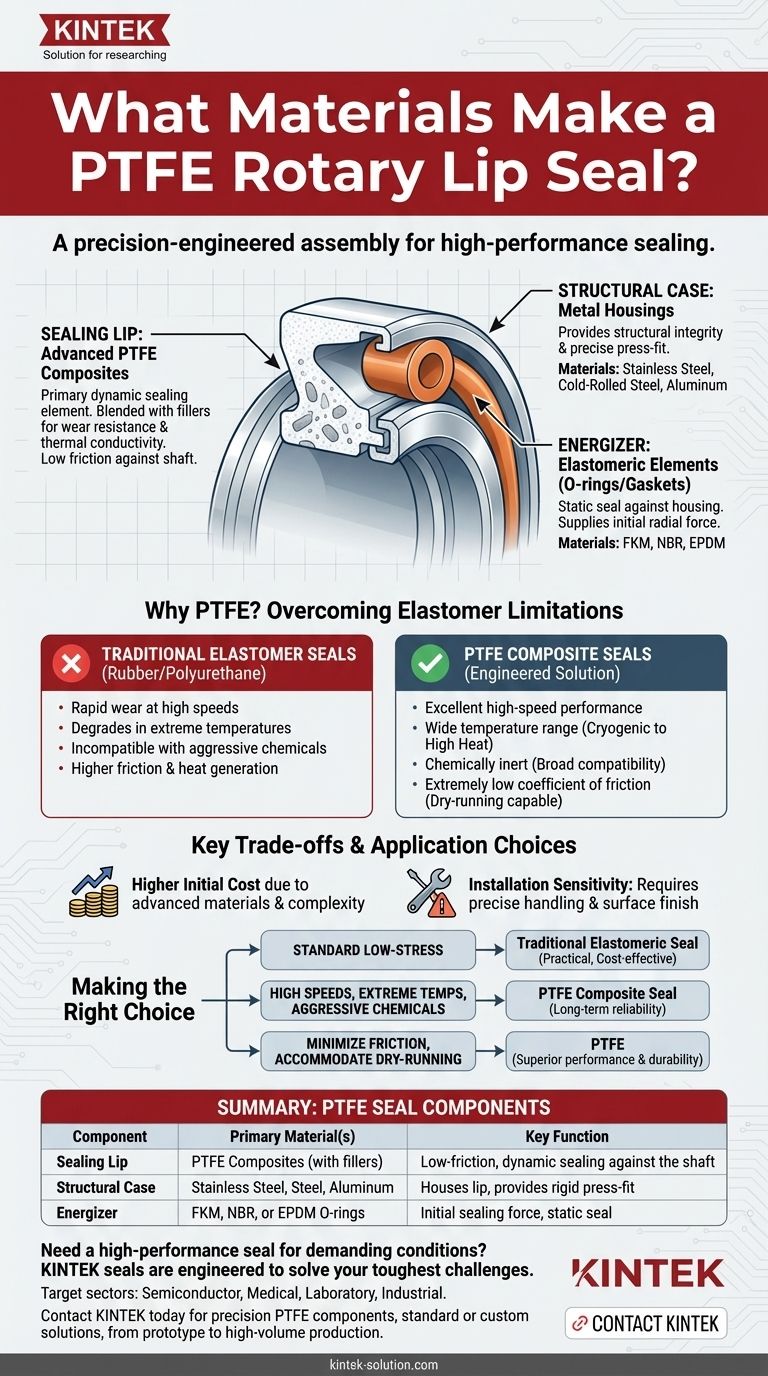
To be precise, a PTFE rotary lip seal is not made from a single material but is a carefully engineered assembly of components. The primary sealing element is a lip made from a PTFE composite, the housing is typically machined from metal, and an elastomeric O-ring is often included as an energizer. Each material is selected to perform a specific function within the seal's demanding operating environment.
The core reason for this multi-material design is to overcome the limitations of traditional rubber seals. A PTFE rotary seal is an engineered solution for applications involving high speeds, extreme temperatures, or aggressive chemicals where a standard elastomeric seal would quickly fail.

