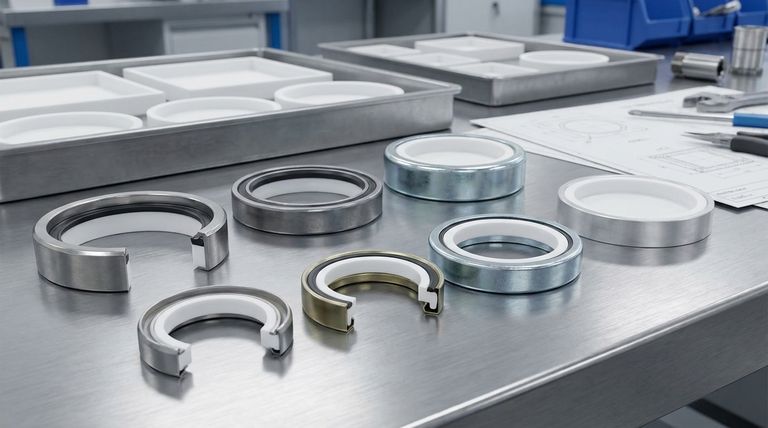

Deconstructing the Casing Materials
While the PTFE lip provides the sealing action, the metal casing provides structural integrity and facilitates installation. Each material option offers a distinct set of properties tailored for different conditions.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is the premium choice for seal casings. Its primary advantage is superior corrosion and chemical resistance.
This makes it the default option for applications with high-purity requirements or exposure to harsh substances. You will commonly find it in food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and chemical systems.
Cold Rolled Steel
Cold rolled steel represents the standard, most cost-effective option. It provides excellent strength and is suitable for a wide range of general industrial applications.
However, it offers minimal resistance to corrosion. It should only be used in controlled, dry environments where exposure to moisture or chemicals is not a concern.
Zinc-Plated Cold Rolled Steel
This material serves as a practical compromise between cost and performance. A layer of zinc plating is applied to a standard cold rolled steel case.
The zinc plating provides a significant increase in corrosion resistance compared to the uncoated version. This makes it a popular and durable choice for many industrial applications, including gearboxes and motors, that require more protection without the full cost of stainless steel.
Aluminum
The defining characteristic of aluminum is its low weight. It offers good corrosion resistance, particularly when compared to plain cold rolled steel.
Its primary use is in applications where minimizing mass is a critical design goal. This includes aerospace systems, robotics, and high-performance motors where every gram impacts overall efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right material requires a clear understanding of the compromises involved. The ideal choice for one application can be a point of failure in another.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct relationship between material cost and environmental resistance. Stainless steel is the most expensive option but provides the highest level of protection.
Cold rolled steel is the most economical, but its use is limited to non-corrosive environments. Zinc-plated steel and aluminum typically fall in the middle, offering a balance of price and capability.
Environmental Factors
The operating environment is the most critical factor. Constant exposure to water, saltwater, cleaning agents, or process chemicals will quickly degrade an unprotected cold rolled steel case.
For any application involving moisture or chemicals, stainless steel is the safest choice. Zinc-plated steel can be a viable alternative in less aggressive or intermittently wet conditions.
Weight Considerations
In static industrial machinery like heavy-duty compressors, the weight of the seal casing is negligible. The durability and cost of steel are the primary concerns.
However, in dynamic or mobile systems like aerospace actuators or robotic arms, the weight savings from aluminum can be a decisive advantage, justifying its potential extra cost over steel options.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the single most important constraint of your design.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance and hygiene: Choose stainless steel for its unmatched protection in demanding food, pharma, or chemical environments.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in a controlled environment: Choose standard cold rolled steel for general-purpose machinery where corrosion is not a risk.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and moderate corrosion protection: Choose zinc-plated cold rolled steel as a versatile and reliable upgrade for most industrial equipment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing weight: Choose aluminum for any application where mass is a critical performance metric, such as in aerospace or robotics.
Ultimately, matching the casing material to the operational reality of your equipment is key to ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
Summary Table:
| Casing Material | Key Properties | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Superior corrosion/chemical resistance, high hygiene | Food, Pharma, Chemical Processing |
| Cold Rolled Steel | Cost-effective, high strength | Dry, controlled industrial environments |
| Zinc-Plated Steel | Good corrosion resistance, cost-effective | General industrial use (gearboxes, motors) |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | Aerospace, robotics, high-performance motors |
Need a Custom PTFE Seal Solution?
Selecting the right metal casing is critical for seal performance and longevity. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom rotary lip seals for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We can help you navigate material selection and deliver a solution tailored to your specific environmental, weight, and budget requirements—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