The Anatomy of a PTFE Seal: A Multi-Material System
A PTFE rotary seal's performance comes from the synergy between its distinct components. Understanding the role of each material is key to appreciating its design.
The Sealing Lip: Advanced PTFE Composites
The dynamic sealing lip, the part that contacts the rotating shaft, is made from Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
This is rarely pure PTFE. It is almost always a PTFE composite, meaning it's blended with fillers to enhance specific properties like wear resistance, thermal conductivity, or rigidity.
The Structural Case: Metal Housings
The PTFE lip is housed in a rigid metal case that provides structural integrity and allows for a precise press-fit into the equipment.
Common materials for this case include stainless steel, cold-rolled steel (often zinc-plated for corrosion resistance), and aluminum, chosen based on the application's chemical exposure and cost constraints.
The Energizer: Elastomeric Elements
Many PTFE seal designs incorporate an elastomeric O-ring or gasket. This component serves as a static seal against the housing and provides the initial radial force needed to press the PTFE lip against the shaft.
Typical materials for this energizing element include fluoroelastomer (FKM), nitrile (NBR), and EPDM, selected for their chemical compatibility and temperature range.
Why PTFE? The Engineering Problem Solved
The move from a simple rubber seal to a complex PTFE assembly is driven by the need for performance in conditions that exceed the capabilities of traditional materials.
The Limitations of Traditional Elastomer Seals
Standard rotary seals are often made from soft, resilient elastomers like rubber or polyurethane.
While effective in some cases, these materials wear quickly at high speeds, degrade at extreme temperatures, and are incompatible with many industrial chemicals. Their operational window is relatively narrow.
PTFE's Superior Performance Profile
PTFE seals are specifically chosen for their durability in harsh environments. They offer excellent performance across a wide temperature range, from cryogenic applications to high-heat processes.
Furthermore, PTFE is nearly chemically inert, making it ideal for industries like chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage where it might be exposed to aggressive media.
Handling High Speeds and Low Friction
Unlike rubber, which can generate significant friction and heat, PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction.
This allows PTFE seals to operate at much higher rotational speeds without overheating or causing excessive wear. This property also enables them to run dry for periods without catastrophic failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly capable, PTFE seals are a specialized solution, and it's important to understand their specific characteristics.
Higher Initial Cost
The advanced materials and more complex manufacturing process mean that PTFE rotary seals typically have a higher upfront cost compared to standard elastomeric seals.
Installation Sensitivity
The relative rigidity of PTFE compared to rubber means it is less forgiving of imperfections on the shaft surface or minor installation errors. Proper handling and surface finish are critical for optimal performance.
Static Sealing Reliance
While the PTFE lip provides excellent dynamic sealing, the initial static sealing often relies on the elastomeric energizer. This is a key reason why the O-ring is an integral part of many designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal material is not about which is "best" overall, but which is right for the specific operational demands.
- If your primary focus is standard, low-stress applications: A traditional elastomeric seal is likely the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high speeds, extreme temperatures, or aggressive chemicals: A PTFE composite seal is the necessary engineering choice for long-term reliability.
- If your primary focus is minimizing friction or accommodating dry-running: The unique low-friction properties of PTFE make it the superior material for performance and durability.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE rotary seal is a deliberate decision to engineer resilience directly into your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Material(s) | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Lip | PTFE Composites (with fillers) | Provides low-friction, dynamic sealing against the shaft |
| Structural Case | Stainless Steel, Cold-Rolled Steel, Aluminum | Houses the lip and provides a rigid press-fit |
| Energizer | FKM, NBR, or EPDM O-rings | Supplies initial sealing force and acts as a static seal |
Need a high-performance seal for demanding conditions?
PTFE seals from KINTEK are engineered to solve your toughest challenges. We specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Whether you require a standard design or a custom-fabricated solution from prototype to high-volume production, our expertise ensures a seal that delivers reliability under extreme temperatures, high speeds, and aggressive chemicals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and get a quote tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















